Vertex Form
advertisement

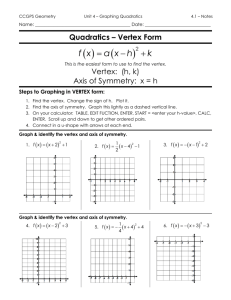
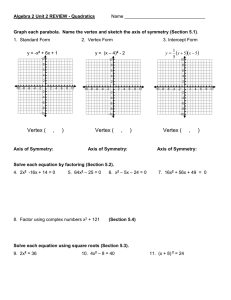
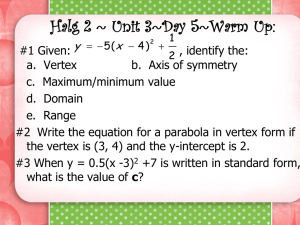
Vertex Form November 10, 2014 Page 34-35 in Notes Objective relate representations of quadratic functions, such as algebraic, tabular, graphical, and verbal descriptions[6.B] Essential Question • What parts of a quadratic function can I determine from the vertex form? Vocabulary • parabola: the shape of a quadratic function • vertex: the highest or lowest point on a parabola • y-intercept: the point where the graph crosses the y-axis • x-intercepts: the points where the graph crosses the x-axis • axis of symmetry: the vertical line that divides a parabola in two equal parts Vertex Form • f(x) = a(x – h)2 + k – “a” reflection across the x-axis and/or vertical stretch or compression – “h” horizontal translation – “k”: vertical translation What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k h k Vertex: (h, k) Axis of symmetry: x=h y-intercept: (0, y) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k h k Vertex: (h, k) Axis of symmetry: x=h y-intercept: (0, y) y=(x–2)2 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 k Vertex: (h, k) Axis of symmetry: x=h y-intercept: (0, y) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 k 0 Vertex: (h, k) Axis of symmetry: x=h y-intercept: (0, y) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 k 0 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) Axis of symmetry: x=h y-intercept: (0, y) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 k 0 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 y-intercept: (0, y) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 k 0 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 k 0 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) y = (x+3)2 – 1 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 y = (x+3)2 – 1 h 2 -3 k 0 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 y = (x+3)2 – 1 h 2 -3 k 0 -1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 y = (x+3)2 – 1 h 2 -3 k 0 -1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 y = (x+3)2 – 1 h 2 -3 k 0 -1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 y = (x+3)2 – 1 h 2 -3 k 0 -1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 k 0 -1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 k 0 -1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 -2 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 k 0 -1 4 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 k 0 -1 4 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) (-2, 4) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 k 0 -1 4 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) (-2, 4) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 x = -2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 k 0 -1 4 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) (-2, 4) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 x = -2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) (0, -8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 k 0 -1 4 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) (-2, 4) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 x = -2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) (0, -8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 y= 2(x+3)2+1 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 k 0 -1 4 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) (-2, 4) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 x = -2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) (0, -8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 y= 2(x+3)2+1 -3 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 -3 k 0 -1 4 1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) (-2, 4) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 x = -2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) (0, -8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 y= 2(x+3)2+1 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 -3 k 0 -1 4 1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) (-2, 4) (-3, 1) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 x = -2 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) (0, -8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 y= 2(x+3)2+1 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 -3 k 0 -1 4 1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) (-2, 4) (-3, 1) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 x = -2 x = -3 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) (0, -8) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 y= 2(x+3)2+1 What can we determine from the Vertex Form? Vertex Form: y=a(x-h)2 + k y=(x–2)2 h 2 -3 -2 -3 k 0 -1 4 1 Vertex: (h, k) (2, 0) (-3, -1) (-2, 4) (-3, 1) Axis of symmetry: x=h x=2 x = -3 x = -2 x = -3 y-intercept: (0, y) (0, 4) (0, 8) (0, -8) (0, 19) y = (x+3)2 – 1 y= -3(x+2)2+4 y= 2(x+3)2+1 To Graph from Vertex Form: 1. Identify the vertex and axis of symmetry and graph. 2. Find the y-intercept and graph along with its reflection. 3. Make a table (with the vertex in the middle) to calculate at least 5 points on the parabola. Example 1 (Left Side): y = (x + 3)2 - 1 -3 -1 vertex:__________ (-3, -1) h:_______ k:_______ x = -3 (0, 8) axis of symmetry: ___________ y-int: ________ x y -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 3 0 -1 0 3 y = (x + 3)2 – 1 y = (0 + 3)2 – 1 y = (3)2 – 1 y=9–1 y=8 Example 2 (Left Side): y = -3(x – 2)2 + 4 2 4 (2, 4) h:_______ k:_______ vertex:__________ x=2 (0, -8) axis of symmetry: ___________ y-int: ________ x y 0 1 2 3 4 -8 1 4 1 -8 y = -3(x – 2)2 + 4 y = -3(0 – 2)2 + 4 y = -3(-2)2 + 4 y = -3 • 4 + 4 y = -8 Assignment 1. f(x) = 2 x –2 2. g(x) = -(x – 4)2 3. h(x) = (x + 2 1) –3 4. j(x) = (x + 2)2 + 2 Reflection 1. How do you know if a parabola will open upward or downward? 2. When does the parabola have a maximum point? 3. When does the parabola have a minimum point?