Culinary 2 Curriculum Map Konkol final draft 104
advertisement

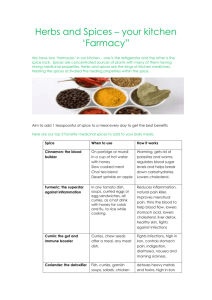
Aleta Konkol High School Culinary Skills 2+ Curriculum Map (9th-12th) (1 Semester Class) Textbook: Foods For Today and Culinary Essentials Month Content Skills Assessments September/ Safety and Sanitation February Skills (Review from CS1) Know basic skills to exhibit safe, secure, and sanitary work procedures. Proper knife handling skills Wash, cover w/ a band aid and wear a glove if you have a cut and want to cook in the lab Sandwiches and appetizers Explain why the 7 steps of the HACCP food safety system are necessary. Describe the difference between direct contamination and crosscontamination of food. Describe what FAT TOM is and explain what each letter stands for. Explain what a foodborne illness is. Avoid crosscontamination Explain 7 knife safety points. Demonstrate the 3 basic cutting techniques. •Explain how to clean & use knives properly Identify first-aid procedures for accidents & injuries Know the temperature Other Resources: King County Food Handler’s card website Essential Questions Objectives Standards All students must pass a variation of the Students must demonstrate an District Safety and Sanitation test with understanding of safety and sanitation 100% before they can participate in food rules as specified by the King County Food labs; students may re-take the test as Handler’s Website and the Washington many times as possible in order to pass Restaurant Association. it w/ 100%. (This test contains: State Standard B1 – Value and true/false, multiple choice, and short demonstrate good sanitation habits. answer questions.) National Standards for Family and PROJECTS Consumer Sciences (NSFCS) 1. In teams, create a pamphlet of 21st Century Skills basic safety guidelines to prevent Essential Questions: Why is it important accidents and injuries. to be safe and sanitary in the kitchen 2. With partners, describe a recent labs? outbreak of a foodborne illness at a How can I use the safety and sanitation food establishment. Describe the learned for cooking at home? specific cause, how many people were affected, and their symptoms. Discuss how the establishment could have avoided the outbreak. 3. If your school has a cafeteria, research its HACCP program. Ask about each step in the program. If possible, watch a food-service worker who is responsible for monitoring a critical control point. Pay attention to the control point for the previous worker’s monitoring procedures and ask to review the logs for that particular critical week. Students will do an oral report on their findings October / March danger zone Standard E2: Apply recognized/ standard procedures for sandwich, hors d’oeuvres, and garnish preparation Describe hot and cold sandwiches Describe the types of hors d’oeuvres, canapés, appetizers and fancy sandwiches Demonstrate the various design and form for garnishes Students will review examples of different types of sandwiches, including simple hot, open-faced, hors d’oeuvres, grilled, deep-fried, and simple cold • Demonstrate preparation of several types of sandwiches, spreads and fillings • Explain the roles of the three components of a sandwich: bread, spread and filling Demonstrate preparation of a variety of hot and cold appetizers Students will watch a movie on best sandwiches found around the United States. From that movie, students will take notes on 10 sandwiches they have never tried or heard of before and their contents. Students will then from these 10 choose recipes for 3 of the sandwiches that they would like to make. From these 3, students will be placed in groups to create market orders of ingredients for 4. They will each divide their sandwiches into two and share their sandwich with one other person. Students will compare and contrast in an essay their sandwiches with the other person’s they tried. Students will further reflect on the situations in which each sandwich would be appropriately served and why based on a rubric they created around components such as: recipe’s level of complexity, availability of ingredients, and cost In what setting is it appropriate to serve a specific appetizer/sandwich and how would you know? 21st Century Skills • Social and Cross-Cultural Students will choose one appetizer from their culture which they like. They will bring in the recipe to make it. In groups of four, students will choose to make one of the recipes in their group to plate and present. In an oral presentation the next day, students will discuss their outcome and present it in terms of a 12 point reflection. • Interact Effectively with Others 9.A.1 Know when it is appropriate to listen and when to speak 9.A.2 Conduct themselves in a respectable, professional manner • Work Effectively in Diverse Teams 9.B.1 Respect cultural differences and work effectively with people from a range of social and cultural backgrounds 9.B.2 Respond open-mindedly to different ideas and values 9.B.3 Leverage social and cultural differences to create new ideas and November/ April Psychology of Foods increase both innovation and quality of work Arrange appetizers in an appealing manner. To have a basic working knowledge of the food service industry with respect to the roll teamwork and project planning play in the overall culinary experience. Students gain hands-on culinary experience and food preparation skills in a lab setting which strongly emulates “reallife” culinary practices and situations. Knowledge & Skills – What are the key knowledge and skills needed to develop desired understandings? • Recognize that food has a cultural and environmental context • Understand the influence that their own culture has on their personal nutrition and eating patterns • Identify the various reasons why we eat what we eat • Appreciate broad diversity of food from The instructor will lead a class discussion regarding the sensory evaluation of food and what influences our evaluation such as cultural heritage, emotions and psychology, religious beliefs and health concerns. Herb Association. Working with one seasoning sample at a time, students will take