What is the spinal cord protected by?
- Bone (vertebrae)
- CT (meninges)
-Fluid (CSF)
Where is the spinal cord located withing the vertebral column?
The vertebral canal
Where does the spinal cord pass through of each individual vertebra?
Through the vertebral foramen.
Where do spinal nerves exit through?
Through the intervertebral foramen.
What are the 3 meninges?
- dura mater
- arachnoid mater
- pia mater
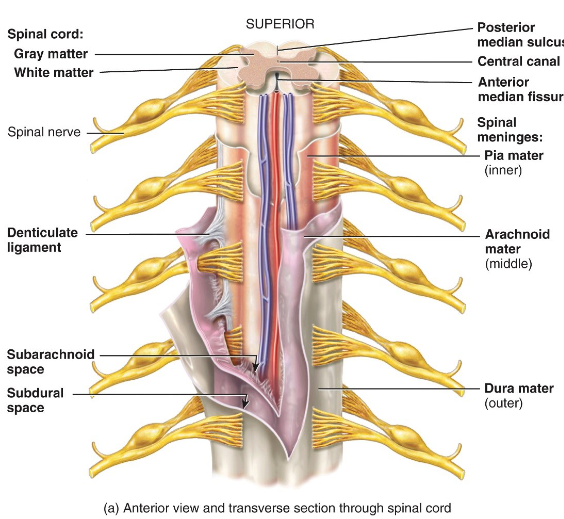
What do denticulate ligaments do?
Hold the spinal cord in place.
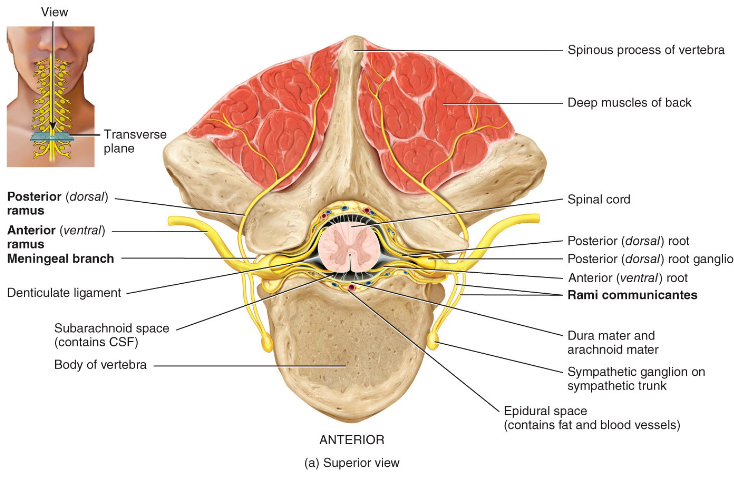
Where is the epidural space located and what is it filled with?
Between the dura mater and vertebral column; filled with fat.
The subdural space is located between the ___ and the ___; it's filled with ___.
dura, arachnoid mater and interstitial fluid.
Where is the subarachnoid space located and what is it filled with?
Located between the arachnoid and pia mater; filled with CSF.
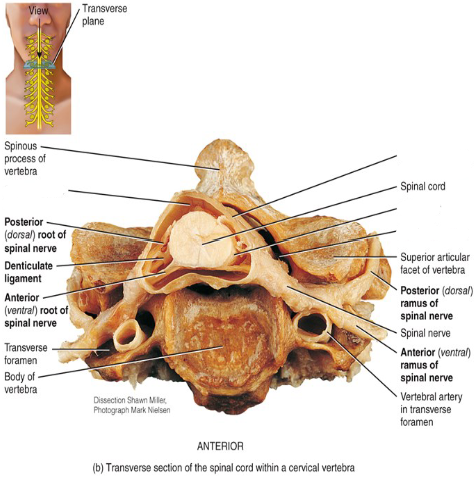
Label the diagram.
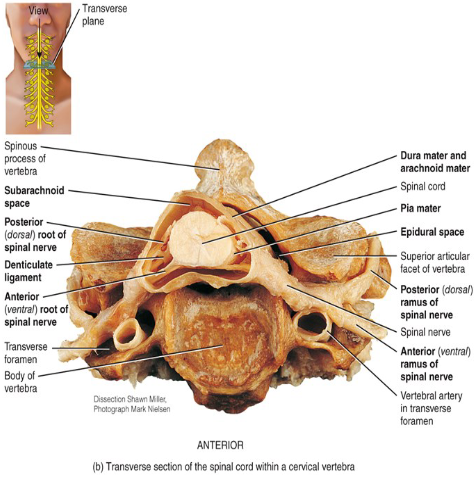
Where is the CSF formed?
