
Chytridiomycota (Unicellular/Multicellular, Hyphae, Examples, Reproduction)
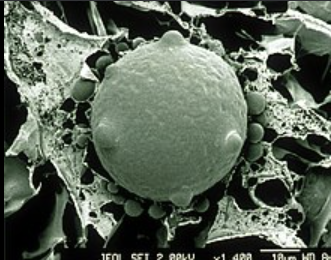
Chytridiomycota (Key Features, Dominant Generation, Ecological Role)

Blastocladiomycota (Unicellular/Multicellular, Hyphae, Examples, Reproduction)
Blastocladiomycota (Key Features, Dominant Generation, Ecological Role)
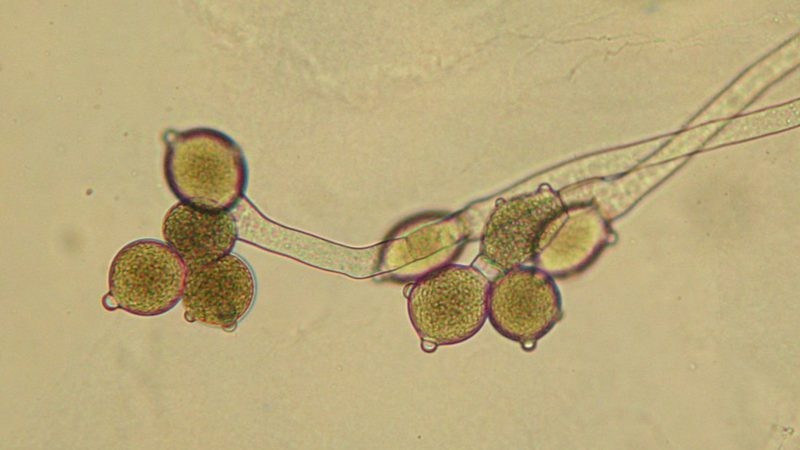
Neocallimastigomycota (Unicellular/Multicellular, Hyphae, Examples, Reproduction)
Neocallimastigomycota (Key Features, Dominant Generation, Ecological Role)
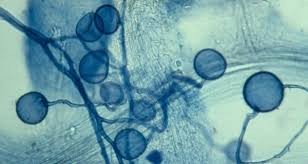
Glomeromycota (Unicellular/Multicellular, Hyphae, Examples, Reproduction)
Glomeromycota (Key Features, Dominant Generation, Ecological Role)

Zygomycota (Unicellular/Multicellular, Hyphae, Examples, Reproduction)
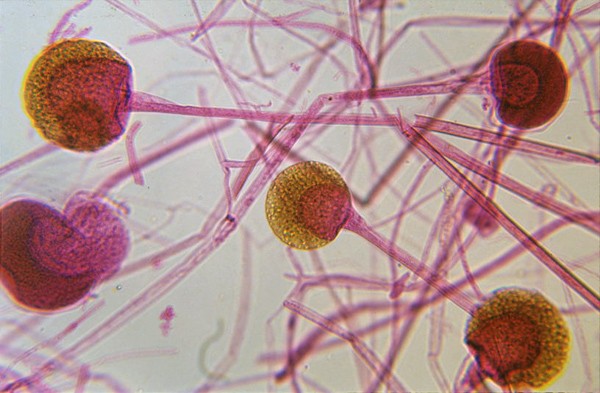
Zygomycota (Key Features, Dominant Generation, Ecological Role)

Ascomycota (Unicellular/Multicellular, Hyphae, Examples, Reproduction)
Ascomycota (Key Features, Dominant Generation, Ecological Role)

Basidiomycota (Unicellular/Multicellular, Hyphae, Examples, Reproduction)
Basidiomycota (Key Features, Dominant Generation, Ecological Role)
Monophyletic Group (Definition & Example)
Paraphyletic Group (Definition & Example)
Monokaryotic Hyphae
A hypha with one nucleus per cell
Dikaryotic Hyphae
A hypha with two haploid nuclei coexisting independently within the same cell
Heterokaryotic Hyphae
A hypha containing nuclei from two genetically distinct individuals
Homokaryotic Hyphae
A hypha containing genetically similar nuclei
Arbuscular Mycorrhizae:
In this type, fungal hyphae penetrate plant root cells and formstructures called arbuscules, facilitating nutrient exchange. Arbuscular mycorrhizae are more common, appearing in about 80% of plant species
Ectomycorrhizae:
In this type, form a sheath around plant roots but do not penetratethe cell walls. Though less common than arbuscular mycorrhizae, they play a significant role in carbon storage
What is obligate symbiosis?
A relationship where at least one organism cannot survive without the other.
What is facultative symbiosis?
A symbiotic relationship where the organisms can live independently but may benefit from the association when it occurs.