Database management in construction refers to the
process of ____, _____, _____, and, _____ construction-related data systematically
using database systems.
collecting, organizing, storing, and accessing
ensures that construction professionals have
easy access to accurate and up-to-date information,
enabling better decision-making and streamlined
project execution.
A well-structured database management system
(DBMS)
can use software like Procore or
Buildertrend to manage project data, including schedules, materials, and work progress
Project Monitoring Systems
can track material inventories to ensure there are no
shortages during construction
Inventory Management for Supplies
to track employee records, work
hours, payroll, and compliance
with safety standards
Labor and Payroll Systems
using a database that stores all
documentation in one place
Document Management for
Permits and Certifications
In large residential housing
developments, such as those by
Ayala Land or SMDC, databases
manage client information, payment schedules, and property details, ensuring efficient processing for buyers.
Real Estate and Housing
Projects
Examples of Database Management in the
Construction Industry
Project Monitoring Systems, Inventory Management for Supplies, Labor and Payroll Systems, Document Management for
Permits and Certifications, Real Estate and Housing
Projects
Importance of Database Management in the
Construction Industry,
Improved Decision-Making, Enhanced Productivity, Cost Control, Compliance and Safety, Collaboration, Risk Management
Accurate and organized data allows stakeholders
to make informed decisions based on real-time
information
Improved Decision-Making
A centralized database minimizes the time spent
searching for critical documents or files, allowing
workers to focus on project execution
Enhanced Productivity
By tracking budgets, expenditures, and resources,
database systems help prevent cost overruns and
improve financial management
Cost Control
In the Philippines, compliance with local building codes
and safety regulations, such as those mandated by the
Department of Labor and Employment (DOLE) and the
Building Code of the Philippines, can be better
managed through a database system.
Compliance and Safety
With shared databases, architects, engineers,
contractors, and clients can collaborate more
effectively and maintain transparency
Collaboration
Identifying potential risks (e.g., delayed shipments,
labor shortages, or safety hazards) becomes easier
with detailed historical data.
Risk Management
Disadvantages of Database Management in the
Construction Industry
High Initial Costs, Complexity of Implementation, Maintenance and Upkeep, Dependence on Technology, Data Entry Errors, Resistance to Change, Scalability Issues, Data Overload
o Too Much Information
o Analysis Paralysis
Data Overload
o Unsuitable for Small Projects
o Growth Limitations
Scalability Issues
o Cultural Barriers
o Adaptation Period
Resistance to Change
o Human Error
o Duplication and Redundancy
Data Entry Errors
o Vulnerability to Cyber Threats
o Power and Internet Dependence
Dependence on Technology
o Ongoing Costs
o Downtime Risks
Maintenance and Upkeep
o Time-Consuming Setup
o Training Requirements
Complexity of Implementation
o Setup Expenses
o Customization Cost
High Initial Costs
is a set of at least two elements that are in some way related to each other such that there are no independent elements.
system
is a set of interrelated components that collect, manipulate, store data, and disseminate information and provide a feedback mechanism to monitor performance
information system
It is an organized combination of people, hardware, software, communications, networks, and data resources that collects data, transforms it, and disseminates information
information system
Components of information system
hardware, software, stored data, personnel, procedures
External and internal devices needed to perform a task
hardware
Set of instructions/programs used to operate computers
software
facts stored in the system
stored data
People who operate the system
personnel
Instructions for the manpower
procedures
permits establishments to achieve greater efficiency by sharing data throughout all the elements or departments of the organization
Data management
The administrative aspect can be categorized into:
time management, cost, quality, security, agreements, materials, equipment, human resources
can be facts related to any object in consideration: name, age, height, etc.
Data
is information processed and stored by a computer: text documents, images, audio clips, etc.
Computer Data
is a systematic collection of data. You can organize data into tables, rows, columns and index which makes it easier to access relevant information.
Database
are software systems used to store, retrieve, and run queries on data. A DBMS serves as an interface between an end-user and a database, allowing users to create, read, update, and delete data in the database.
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
examples of Database Management Systems (DBMS)
Ms Access, MySQL Database, Oracle Database
INFORMATION SYSTEMS in CONSTRUCTION
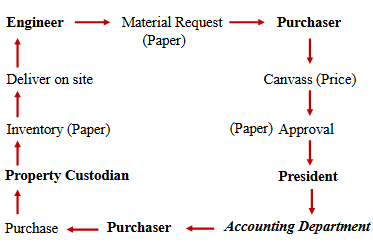
describes any technology that helps to produce, manipulate, store, communicate, and/or disseminate information
Information technology (IT)
Two general parts of information technology
computer technology, communications technology
is a programmable, multi-use machine that accepts data (i.e. raw facts and figures) and processes, or manipulates it into information we can use, such as summaries, totals, or reports Its general purpose is to speed up problem solving and increase productivity
computer
It refers to inventions related to or associated with computers and devices with a central processing unit, such as hardware and software of computers, the internet and storage devices
Computer Technology
It is the act of transferring information from one place, person, or group to another
Communication
also called telecommunications technology consists of electromagnetic devices and systems for communicating over long distances
Communications technology
The main components of a telecommunications system are:
transmitter, atmosphere or cable, receiver
- a device that originates communication
transmitter
the medium over which the transmission takes place
atmosphere or cables
the end point of the transmission
receiver
Information technology (IT) in some companies is referred to as
Management Information Services (MIS) or simply as Information Services
How does Information Technology (IT) help in design and modeling?
IT can help engineers produce better designs that are almost impossible to produce manually
Examples of IT in design and modeling
CAR, Tekla Structures, AUTODESK REVIT Structures, MidasGen, AUTOCARD, AUTODESK REVIT ARCHITECTURE, SOLIDWORKS
is an interactive drawing system designed to permit a user to construct or edit a drawing on a graphics display screen
AutoCAD
Common Problems in Surveying
unfavorable sites, topography, heavy equipment
Geographical Information System (GIS)
is a computer system for capturing, managing, integrating, manipulating, analyzing, and displaying data which is spatially referenced to the Earth
Examples of GIS
ArcGIS, SAGA, QGIS
is the study of phenomenon sensed from air or satellites, provides engineers with an opportunity to interpret data as seen from space
Remote sensing
How does Information Technology (IT) help in Project Management?
Information technology helps in understanding the theory and techniques associated with computer-based planning, analysis, and control
IT can be applied in project management by the following
practical orientation, construction operations monitoring, project planning, management and control, time-money analysis, other standard quantitative and qualitative techniques
PRIMAVERA
Personalized Retrieval and Indexing of Media Assets in Virtual Environments for Real-Time Access
The PRIMAVERA software is capable of the following functions:
Project management • Dissemination of results, conversation with other projects, standardization • Exploitation of project results • General system design, interface specification, system integration • Development of advanced indexing and retrieval techniques • Development of user profile generation and management • Development of new user interfaces and visual interaction paradigms