In a network of b. capillaries (choroid plexus) in the lateral ventricles of the brain.
Where does the spinal cord begin and end?
Begins at the foramen magnum and terminated at L2.
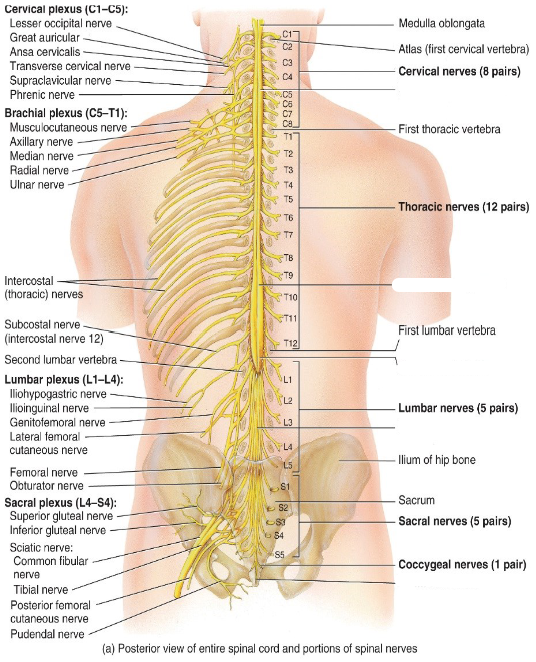
Label the diagram.
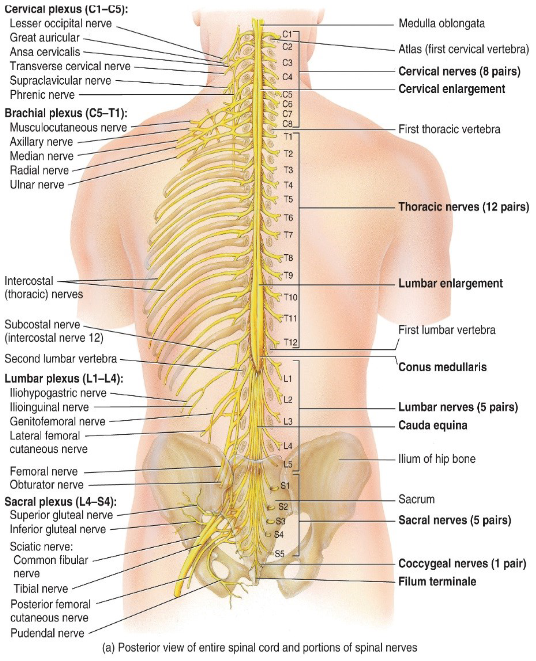
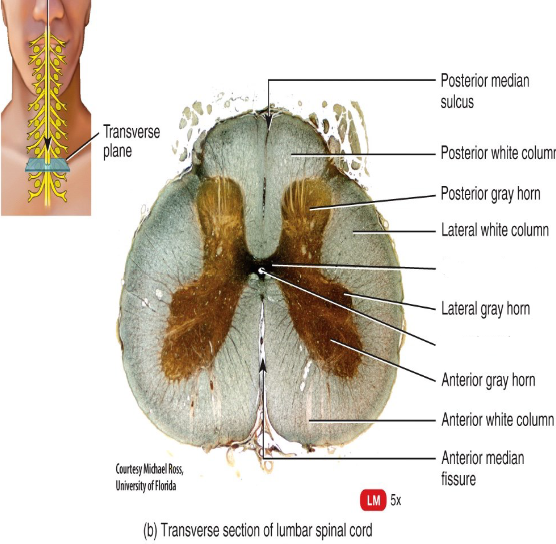
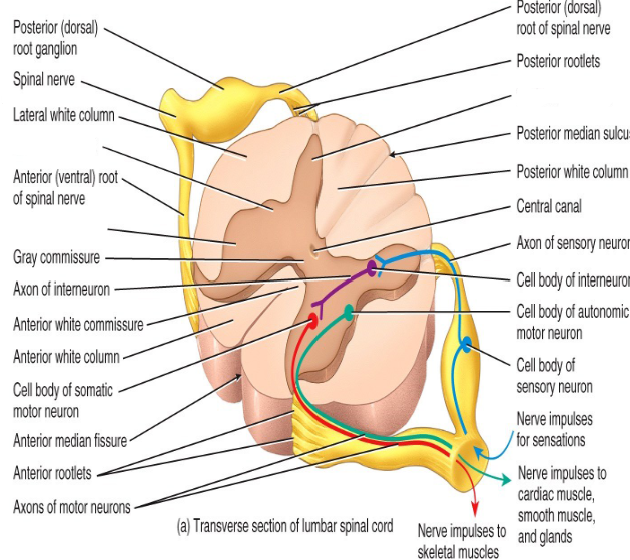
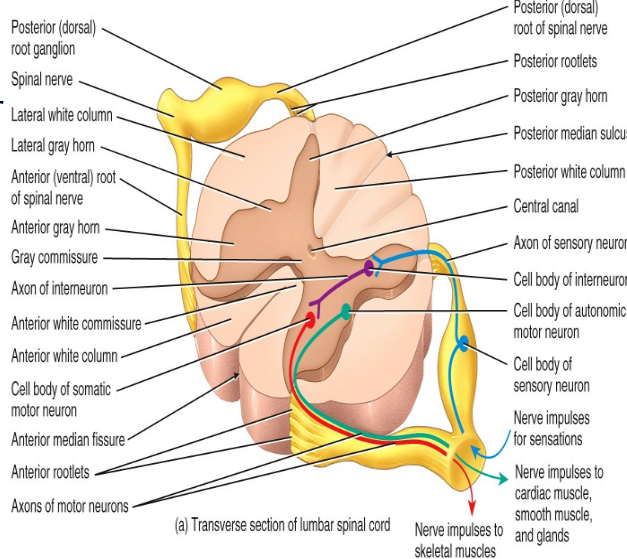
What structures of the spinal cord divide it into left and right sides?
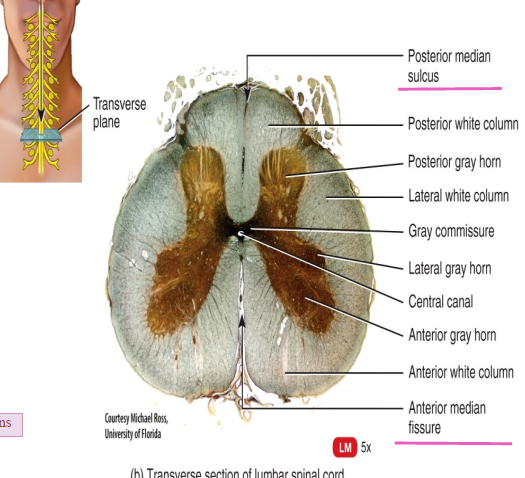
