Name some of the homeostatic functions of the kidney?
- Regulates ionic composition of blood.
- Regulates blood pH.
- Regulates blood volume through excretion and retention of urine.
- Regulates bp.
What do the kidney excrete?
Excretes metabolic wastes and foreign substances (drugs/toxins).
From superficial to deep, name the layers of the kidney and their functions.
1. Renal fascia - anchors kidneys to other structures
2. Perirenal fat - protection
3. Fibrous capsule - innermost layer
Where do blood vessels, the ureters, and nerves enter and exit the kidney?
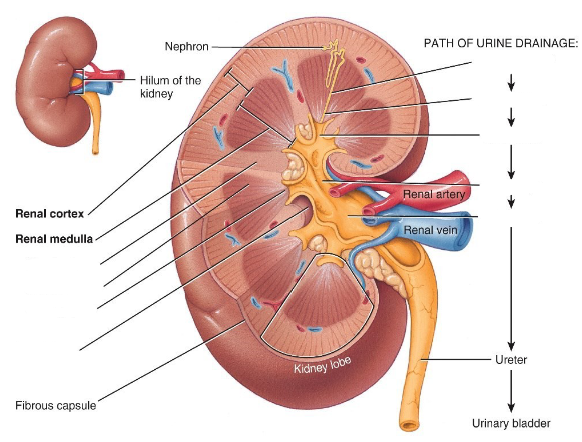
Label the diagram.
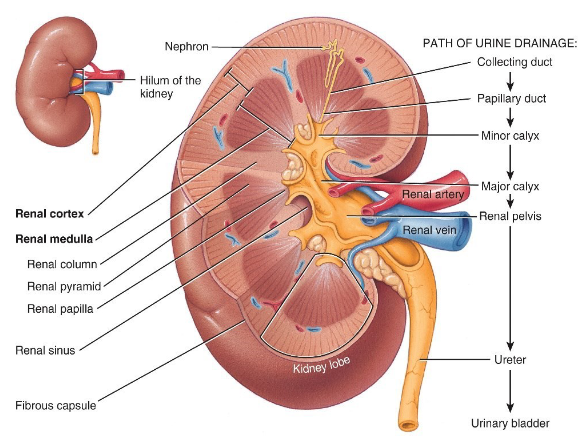
Within the renal medulla is a renal pyramid. What is the apex called of each renal pyramid?
The renal papilla
Filtrate is formed from the ___ and is drained into the ___.
Formed in the nephrons and drained into the collecting ducts.
At what structure does the filtrate turn into urine?
The minor and major calyces.
___ is the most functional unit of the kidney
The nephron
What are the three basic functions of the nephrons?
- Glomerular filtration
- Tubular reabsorption
- Tubular secretion
The renal corpuscle filters blood plasma, into which the filtrate enters the renal tubule. What does the renal tubule do?
Converts filtrate into urine.
___ drain into a single collecting duct.
Distal convoluted tubules
What are the two types of nephrons?
- cortical
- juxtamedullary
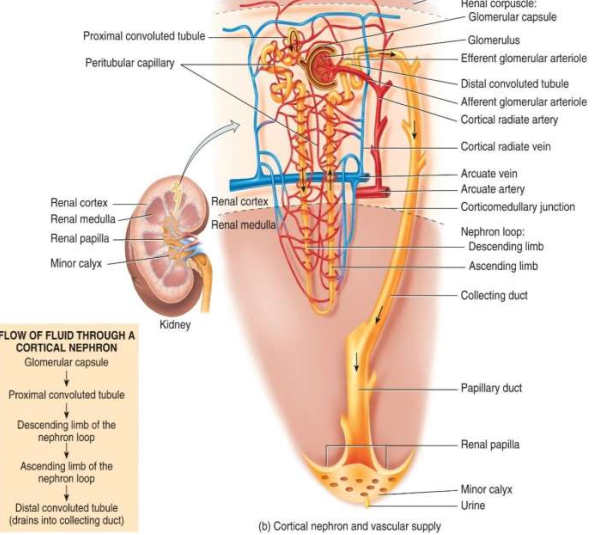
What kind of nephron is this?
Cortical nephron and they comprise 80-85% of nephrons.
What do cortical nephrons do?
They are responsible for the majority of urine formation and has similar osmolarity to blood.
What do juxtamedullary nephrons do?
It enables the kidney to make very concentrated urine.
What is the main difference between the cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons?
The juxtamedullary nephron has the vasa recta.
What type of cells is the visceral layer of the renal corpuscle made of?
Modified simple squamous epithelial cells - podocytes