course title (course code)
advertisement
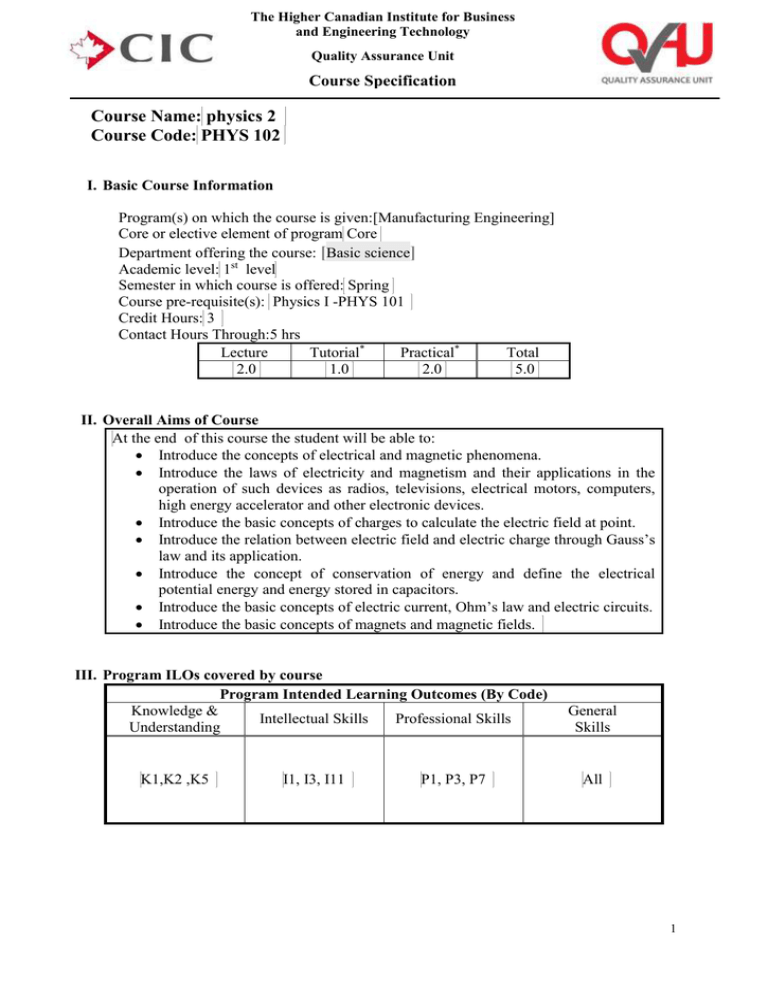
The Higher Canadian Institute for Business and Engineering Technology Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification Course Name: physics 2 Course Code: PHYS 102 I. Basic Course Information Program(s) on which the course is given:[Manufacturing Engineering] Core or elective element of program Core Department offering the course: [Basic science] Academic level: 1st level Semester in which course is offered: Spring Course pre-requisite(s): Physics I -PHYS 101 Credit Hours: 3 Contact Hours Through:5 hrs Lecture Tutorial* Practical* Total 2.0 1.0 2.0 5.0 II. Overall Aims of Course At the end of this course the student will be able to: Introduce the concepts of electrical and magnetic phenomena. Introduce the laws of electricity and magnetism and their applications in the operation of such devices as radios, televisions, electrical motors, computers, high energy accelerator and other electronic devices. Introduce the basic concepts of charges to calculate the electric field at point. Introduce the relation between electric field and electric charge through Gauss’s law and its application. Introduce the concept of conservation of energy and define the electrical potential energy and energy stored in capacitors. Introduce the basic concepts of electric current, Ohm’s law and electric circuits. Introduce the basic concepts of magnets and magnetic fields. III. Program ILOs covered by course Program Intended Learning Outcomes (By Code) Knowledge & Intellectual Skills Professional Skills Understanding K1,K2 ,K5 I1, I3, I11 P1, P3, P7 General Skills All 1 The Higher Canadian Institute for Business and Engineering Technology Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification IV. Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs) a. Knowledge and Understanding On completing the course, students should be able to: [k1 Recognize the methodology of solving engineering problems by using the first and second law of thermodynamics, thermal expansion, entropy, Kirchhoff's law, faraday law, ampere law, electromotive farce, electric and magnetic current, Maxwell equation, and Boltzmann distribution law. k2. State law of thermodynamics, kinetic theory of gases, faraday law, Kirchhoff’s rules, ohm’s law and electric power to discipline. k3. Locate and classify principles of heat and thermodynamics, entropy, magnetic field, electromotive force and potential force difference. k4. Explain faraday’s law, gauss’s law, ampere’s law, Kirchhoff’s rules, ohm’s law, car not engine and thermal expansion. k5. Describe Maxwell’s equation, the first and second law of thermodynamics, thermal expansion, faraday law and their application, magnetic force acting on current carrying conductor-motion of charged particles. k6. Interpret thermodynamics, entropy, faraday’s law, gauss’s law, ampere’s law, conductors to solve engineering problems of data collection and interpretation.] b. Intellectual/Cognitive Skills On completing the course, students should be able to: i1 Plan Kirchhoff’s law, ampere’s law, ohm’s law, entropy, electric power, absolute temperature, kinetic gas theory scale to think innovative way in problem solving and circuit design i2 Construct circuits using ampere’s law, ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s rules for solving problems and design. i3. Use the numerical methods in electrical circuits. c. Practical/Professional Skills On completing the course, students should be able to: p1 Use thermodynamics laws, Kirchhoff's rules, Maxwell equation, faraday’s law, gauss’s law and ampere’s law apply numerical physical modeling methods to solve engineering problems. p2 Practice Kirchhoff's rules, series and parallel capacitors and resistance and thermal expansion. p3 Resolve engineering problems by using Kirchhoff's rules, faraday’s law, entropy, gauss’s law. d. General and Transferable Skills On completing the course, students should be able to: g1.Cooperate effectively within multi disciplinary team. g2. To work in stressful environment and within constraints. g3. To Communicate effectively. g4. Use the efficient IT capabilities. g5 Management the tasks efficiently. g6 To Acquire entrepreneurial skills. g7 Refer to relevant literature effectively. g8. Searching for the information and going to self learning a new topic g9. Lead a group of research. 