The posterior median sulcus and anterior median fissure.
Label the diagram.
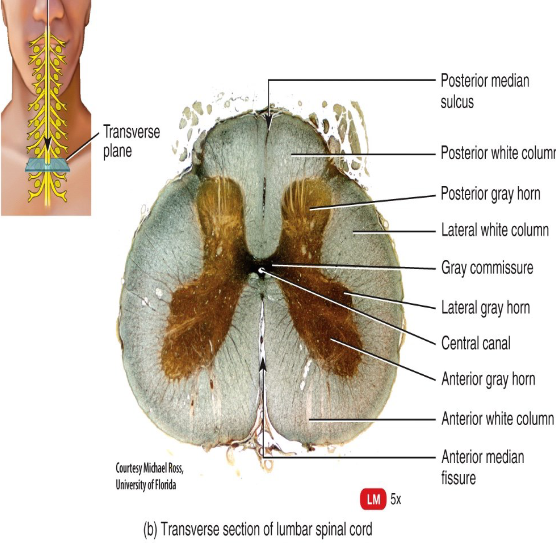
What structure of the spinal cord contains CSF?
The central canal
What do the posterior gray horns contain?
Axons of sensory neurons and cell bodies of interneurons.
What do the anterior gray horns contain?
Somatic motor nuclei (clusters of their cell bodies) which provide impulses for skeletal muscle contraction.
What do the lateral gray horns contain?
Autonomic motor nuclei that regulate the activity of cardiac muscle.
