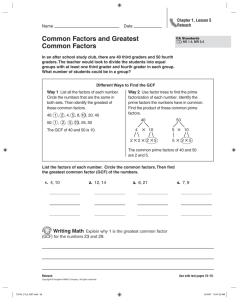
Lesson 2.7 Greatest Common Factor
advertisement

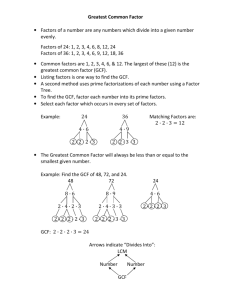
2-7 Greatest Common Factor Warm Up Problem of the Day Lesson Presentation Lesson Quizzes 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Warm Up Write the prime factorization of each number. 1. 20 22 · 5 2. 100 22 · 52 3. 30 2·3·5 4. 128 27 5. 70 2·5·7 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Problem of the Day: Part I Use the clues to find the numbers being described. 1. a. The greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers is 5. b. The sum of the numbers is 75. c. The difference between the numbers is 5. 35 and 40 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Problem of the Day: Part II Use the clues to find the numbers being described. 2. a. The GCF of three different numbers is 4. b. The sum of the numbers is 64. Possible answer: 12, 16, 36 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Learn to find the greatest common factor of two or more whole numbers. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Vocabulary greatest common factor (GCF) 2-7 Greatest Common Factor The greatest common factor (GCF) of two or more whole numbers is the greatest whole number that divides evenly into each number. One way to find the GCF of two or more numbers is to list all the factors of each number. The GCF is the greatest factor that appears in all the lists. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Additional Example 1: Using a List to Find the GCF Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of 12, 36, 54. Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12 Factors of 36: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36 Factors of 54: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, 54 List all of the factors of each number. Circle the greatest factor that is in all the lists. The GCF is 6. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Check It Out: Example 1 Find the greatest common factor of 14, 28, 63. 14: 1, 2, 7, 14 28: 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28 63: 1, 3, 7, 9, 21, 63 List all of the factors of each number. Circle the greatest factor that is in all the lists. The GCF is 7. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Additional Example 2A: Using Prime Factorization to Find the GCF Find the greatest common factor (GCF). 40, 56 40 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 5 Write the prime factorization of each number and circle the 56 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 7 common prime factors. 2·2·2=8 The GCF is 8. Multiply the common prime factors. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Additional Example 2B: Using Prime Factorization to Find the GCF Find the greatest common factor (GCF). 252, 180, 96, 60 Write the prime factorization 252 = 2 · 2 · 3 · 3 · 7 of each number and circle 180 = 2 · 2 · 3 · 3 · 5 the common prime factors. 96 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 2 · 2 · 3 60 = 2 · 2 · 3 · 5 2 · 2 · 3 = 12 The GCF is 12. Multiply the common prime factors. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Check It Out: Example 2A Find the greatest common factor (GCF). 72, 84 72 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 3 · 3 Write the prime factorization of each number and circle 84 = 2 · 2 · 7 · 3 the common prime factors. 2 · 2 · 3 = 12 Multiply the common prime factors. The GCF is 12. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Check It Out: Example 2B Find the greatest common factor (GCF). 360, 250, 170, 40 360 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 3 · 3 · 5 Write the prime 250 = 2 · 5 · 5 · 5 170 = 2 · 5 · 17 40 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 5 2 · 5 = 10 The GCF is 10. factorization of each number and circle the common prime factors. Multiply the common prime factors. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Additional Example 3: Problem Solving Application You have 120 red beads, 100 white beads, and 45 blue beads. You want to use all the beads to make bracelets that have red, white, and blue beads on each. What is the greatest number of matching bracelets you can make? 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Additional Example 3 Continued 1 Understand the Problem Rewrite the question as a statement. • Find the greatest number of matching bracelets you can make. List the important information: • There are 120 red beads, 100 white beads, and 45 blue beads. • Each bracelet must have the same number of red, white, and blue beads. The answer will be the GCF of 120, 100, and 45. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor 2 Additional Example 3 Continued Make a Plan You can list the prime factors of 120, 100, and 45 to find the GCF. 3 Solve 120 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 3 · 5 100 = 2 · 2 · 5 · 5 45 = 3 · 3 · 5 The GCF of 120, 100, and 45 is 5. You can make 5 bracelets. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Additional Example 3 Continued 4 Look Back If you make 5 bracelets, each one will have 24 red beads, 20 white beads, and 9 blue beads, with nothing left over. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Check It Out: Example 3 Nathan has made fishing flies that he plans to give away as gift sets. He has 24 wet flies and 18 dry flies. Using all of the flies, how many sets can he make? 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Check It Out: Example 3 Continued 1 Understand the Problem Rewrite the question as a statement. • Find the greatest number of sets of flies he can make. List the important information: • There are 24 wet flies and 18 dry flies. • He must use all of the flies. The answer will be the GCF of 24 and 18. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Check It Out: Example 3 Continued 2 Make a Plan You can list the prime factors of 24 and 18 to find the GCF. 3 Solve 24 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 3 18 = 2 · 3 · 3 2·3=6 Multiply the prime factors that are common to both 24 and 18. You can make 6 sets of flies. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Check It Out: Example 3 Continued 4 Look Back If you make 6 sets, each set will have 3 dry flies and 4 wet flies. 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Lesson Quizzes Standard Lesson Quiz Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Lesson Quiz: Part I Find the greatest common factor (GCF). 1. 28, 40 4 2. 24, 56 8 3. 54, 99 9 4. 20, 35, 70 5 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Lesson Quiz: Part II 5. The math clubs from 3 schools agreed to a competition. Members from each club must be divided into teams, and teams from all clubs must be equally sized. What is the greatest number of members that can be on a team if Georgia has 16 members, William has 24 members, and Fulton has 72 members? 8 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 1. Identify the greatest common factor (GCF) of 49 and 63. A. 6 B. 7 C. 8 D. 9 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 2. Identify the greatest common factor (GCF) of 25 and 15. A. 8 B. 6 C. 5 D. 4 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 3. Identify the greatest common factor (GCF) of 32 and 40. A. 3 B. 4 C. 6 D. 8 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 4. Identify the greatest common factor (GCF) of 24, 16, and 32. A. 4 B. 6 C. 8 D. 9 2-7 Greatest Common Factor Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 5. A florist has 20 roses, 35 lilies, and 75 daffodils. He arranges all the flowers in vases so that each vase has one type of flower and every vase has the same number of flowers. What is the greatest number of flowers in each vase? A. 8 flowers B. 7 flowers C. 6 flowers D. 5 flowers