What is sensation and perception?
Sensation - conscious/subconscious awareness of changes in the environment
Perception -conscious interpretation of sensations
What is sensory modality?
Each type of sensation (touch, pain, etc.)
Define what general senses and special senses are?
General - receptors distributed throughout the body
Special - receptors localized to specific sensory organs (nose for smell, etc.)
What are the 4 events of sensing?
- Stimulation
- Transduction (receptor must pick up stimulus)
- Conduction (must go through a neural pathway, axon)
- Translation (translates or interprets stimulus into sensation).
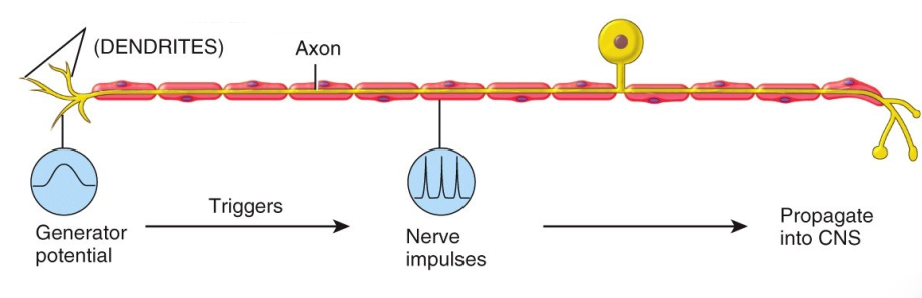
What type of nerve ending is this and what does it detect?
Free; temp., itchiness and some touch.
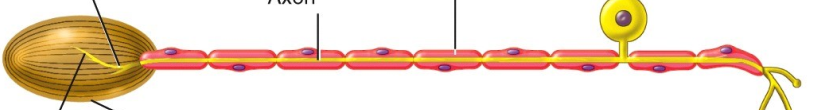
What type of nerve ending is this and what does it detect?
Encapsulated; detects pressure, vibration and some touch.
What are extero and interoreceptors?
Exteroreceptors - near the body surfaces
Interoreceptors - in the bv or visceral organs (usually monitors the internal environment)
Proprioceptors are located in ___ and provide information on ___.
muscles, tendons and provide information on the posture, body position etc.
What is the name for receptors that detect pain?
Nociceptors

What do each of them detect?
1. mechanical stimuli (touch, pressure, vibration, etc.)
2. changes in temp.
3. pain
4. light that strikes the retina
5. chemicals in mouth (taste), nose (smell) and body fluids
6. osmotic (water) pressure of body fluids
Most sensory receptors are capable of ___, which decreases its sensitivity the longer its exposure to the stimuli.
adaptation
What structures of the body have the highest density of sensory receptors?
Tip of tongue, lips and fingertips
What are the 4 groups of somatic sensations?
1. Tactile - touch, pressure...
2. Thermal - temp.
3. Proprioceptive - movement or strain (kinesthesia)
4. Pain - pain
What are the 2 receptors in the skin?
- Corpuscle of touch/meissner's corpuscle (papillary of dermis, superior)
- Pacinian corpuscle (reticular, close to subcutaneous layer)
Why is pain such a vital sensation?
Because it warns us of actual or impeding tissue damage.
What are the 2 pathways that somatic pain is carried off to in the parietal lobes?
- spinothalamic (spinal cord to thalamus, ascending)
- trigeminothalamic (trigeminal nerve to the thalamus)
Why is sharp pain conducted quickly?
Because it's myelinated
Tendon organs have what type of receptors?
Proprioceptors
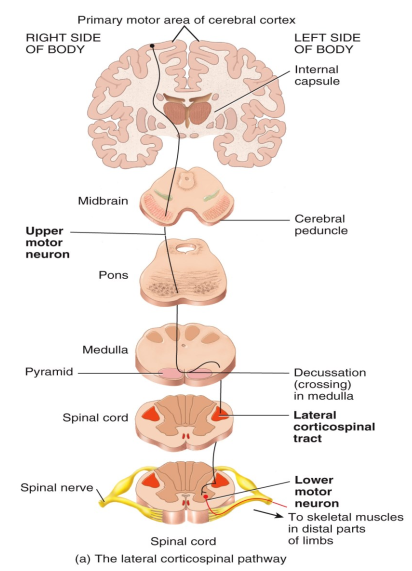
First order neurons do what?
Conduct info from the somatic sensory receptors to second-order neurons.
Where are the cell bodies or first, second and third order neurons located?