2 The Higher Canadian Institute for Business and Engineering Technology Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification V. Course Matrix Contents Main Topics / Chapters 1- Temperature Heat and 1st 2- law of thermodynamics The kinetic 3theory of gasses Heat engine ,entropy, and 42nd law of thermodynamics 5- Electric fields 6- Gauss law [Capacitance 7and dielectric] [Current and 8- resistance-direct current circuits] [Magnetic 9fields] [Sources of the 10magnetic field] Net Teaching Weeks Duration (Weeks) Course ILOs Covered by Topic (By ILO Code) I.S. P.S. i1,i2 p1,p2 1 K&U k1 G.S. g3 2 k1,k2,k5,k6 i1,i2 p1,p3 g1,g2,g3,g6 2 k1,k2 i1 p1 g1,g2,g3,g6,g5 2 k1,k2,,k6 p1 g1,g2,g3,g6,g5 1 1 k1 k4,k6 p1,p2 P1,p3 [1] [k1,k2,k5,k6] [i1,i2] [p2] g1,g2,g3,g4g5,g6 g1,g2,g3,g4g5,g6 [g1,g2,g3,g4g5,g6 ] [1] [k1,k2,k5,k6] [i1,i2] [p1,p2,p3] [1] [k5] [i1,i2] [p1,p3] [g1,g3] [1] [k1,k2,k3,k4,k5,k6] [i1,i2] [p1,p2,p3] [g8, g9] [g1,g2,g3,g6,g7] [13] VI. Course Weekly Detailed Topics / hours / ILOs Week No. 1 2 3 4 Sub-Topics Temperature –zeroth law of thermodynamics-thermometer and Celsius temperature scale-constant volume gas – thermal expansion of solids and liquid-macroscopic description of an ideal gas Heat and internal energy-heat capacity and specific heat-latent heat-work and heat in thermodynamic process The 1st law of thermodynamics-some application of 1st law of thermodynamicsenergy transfer mechanisms Molecular model of an ideal gas-molar specific heat of an ideal gas-adiabatic process for an ideal gas-the equilibrium Total Hours Contact Hours Theoretical Practical Hours Hours* 3 3 5 3 2 5 3 2 5 3 2 3 The Higher Canadian Institute for Business and Engineering Technology Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 of energy-Boltzmann distribution lawmean free path Heat engine and the 2nd law of thermodynamics-reversible and 5 irreversible process- the car not engine Heat pumps and refrigerator-entropy5 entropy changes in irreversible process Midterm Exam Properties of electric charges-insulators and conductors-coulomb's law- electric fields of continuous charge distribution5 electric field lines-motion of charged particles in a uniform electric fields Electric flux-gauss's law-application of gauss law to charged insulator5 conductors in electrostatic equilibrium Definition of capacitance-calculating capacitance-combination of capacitors5 energy stored in a charged capacitorscapacitors with dielectrics Electric current-resistance and ohm's law-a model for electrical conduction5 electromotive force-resistor is series and parallel-Kirchhoff's rule-RC circuit Magnetic fields-magnetic force acting on a current carrying conductor- torque on a current loop in a uniform magnetic field3 motion of a charged particle in uniform magnetic field The biot savart law-magnetic force between 2-parallel conductors-amperes 3 law-the magnetic field of a solenoid – magnetic flux-gauss's law in magnetism Revision 3 Final Exam Total Teaching Hours 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 0 3 0 3 0 4 The Higher Canadian Institute for Business and Engineering Technology Quality Assurance Unit Course Specification Teaching/Learning Method Selected Method VII. Teaching and Learning Methods Lectures & Seminars Tutorials Practical lab Work Reading Materials Research & Reporting Problem Solving / Problem-based Learning Group Work Presentations Course ILOs Covered by Method (By ILO Code) k1,k3 k4 k6 k1,k2,k4 k5,k6 Intellectual Skills i1 i2 i2 i1 i1,i2 Professional Skills p1 p2 p2 p1,p3 p3 General Skills g3 g1,g3 g1,g3,g2 g4,g5 g4,g5 k2,k3,k4 i1,i2 p3 g3,g5,g6 k5,k6 k1,k3 i2 i1 p2,p3 p2,p3 All All K&U Selected Method VIII. Assessment Methods, Schedule and Grade Distribution Course ILOs Covered by Method (By ILO Code) Assessment Method K&U I.S. P.S. G.S. Midterm Exam Final Exam Quizzes Course Work Report Writing Practical total 10 k1,k5,k3 50 5 10 k5,k6 k5,k1 k1,k2,k4 5 20 100 All Assessment Weight / Percentage Week No. 10% All p2 p1 g1,g7 g6,g7 50% 5% 10% k5 p1 g5,g3 5% k5 p1 g1 20 100% IX. List of References Essential Text Books Physics for Scientists and Engineers 6 th Ed , Raymond A. Serway Physics for Scientists and Engineers 6 th Ed , Raymond A. Serway Course notes Recommended books Periodicals, Web sites, etc … X. Facilities required for teaching and learning List the facilities required Pdf version from the text book, power point online Course coordinator: Dr. Ahmed Baday Head of Department: [Associate Professor Dr. Hamdy hussein] Date:15/9/2014 5