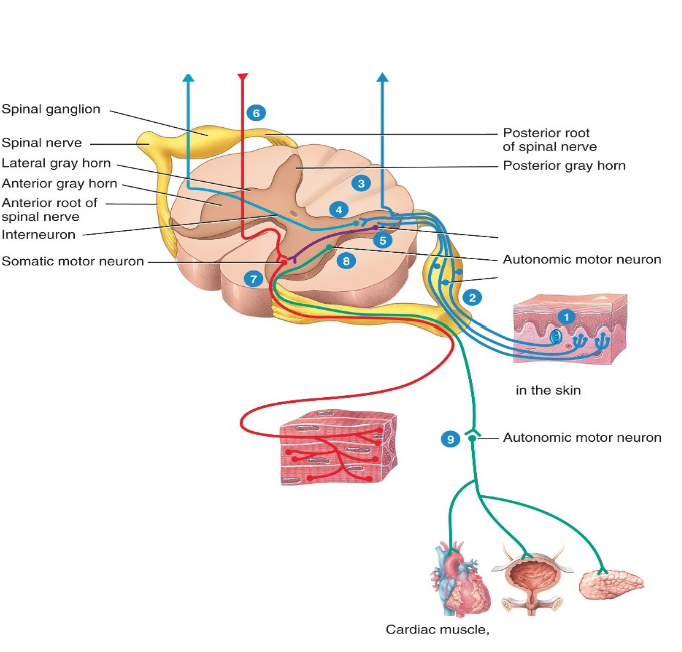
Label the diagram.
Bundles of nerve axons are called what in the CNS and PNS respectively?
CNS - tracts
PNS - nerves
Where do sensory (ascending) tracts send nerve impulses to?
Toward the brain
Where do motor (descending) tracts send nerve impulses to?
Down the spinal cord.
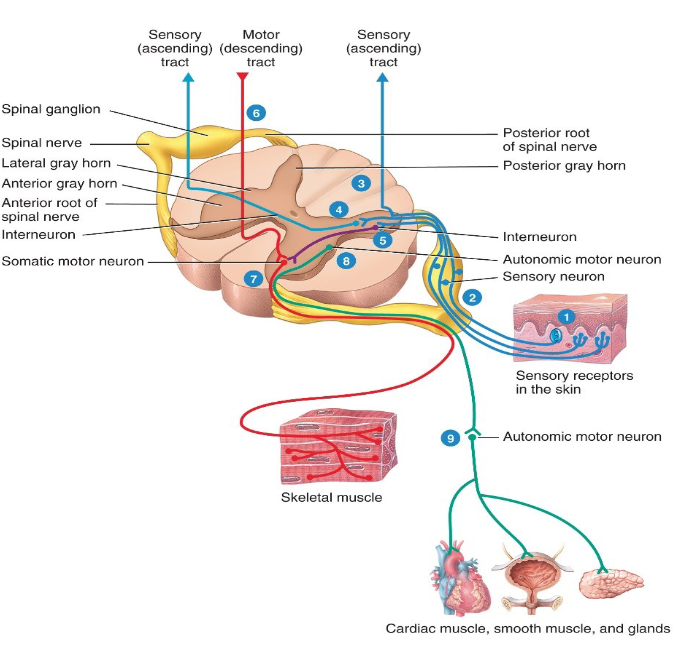
Label the diagram.
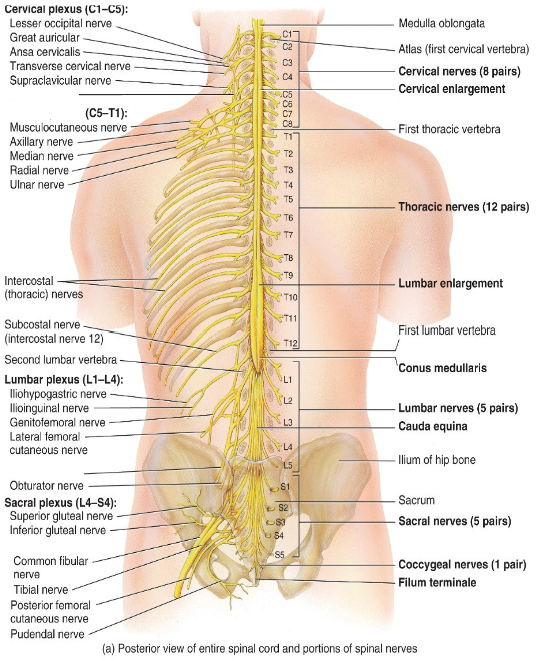
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31 pairs
___ pairs of cervical nerves (C1-___)
___ pairs of thoracic nerves (T1-___)
___ pairs of lumbar nerves (L1-___)
___ pairs of sacral nerves (S1-___)
1 pair of coccygeal nerves
8, C8
12, T12
5, L5
5, S5
What type of nerve is a spinal nerve?
A mixed nerve.
What does the posterior root do?
Conducts nerve impulses from the periphery into the spinal cord.
What does the posterior root ganglion contain?
The cell bodies of the unipolar sensory neurons.
What does the anterior root do?
Conducts impulses from the spinal cord to the periphery.
Why is a spinal nerve a mixed nerve?
Because the posterior root contains sensory axons and the posterior root has motor axons; thus mixed.
