Telomeres - kenickbiochems12
advertisement
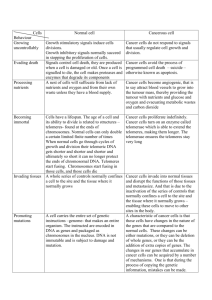
Telomeres & Telomerase Immortality or Death By Gretchen K. DeLue What are Telomeres ? • Specialized Proteins • Simple Repetitive DNA nucleotide sequence, located on ends of chromosomes • (TTAGGG) • (AATCCC) • multiple repeats of this hexanucleotide sequence over a 5kb span • Double-stranded telomeric repeats with only the extreme terminus consisting so single-stranded G-rich sequences (Gstrand/3’-single-stranded overhang • Protective Caps that serve as Buffers on Chromosomal Ends (15,000 BP long) Telomere Function • Essential for Maintaining the Integrity of DNA near Ends of Chromosomes • Stabilizes Chromosome • Protects from Deterioration and/or Merging with other Chromosomes - Preventative against Chromosomal Rearrangement/ Sticking together • Act as marker to distinguish between gaps and ends of DNA •Telomere Function is controlled by 2 Methods 1.) Erosion- Occurs each time cell divides 2.) Addition- Determined by action of Telomerase Telomere Figures •In a Human blood cell •-8000 telomeres at birth •-3000 telomeres in middle adulthood •-15oo in elderly adult - 30 to 200 base pairs lost from the ends of telomeres with each cell division - Progressively shorten with each completion of mitosis - Cell can divide around 50 to 70 times until telomeres become progressively shorter The Problem with Replication •Telomeres degrade further with each cell division •DNA is replicated bilaterally •DNA polymerases act unidirectionally •DNA polymerase require primer to initiate replication •20-500 base pairs unreplicated at 3’ end, each round of cell replication •Cells with telomeres are 10-12kb in length •Once telomeres are 4-6kb, cell dies What is Telomerase ? • Enzyme that repairs telomeres at the end of DNA by synthesizing telomeres • Restores telomeres to 3’end using own RNA as template • Responsible for maintaining telomere length • Located only in reproductive cells in humans; Telomerase is not active in other cells • Distinct sub-group of Proteins because so similar between diverse species Subunit Structure: - composed of a catalytic subunit, hTERT (human telomerase reverse transcriptase) -hTER (human telomerase ribonucleic acid) -Various other proteins -- Repairs telomeres located at ends of DNA - Elongates telomeric DNA at its 3’ overhang • Telomerase Structure: - Multi-subunit specialized ribonucleoprotein complex - Composed of: - TERC (Internal Telomerase RNA Template) & - TERT (Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase) Regulatory Factors of Telomerase • TERT: Catalytic component of the telomerase holoenzyme complex main activity is the elongation of telomeres by acting as a reverse transcriptase, adds simple sequence repeats to chromosome ends by copying a template sequence within the complex • The catalytic cycle involves primer binding, primer extension and release of product once the template boundary has been reached • Followed by further extension. •Telomerase activity is regulated by a number of factors -telomerase complex-associated proteins -chaperones and polypeptide modifiers (modulates Wnt) signaling. Plays important roles in aging and antiapoptosis Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase •TERT/hTERT • Subunit of Enzyme Telomerase (RNA component of the enzyme) • Catalytic component of the telomerase holoenzyme complex • Main activity is the elongation of telomeres by acting as a reverse transcriptase • Adds simple sequence repeats to chromosome ends by copying a template sequence within the RNA component of the enzyme. • Catalyzes the RNA-dependent extension of 3'-chromosomal termini with the 6-nucleotide Telomeric repeat unit, 5'-TTAGGG-3'. • More Active in sequences with 2 or 3 telomere repeats • Genome studies implicate TERT as gene responsible for many types of cancer Telomerase Paradox -The Absence of telomerase is correlated to telomere shortening, which is associated with aging and ultimately death of the somatic cells -However…. Highly active telomerase is present in over 90% of cancer cells in humans. - Theorized that the lack of Telomerase is a natural defense against developing cancer cells Telomerase Expression • Telomerase expression plays a role in cellular senescence, as it is normally repressed in postnatal somatic cells resulting in progressive shortening of telomeres. • Deregulation of telomerase expression in somatic cells may be involved in oncogenesis. Senescence: Cellular Aging • Process by which cells become old and die • Due to shortening of telomeres causing chromosome to reach critical length • What if Telomerase was in all somatic cells? Telomerase & Cancer • The presence of telomerase is what allows cancer to proliferate • 10-20 times the normal presence of telomerase is detected in malignant cancer cells •Cancer