Styles of Parenting
advertisement

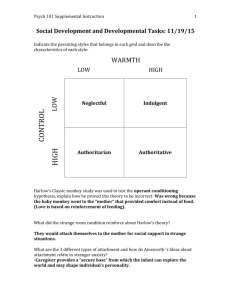
Infancy & Childhood Chapter 10 Section 1: The Study of Development Prenatal Care • • • • Must get enough to eat Take folic acid Best to be under age 40 No smoking, alcohol, or drugs • STDs can be detrimental Prenatal Development • Zygote • Embryo • Fetus Infants • APGAR Test (1-10 Score range) Developmental Psychology • Study of growth and change of people throughout the life span • Longitudinal Studies vs. Cross-Sectional Studies Nature vs. Nurture • Nature – – Maturation – – Critical period – time when human / animal is best suited to learn a particular skill or behavior pattern Nature vs. Nurture • Nurture – environment – Tabula Rosa – John Locke believed the mind of the infant is a blank slate Stages vs. Continuity • Does development occur in stages or as one continuous process? • Both, depending on the situation – Sit / crawl / stand / walk in stages – Growth in weight and height from ages 2-11 is continuous Section 2: Physical Development Height and Weight • Most dramatic gains in height and weight occur before infant is born • Slows down throughout rest of childhood Motor Development • Purposeful movement that usually occurs in stages Reflexes • Involuntary reaction or response (inborn) – Examples: breathing, blinking, swallowing, sucking, etc. – Rooting Reflex – Moro Reflex – Babinski Reflex Perceptual Development • Vision – At first, prefer pictures with complex patterns – Eventually prefer pictures of human faces • Depth Perception – the visual cliff experiment Perceptual Development (cont’d) • Hearing – Respond more to high-pitched sounds & mother’s voice • Smell and Taste – Respond immediately to strong odors Section 3: Social Development Development of Attachment • Attachment – emotional ties that form between people • Stranger Anxiety – • Separation Anxiety – Contact Comfort • Used to believe we became attached to those that fed us • Harlow’s monkey experiments proved we have a basic need to touch and be touched by something soft (skin or fur) – Stronger than need for food Imprinting • Attachment can be instinctual • Some animals attach during a critical period just after birth • First moving object is imprinted on young animal Secure vs. Insecure Attachment • When parents are affectionate and reliable, infants become securely attached • Unresponsive and unreliable parents cause insecure attachment Styles of Parenting •Strict Demanding Possessive Controlling Dictatorial Antagonistic • Cold Neglecting Indifferent Careless Negligent Detached Supportive Protective Affectionate Flexible Caring Lenient Democratic Inconsistent Overindulgent •Permissive • Warm Styles of Parenting Warm Parents • Lots of affection • Enjoy kid’s company –show it • Better off with warm parents • Better adjusted • Develop a conscious Cold Parents • More interested in escaping punishment than doing the right thing Styles of Parenting (continued) Authoritative • Warmth and positive strictness • Expect a lot, but explain why and offer help Authoritarian • Obedience for the sake of obedience • Strict without questions • Cold and rejecting Styles of Parenting (continued) Uninvolved • Tend to leave their children on their own • Make few demands, show little warmth or encouragement Permissive Parents • Easygoing • Less rules and let kids do what they want • Warm and supportive, but poor communicators Childcare • More than half of mothers work outside home • Effects of day-care – Quality important: learning resources, individualized attention, many caregivers important • Effects on parent-child attachment • Can be positive and negative Child Abuse and Neglect • Abuse – • Seriously underreported • Neglect – failure to give kid adequate food, shelter, emotional support, clothing, etc. • Effects: – Usually causes more problems Why does abuse happen? 1. 2. 3. 4. Stress History of abuse Substance abuse Lack of attachment Abuse runs in families • Kids imitate behavior • See it as normal • Pattern usually doesn’t continue Self-Esteem • Value or worth that people attach to themselves • Unconditional positive regard – Accept kids for who they are, kids know they’re not terrible people if they do something wrong • Conditional positive regard – Parents show love only when behaving in accepted ways – Kids will seek approval from others as adults Other factors that effect Self-Esteem • Feeling competent about a skill / task • Gender • Age Section 4: Cognitive Development Jean Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development • Sensorimotor Stage • Preoperational Stage • Concrete Operational Stage • Formal Operational Stage Kohlberg’s Theory of Moral Development • Pre-conventional Level (stages 1 & 2)– base judgments on consequences of behavior • Conventional Level (stages 3-4)– • Post-conventional Level (stages 5-6) – Reasoning based on a person’s own moral standards of goodness