lecture 5 - INAYA Medical College
advertisement

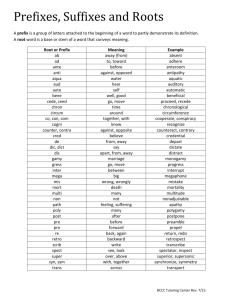
Foundation year T. sanaa abdel hamed MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Are to: 1. Describe the compositions of the blood plasma. 2. Describe and give the functions of the three types of blood cells. 3. Label picture of blood cell. 4. Interpret abbreviations used in blood studies. 5. List and describe major disorders of the blood. 6. Analyze several case studies involving the blood. The average human has 5 litres of blood. It is a transporting fluid. It carries vital substances to all parts of the body. X 500 X 500 • plasma (55%) • red blood cells • (Male: 4.32-5.72 trillion cells/L* (4.32-5.72 million cells/mcL**) Female: 3.90-5.03 trillion cells/L (3.90-5.03 million cells/mcL) • white blood cells • (3.5-10.5 billion cells/L) platelets ( 150,000 to 450,000 ) PLASMA • liquid part of blood. • plasma transports:- 1. Soluble food molecules. 2. waste products. 3. Hormones. 4. Antibodies. RED BLOOD CELLS 1. transport oxygen. 2. biconcave shape: increases the surface area so more oxygen can be carried. 3. Also carry CO2. 4. no nucleus. 5. contain haemoglobin. • (the oxygen carrying molecule) WHITE BLOOD CELLS • • • • • the bodies “defence”. part of the immune system. much larger than RBCs. far fewer. have a nucleus. • (3.5-10.5 billion cells/L) • 5 types. neutrophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, eosinophils and basophils if you get cut; platelets produce tiny fibrin threads. These form a web-like mesh that traps blood cells. Which forming a clot . MEDICAL TERMS RELATED TO THE BLOOD • 1. To coagulate (v): means to clot, to change from liquid to semi-solid. • 2. To arrest (v): means to stop. arrest - noun. • 3. Haemostasis (n) means stopping bleeding or slowing the movement of blood. • 4. Haemorrhage (n) means heavy bleeding. • 5. Haemophilia (n) means a hereditary haemorrhagic disease due to deficiency of coagulation factor VIII (a clotting facto • haemophiliac – adj. • 6. Leukocytes (n)[loo-ko-syt]: means white blood cell. The prefix leuko- means white. The suffix -cyte means cell. • 7. Leukaemia (n)[loo-keem-ia]: means a malignant disease where an abnormal number of leukocytes form in the blood. • Leukoaemic – adj. • 8. Septicemia (n)[septi-seem-ia]: means blood poisoning; a condition where the bacteria or their toxins are present in the blood and cause very severe illness. The prefix septo- means sepsis. • 9. Thrombin (n) means a substance which converts fibrinogen to fibrin and so coagulates blood. • 10. Thrombosis (n): means blood clotting. The combining form thromb/o- means blood clot. • 11. Erythrocyte (n): means red blood cell. The prefix erythromeans red. • 12. Haematology (n): means scientific study of blood. The combining form haemat/o means blood. • 13. Haematemesis (n): means vomiting blood. The suffix – emesis means vomiting. • 14. Haematoma (n): means collection of blood within the tissues that clots to form a solid swelling. The combining form –oma means tumour or swelling. • 15. Embolism (n): means blocking of an artery by a mass material (embolus). Emboli – plural. • 16. Cholesterol (n)[kol-est-er-ol] is a fatty substance (lipid) that circulates in the bloodstream, that is a main component of cell membranes and is important in • metabolism and hormone production. • 17. Hyperlipidaemia (n): means a high fat concentration in the blood. The prefix hyper- means high or excessive. The combining form lipid/o means fats. The suffix –emia means abnormal condition of blood. • Thank you