cells are considered to be immortal cells since high levels of telomerase constantly repairs telomeres on end of cancer genome by adding new nucleotides •If telomerase activity could be turned off, the telomeres would inevitably shorten within the cancerous cell •This shortening would ultimately make replication impossible, cancer would then be mortal rather then immortal just as human somatic cells are currently mortal by the same action. Cancer Detection/Treatment • Measuring telomerase may be a new way to detect cancer. • Inhibiting/Stopping Telomerase in cancer cells theoretically would cause cells to age and die. • Studies have blocked telomerase activity in human breast and prostate cancer cells in laboratory setting, prompting the tumor cells to die. Risks of Blocking Telomerase: Impairs: - Fertility - Wound healing, - Production of blood cells - Immune system cells. Telomere Shortening & Aging •Shorter telomeres linked to shorter lives and higher susceptibility to infectious disease •Adults over age 60 with shorter telomere sequences were 3 times more likely to develop heart disease and 8 times more likely to circum to infectious disease •Unclear whether telomere shortening actually contributes to/or is an attribute of the aging process. Telomerase & Immortality • Estimates currently concede 30 years of life may be added by lengthening telomere •Adults over 60 with longer telomeres live an average of five years longer •If gene that produces telomerase can be turned on, the aging process may be slowed, reversed or stopped entirely •If all aspects that contribute to aging were eliminated, it is estimated people may live 1000 years. References AMA(American Medical Assoc.)Reference ListPhatak P, Burger A. Telomerase and its potential for therapeutic intervention. British Journal Of Pharmacology [serial online]. December 2007;152(7):1003-1011. Available from: Academic Search Premier, Ipswich, MA. Accessed April 10, 2012. APA(American Psychological Assoc.)ReferencesPhatak, P. P., & Burger, A. M. (2007). Telomerase and its potential for therapeutic intervention. British Journal Of Pharmacology, 152(7), 1003-1011. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707374 AMA(American Medical Assoc.)Reference ListZvereva M, Shcherbakova D, Dontsova O. Telomerase: Structure, functions, and activity regulation. Biochemistry (00062979) [serial online]. December 15, 2010;75(13):1563-1583. Available from: Academic Search Premier, Ipswich, MA. Accessed April 10, 2012. APA(American Psychological Assoc.)ReferencesZvereva, M. M., Shcherbakova, D. D., & Dontsova, O. O. (2010). Telomerase: Structure, functions, and activity regulation. Biochemistry (00062979), 75(13), 1563-1583. doi:10.1134/S0006297910130055 AMA(American Medical Assoc.)Reference ListAhmed A, Tollefsbol T. Telomeres, Telomerase, and Telomerase Inhibition: Clinical Implications for Cancer. Journal Of The American Geriatrics Society [serial online]. January 2003;51(1):116-122. Available from: Academic Search Premier, Ipswich, MA. Accessed April 10, 2012. APA(American Psychological Assoc.)ReferencesAhmed, A., & Tollefsbol, T. (2003). Telomeres, Telomerase, and Telomerase Inhibition: Clinical Implications for Cancer. Journal Of The American Geriatrics Society, 51(1), 116-122. doi:10.1034/j.1601AMA(American Medical Assoc.)Reference ListShin J, Hong A, Solomon M, Soon Lee C. The role of telomeres and telomerase in the pathology of human cancer and aging. Pathology [serial online]. April 2006;38(2):103-113. Available from: Academic Search Premier, Ipswich, MA. Accessed April 10, 2012. APA(American Psychological Assoc.)ReferencesShin, J., Hong, A., Solomon, M., & Soon Lee, C. C. (2006). The role of telomeres and telomerase in the pathology of human cancer and aging. Pathology, 38(2), 103-113. doi :10.1080/0031320600580468 AMA(American Medical Assoc.)Reference ListMcChesney P, Turner K, Jackson-Cook C, Elmore L, Holt S. Telomerase Resets the Homeostatic Telomere Length and Prevents Telomere Dysfunction in Immortalized Human Cells. DNA & Cell Biology [serial online]. May 2004;23(5):293-300. Available from: Academic Search Premier, Ipswich, MA. Accessed April 10, 2012. APA(American Psychological Assoc.)ReferencesMcChesney, P. A., Turner, K. C., Jackson-Cook, C., Elmore, L. W., & Holt, S. E. (2004). Telomerase Resets the Homeostatic Telomere Length and References AMA(American Medical Assoc.)Reference ListLuis E. D. Telomeres in cancer and ageing. Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society B: Biological Sciences [serial online]. January 12, 2011;366(1561):76-84. Available from: Academic Search Premier, Ipswich, MA. Accessed April 10, 2012. APA(American Psychological Assoc.)ReferencesLuis E., D. (2011). Telomeres in cancer and ageing. Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 366(1561), 76-84.