a small portion of the herb or spice and crush it in the palm of their hands to release the aromatic oils. They will sniff each sample and consider what foods come to mind. They will record those foods or cuisine type in a worksheet provided by the instructor. Some examples of herbs or spices that may be used are: basil, cinnamon, cloves, parsley, ginger, cilantro, cumin, dill, oregano and sage. Once students have completed this exercise they will create a compound butter utilizing at least 2 of the herbs or spices that they experienced in the exercise. Students will create a matrix of herbs and spices and identify what foods come to mind as well as perhaps what emotions they might associate with them. Students will write a reflection essay about what they believe may have shaped Enduring Understanding(s) – “big idea(s)” • The complexity of the role played by all human senses in the evaluation of food is an essential element of food preparation. • Evaluate and understand that their personal food preference is constantly evolving and changing. • How do my emotions impact my food preferences? • How can I develop my palate to accommodate more sophisticated flavors and flavor combinations? 21st Century Skills Social and Cross-Cultural Interact Effectively with Others 9.A.1 Know when it is appropriate to listen and when to speak 9.A.2 Conduct themselves in a respectable, professional manner Work Effectively in Diverse Teams 9.B.1 Respect cultural differences and work effectively with people from a range of social and cultural backgrounds 9.B.2 Respond open-mindedly to different ideas and values 9.B.3 Leverage social & cultural differences to create new ideas & increase both innovation and quality of work December/ May Stocks, soups and sauces other cultures their food choices and share portions of their reflections which might explain the emotions they associated with certain herbs in the matrix. Students will create one of the mother sauces and then create their own noodles to go with the sauce. Lab – sauces Lab - Soup and stocks Lab – Make own noodles using a variety of ingredients from spinach to basil and sundried tomatoes Identify the four essential parts of stock and the proper ingredients for each. Other students will evaluate their combination to see if the ingredients Demonstrate three complement each other. Students then methods to prepare will see if they can determine what herbs bones for stock and spices are present in the sauces of Identify the two basic four other groups. kinds of soups and give an example of On one particular day, in groups, students each. will compete in an All or Nothing Iron Chef competition to see which group is Demonstrate the able to prepare the best Hollandaise preparations of Sauce for their Egg Benedict. Students broth, consommé, will be scored on a 5 point rubric on taste, puree, clear, cream texture and presentation. soups Identify the mother sauces and describe other sauces made from them. Students will conclude this unit reflecting Prepare various on herbs and spices and how they change Sauces and the taste of sauces, soups, and stocks. demonstrate their use with appropriate foods Writing Standards 1.0 Student writes clearly and effectively. 2.0 Student writes in a variety of forms for different audiences and purposes. Reading 2.1 Demonstrate evidence of reading comprehension Math 1.1 Understand and apply the concepts and procedures of math 21st Century Skills How do grains, herbs, spices, and liquids and other flavoring ingredients give each type of sauce its uniqueness? January/ June Meat/Poultry/Seafood Identifying the different kinds of meat, poultry and seafood, understanding various methods of inspection and grading, handling, preparation techniques, and safe food storage enable me to make the best informed, desired selections of product ; choose appropriate preparation technique s contingent on time limitations and technique preference, and assist me in making the best recipe choices. Describe the various kinds of meat, poultry and seafood Demonstrate a variety of cooking methods to me used with different meats Demonstrate safe food storage, handling, and preparation techniques that prevent crosscontamination from potentially hazardous foods, • Demonstrate knowledge of how to prevent accidents and injuries Students will choose 3 separate meats and choose 3 different ways of preparing them. Using pictures from their preparation processes and quotes from tasters, students will prepare a power point to persuasively convince their audience that their three preparations of meats were the best. Using exit slips after each presentation, students will evaluate how well they were convinced by each group of presenters. Why is it important to understand that the way we cook meat, poultry and seafood affects its outcome? • Why is meat the most important and most expensive part of a meal prepared in a restaurant? •In what ways does meat consumption affect our environment and our world? LEARNING AND INNOVATION Creativity and Innovation Students will complete a portfolio Think Creatively throughout the semester. It will include Work Creatively with Others a recipes, pictures of student preparing Implement Innovations the meal, pictures of final presentation. Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Reason Effectively Make Judgments and Decisions Solve Problems Communication and Collaboration Communicate Clearly INFORMATION, MEDIA & TECHNOLOGY SKILLS Information Literacy Students in Culinary 2+ classes must Create Media Products complete 20 hours of community service Information, Communications and and then reflect on what they did, Technology (ICT Literacy) learned, etc. Students must get the Apply Technology Effectively signature of the immediate supervisor LIFE & CAREER SKILLS who can attest that they completed Flexibility and Adaptability their 20 hours. Be Flexible Initiative and Self-Direction Manage Goals and Time Work Independently Be Self-Directed Learners Productivity and Accountability Manage Projects Produce Results Leadership and Responsibility Guide and Lead Others Be Responsible to Others