File
advertisement
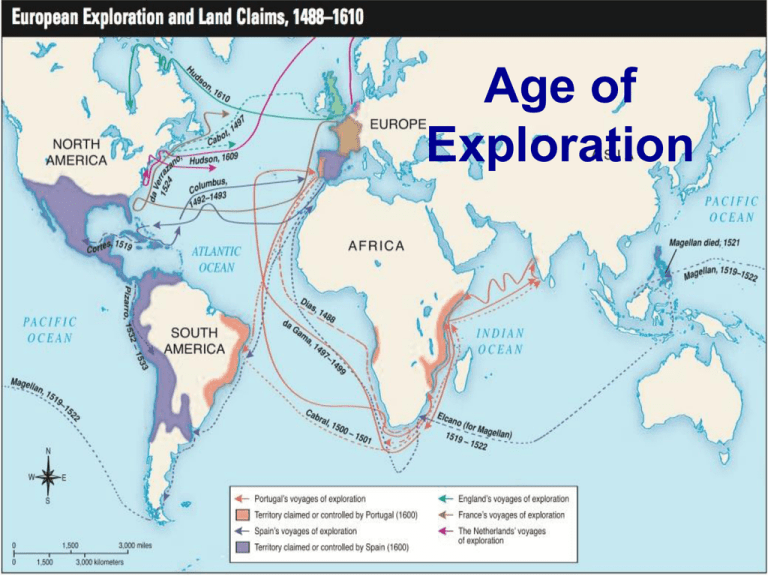
Age of Exploration The Powers That Be (Were) The “Big Three” countries in Europe who were competing for land were… France England Spain The Three G’s All three countries explored for the same reasons: “The Three G’s” Gold God Glory Why they set out Gold: Natural resources and precious metals brought many explorers. Native American tales of cities of gold like El Dorado in South America and Cibola in North America also spread around Europe. God: Missionaries where sent to spread Christianity to native groups. Glory: Wanted to become famous and wealthy for adding land to their empires. Travel/Trade: Wanted to find a route to trade with Asia by sea, for faster trade. Technology Sailors now had instruments such as the astrolabe and the compass to find new routes. More accurate maps allowed sailors to travel from one port to the next using the open sea and not having to follow the coast. Shipbuilding, especially by the Portuguese, made new ships with better sails and better steering. Spain Conquistadors Spain jumped out to an early lead in the race for empire. In 1492, Christopher Columbus claimed the Americas for Spain. Within a few years, Spanish explorers had brought amazing amounts of riches back to Spain. Hernán Cortés conquered the Aztecs in 1521. Mexico (New Spain) became the center of Spanish rule in the New World. More conquistadors (conquerors) followed . . . Conquistadors Did I turn off the coffee pot before we left??? This metal underwear is killing me!!! Who brought the map??? Cabeza de Vaca In 1527, survivors of a failed Spanish expedition to Florida were shipwrecked on (probably) Galveston Island. One of them, Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca, spent several years living with local Indian tribes (including the Karankawa and Coahuiltecans). Cabeza de Vaca It took Cabeza de Vaca 8 years to walk from Texas to the Pacific Ocean. He later wrote a book about his experiences called La Relación (The Report). In it, he mentioned Indian legends about Cibola, the Seven Cities of Gold. Francisco Coronado In 1540, Coronado led a large expedition from New Mexico to search for Cibola. He found . . . no gold. Coronado did not treat the Indians he met very well, killing or enslaving many of them. Also, horses from his expedition escaped and bred. Much later, the Plains Indians like the Comanche learned how to tame them and become extraordinary hunters and warriors. France France Moves In (and Spain is NOT happy about it) Meanwhile, France was exploring further east. In 1682, René-Robert Cavalier, Sieur de La Salle canoed down the Mississippi River. He claimed the whole region for France and named it Louisiana in honor of the French king. In 1684, King Louis XIV gave La Salle 4 ships to sail to the mouth of the Mississippi and set up a colony there (before the Spanish could interfere). But La Salle sailed too far and actually landed near Matagorda Bay in Texas. La Salle La Salle built Fort St. Louis in 1685. In 1687, en route to Canada to gain help for his beleaguered colony, the explorer was ambushed and killed by several of his men in east Texas. The next year, Karankawa Indians attacked the fort and killed all the settlers. France vs. Spain VS Spain hears about La Salle’s expedition and becomes concerned about French ambitions. A Spanish expedition sent to destroy the fort finds it ruined in 1689. Is France after Mexico? Since Texas lies between Spanish Mexico and French Louisiana, Spain takes a renewed interest in exploring and settling Texas. Spain decides to develop a system of missions and presidios to assert their control over their The MissionPresidio System The MissionPresidio System A mission was a settlement set up in Indian territory by Spanish Friars, members of the clergy who belonged