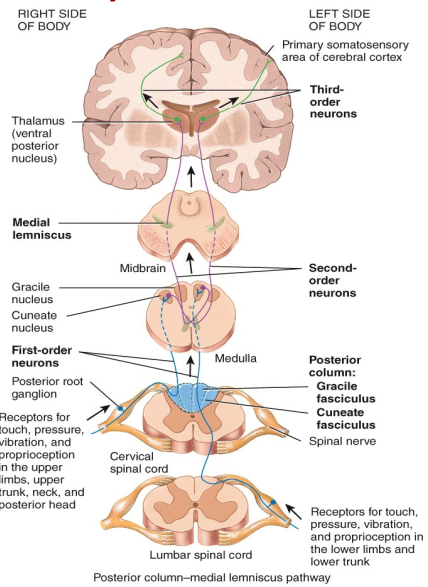
1. posterior root ganglion
2. brain stem or spinal cord
3. thalamus
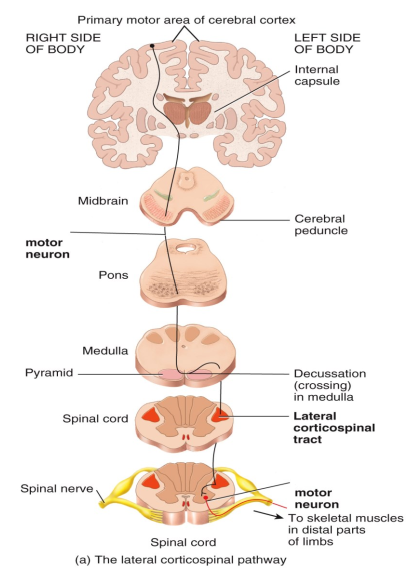
Somatic motor pathways consists of a chain of two neurons. Label them in the diagram.
What does the homunculus represent in the brain?
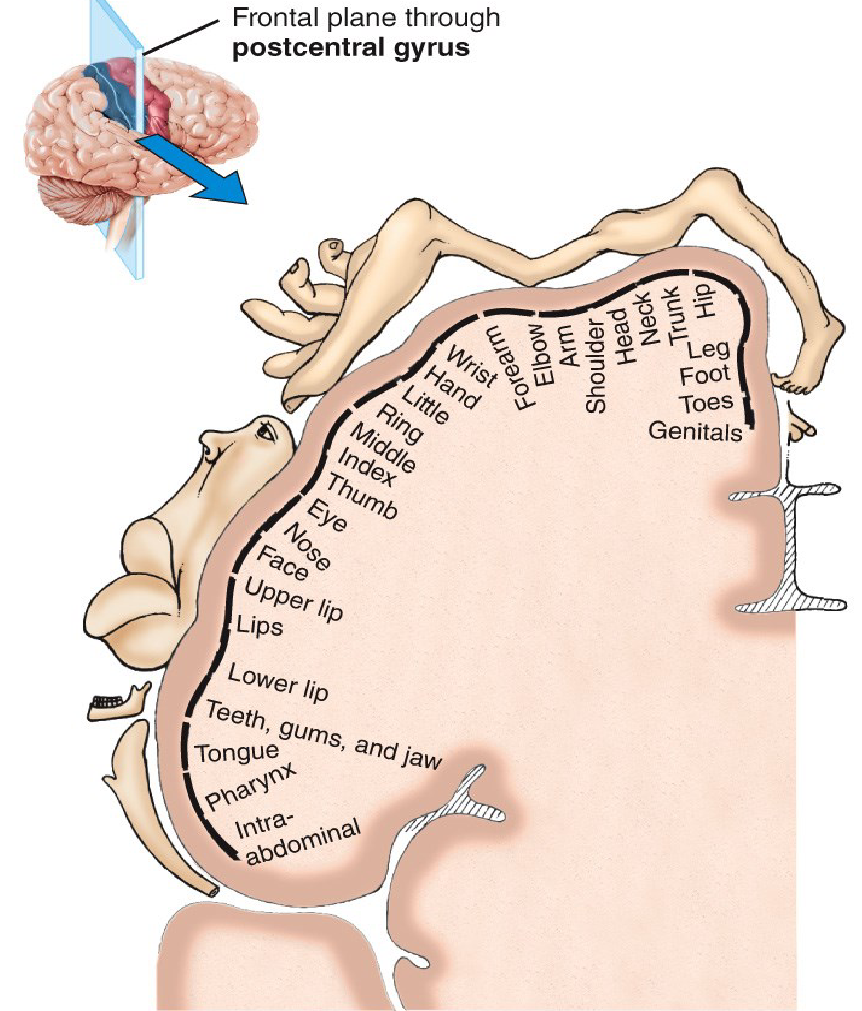
Senses that are being catered to in the primary somatosensory area in the postcentral gyri.