What is a nerve fiber covered with?
Endoneurium
What covers the entire nerve?
Epineurium
What covers a nerve fascicle?
Perineurium
Are nerves vascular or avascular?
Vascular
What kind of vertebra is this?
Thoracic
After passing through its intervertebral foramen, a spinal nerve divides into branches called a ___.
rami
Which spinal nerves don't form a plexus?
Thoracic
What do the thoracic nerves innervate?
The intercostal muscles and the skin overlying them.
What do the posterior ramus innervate?
The deep muscles and skin of the posterior trunk.
What do the anterior ramus innervate?
Muscles and skin of the upper and lower limbs.
Which spinal nerve does NOT innervate a segment of the skin?
C1
Label the diagram.
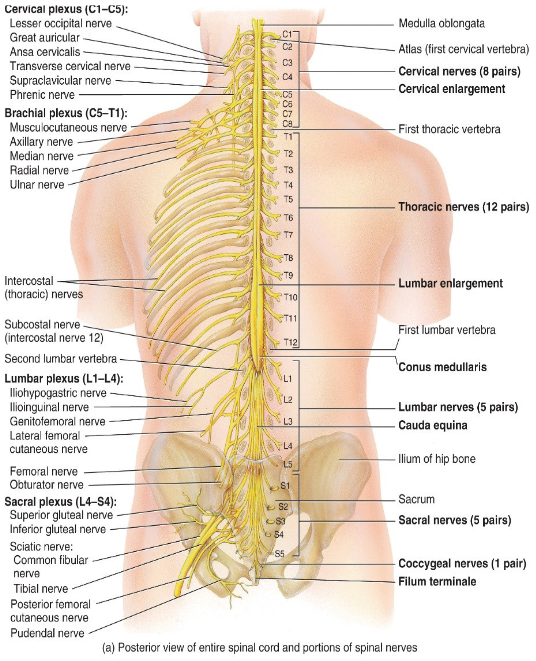
What does the phrenic nerve innervate?
The diaphragm
Why does damage to C3-C5 cause respiratory arrest?
Because it damages the phrenic nerve, which innervates the diaphragm.
What nerve when compressed causes carpal tunnel syndrome?
Median nerve
What does the femoral nerve innervate?
The muscles of the quadriceps femoris
What does the sciatic nerve (longest nerve) innervate?
Hamstrings and muscles of the leg and foot?
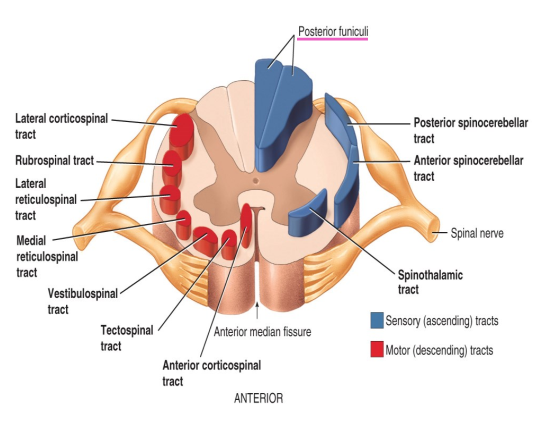
What do the posterior funiculi convey?
Nerve impulses for touch, pressure, vibration and conscious proprioception.
Where does the integration of spinal reflexes occur in the spinal cord?
The gray matter.
What is a reflex?
A fast, autonomic response to changes in the environment that helps to maintain homeostasis.
What is the stretch reflex?
The contraction of a muscle that has been stretched.
What is a monosynaptic reflex arc?
When a reflex arc only has one synapse in the CNS
What do these terms mean:
Ipsilateral =
Contralateral =
Monosynaptic =
Polysynaptic =
Reciprocal innervation =
I. = same side
C. = opp. side
Ms. = one
Ps. = more than one
RI = neural circuit simultaneously contracting one muscle and relaxes its antagonists.
Where is the phrenic nerve located?
In the cervical plexus.
Where is the median nerve located?
In the brachial plexus.
Describe the general steps of a reflex arc?
1. Sensory receptors receives stimulus
2. Stimuli travels through the sensory neuron(s) and goes through the dorsal root gnaglion
3. Stimulus is integreted
4. Stimulus travels through the anterior gray horn through somatic motor neurons and uses that to relay information to the effectors.
Cervical nerves 3, 4 and 5 keep the ___.
diaphragm alive (where the phrenic nerve is).
What does the sciatic nerve innervate?
The hamstrings and the leg and foot.
What does the femoral nerve innervate?
The quadriceps femoris.