to religious groups called “orders.” Friars invited natives to live at the missions and learn about Christianity and the language and customs of Spain. The goal of missions was to transform natives into Christians who were loyal to Spain A typical Spanish crucifix of the mission era. A reconstructed scene of Mission San Jose by artist Ernst Schuchard helps bring the color and cultures of the Spanish mission to life. The MissionPresidio System Missionaries believed that after about 10 years, they could move on and leave behind Spanish settlements, which worked well in Mexico. Presidios were forts that protected missions from unfriendly natives and helped control the natives living in the missions. Soldiers from the presidios caught natives who ran away from the missions. The MissionPresidio System In 1718 , a Spanish expedition went to Texas to find a good halfway point between the Rio Grande and East Texas. The Spanish picked an area on the San Antonio river and built Mission San Antonio de Valero, a site offering many benefits to its settlers. The Spanish soon built a presidio nearby called San Antonio de Bexar (BEH-hahr), proving to be one of the most important communities in Spanish Texas. The site of this mission is today known as the Alamo. Problems with the MissionPresidio System An epidemic is the rapid spread of a disease over a short period of time. Thousands of natives died due to epidemics, and some entire tribes died out. The survivors often blamed the Spanish and became hostile. While some natives devoted themselves to Christianity and took up ranching and farming, many natives refused to accept the Spanish lifestyle of living in missions and working the land. England England The British sent explorers around the same time, but were late to the scene in terms of colonization Because there was no money left after war with Spain, private funds rather than royal treasury funded English settlement in North America. Joint-stock companies, the forerunner of the modern corporation, were formed to establish colonies. Individuals bought stock in the companies, which paid for ships and supplies, hoping to realize a profit from their investment. England vs. France VS Both sides traded for fur with the Native Americans living in the Ohio Valley. British colonists kept pushing farther westward into France’s territory in search of more land to farm. This escalated into the Seven Years War when France captured British trading posts and built Fort Duquesne at the present day site of downtown Pittsburgh. Initially France dominated the battlefield, but England succeeded in either forming alliances with or otherwise convincing France’s Native American allies to abandon her. Problems with the MissionPresidio System When France lost the Seven Years War to Great Britain in 1763, they decided to cede (formally give up ownership) Louisiana to Spain. Since Spain no longer had to worry about competing with France for Texas and Louisiana territory, in 1767 they decided to send Marqués de Rubí to Texas to review their North American colonies. Problems with the MissionPresidio System Rubí reported that Spanish power was spread too thin, and Comanche and Apache attacks on missions and presidios were only getting worse. As a result of Rubí’s findings, Spain decided to close most of the missions and presidios in Texas. By the 1770s, only a few remained and although Spain still claimed much of North America, they didn’t have enough people living there to actually control it. Portugal What about the Natives? Remember the Columbian Exchange? While contact with Europeans provided the Indians with horses, better weapons, cloth and metal, it also meant they were exposed to diseases like smallpox. Perhaps as many as 80-90% of Native Americans were eventually killed by those European diseases.