Three main parts of HRM?
Strategic Importance, Legal, Social Environment
Explain Strategic Importance of HRM?

A number of laws and statutes dictate and regulate in key areas of Legal Environment?
Equal Opportunities, Compensation and Benefits, Labour Relations, Health & Safety
Social Environment of HRM?

What are the way of Recruiting Human Resources?
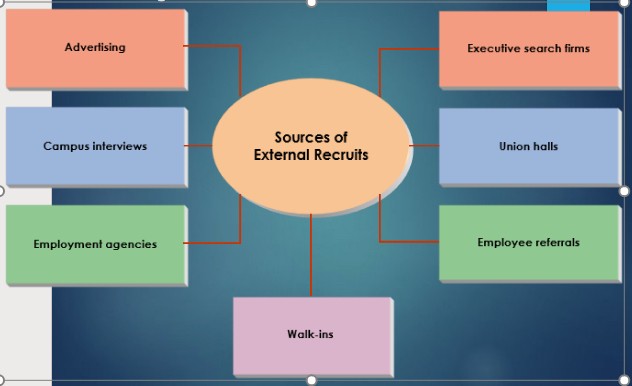
What are the way of Human ResourcesTalent Building?

Explain Performance Management of HR – Performance Appraisals?
-Performance Appraisal: A formal assessment of how well workers do their jobs.
-Reasons for Performance Appraisal:
Validates selection process and effects of training.
Aids in making pay raise, promotion, and training decisions.
Provides feedback to workers to improve their performance and plan future careers.
Explain Compensation of HR – Performance Appraisals?
-The financial remuneration given to employees in exchange for their work – Incentives, Salary, Wages.
-Provide means to maintain a reasonable standard of living.
-Tangible measure of the value of the individual to the organization.
Explain Objective Measures of Performance of HR – Performance Appraisals?
-Can be actual output (units produced), scrap rate, euro volume of sales, and claims processed, also can become contaminated by outside factors resulting in “opportunity bias” where some have a better chance to perform than others.
-Special performance tests assess each employee under standardized conditions.
-Performance tests measure ability and not motivation
Explain Performance Feedback of HR – Performance Appraisals?
-Is best given in a private meeting between the employee and immediate supervisor.
-Discussion should focus on the facts.
-The assessed level of performance
-How and why the assessment was made.
-How the employee’s performance can be improved.
-Properly training managers can help them conduct more effective feedback interviews.
Explain 360 Degree Feedback Technique of HR – Performance Appraisals?
-Managers are evaluated by everyone around them:
Line Manager, Subordinates, Peers.
-Provides a richer array of performance information on which to base an appraisal.
What are 5 Stages of Group Development?(Bruce Tuckman)
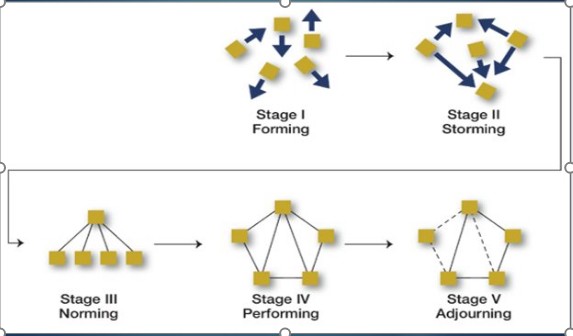
What is Stages 1 Forming of Group Development?(Bruce Tuckman)
-In this stage, most team members are positive and polite, Some are anxious, as they haven't fully understood what work the team will do. Others are simply excited about the task ahead.
-As a Manager, you play a dominant role at this stage, because team members' roles and responsibilities aren't clear. This stage can last for some time, as people start to work together, and as they make an effort to get to know their new colleagues.
What is Stages 2 Storming of Group Development?(Bruce Tuckman)
-Next, the team moves into the storming phase, where people start to push against the boundaries established in the forming stage. This is the stage where many teams fail.
-Storming often starts where there is a conflict between team members' natural working styles and different styles causes frustration. Team members may challenge your authority, Or, if you haven't defined clearly how the team will work, people may feel overwhelmed by their workload, or they could be uncomfortable with the approach you're using.
-Some may question the project, and they may resist taking on tasks. Team members who stick with the task at hand may experience stress, particularly as they don't have the support of established processes or strong relationships with their colleagues.
What is Stages 3 Norming of Group Development?(Bruce Tuckman)
- Gradually, the team moves into the norming stage. This is when people start to resolve their differences, appreciate colleagues' strengths, and respect your authority as a Manager. At this stage teams may socialise together, and they are able to ask one another for help and provide constructive feedback.
-People develop a stronger commitment to the task, and you start to see good progress towards completion. There is often a prolonged overlap between storming and norming, because, as new tasks come up, the team may lapse back into behaviour from the storming stage.
What is Stages 4 Performing of Group Development?(Bruce Tuckman)
-The team reaches the performing stage, when hard work leads, without friction, to the achievement of the team's goal, also the project structures and processes that are set up support this stage well.
-As a Manager, you can comfortably delegate tasks, and you can concentrate on overall project delivery. It feels easy to be part of the team at this stage, and people who join or leave won't disrupt performance.
What is Stages 5 Adjourning of Group Development?(Bruce Tuckman)
-Some larger project teams will reach this stage eventually. For example, some teams exist for only a fixed period, and even permanent teams may be disbanded through organisational restructuring.
-Team members who like routine, or who have developed close working relationships with colleagues, may find this stage difficult, particularly if their future now looks uncertain.
Does a group become more effective as it progresses through the first four stages? (Group Effectiveness)
-Some groups don’t get beyond the forming or storming stages. These groups may have serious interpersonal conflicts, turn in disappointing work, and get poor performance reviews.
-The assumption that a group becomes more effective as it progresses through the first four stages may be generally true, but what makes a group effective is complex.
-Under some conditions, high levels of conflict are conducive to high levels of group performance. There might be situations in which groups in the storming stage outperform those in the norming or performing stages.
What are the basic foundation for understanding Group Behavior?
Roles, Norms and conformity, Status systems, Group size, and Group cohesiveness.