Gilded Age - Progressive Era - Grapevine
advertisement

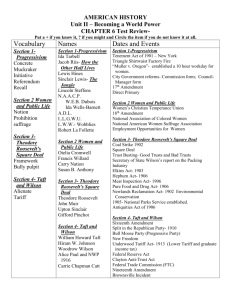
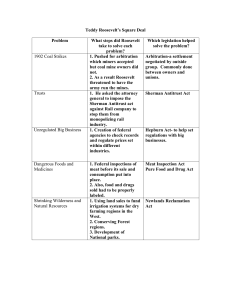
Gilded Age Progressive Era (1870’s1920’s) Political Parties Republicans: the republican party which arose in 1854 consists mainly of northern white Protestants, businessmen, small business owners, professionals, Factory workers, farmers, and African Americans The Republicans formed due to the Kansas-Nebraska Act and have been a leading political party ever since. Platform *Pro- Business *Expanding Railroads, Businesses and Banks *Gold Standard *Protective tariffs for workers Political Parties Democrats: The Democratic party came as a spin off from the DemocraticRepublican party, and formed to oppose the federalist party. The Democrats opposed a National Bank, and the United States working with Britain. Platform * Weak Federal Government *States Rights *Strict policy of following the constitution Political Parties Populists: The populist party arose in favor of the Western and Southern farmers who were affected by the Mckinley tariff, because of this tariff the farmers were forced to buy expensive manufactured goods. The Populist party was formed when the “Farmers Alliance” merged with many small democratic parties. Platform *Cheap Silver Money 16 ounces of Silver to 1 ounce of Gold *Government ownership of railroads and telephone companies *Graduated income tax *Direct election of senators *Immigration restrictions *Shorter work days Political Parties Progressives: Founded by Theodore Roosevelt, after him and Taft split the Republican Party. Platform: Minimum wage law for women 8 Hour work day Farmers Relief Workers Compensation Federal Income tax Diminishing business corruption and political corruption Rutherford B. Hayes (March 4, 1877- March 4. 1881) Republican Rutherford B. Hayes won his election due to the Compromise of 1877 in which the democrats agreed to Hayes’ controversial victory only if Hayes agreed to end all federal army intervention in the souths politics. Hayes believed in equal treatment of all races, improvements in education, he put in place civil service reforms, and advocated the gold standard. Railroad strike of 1877- Railroads workers went on strike because of salary cuts, hayes ended this strike by using troops to suppress strikes. Vetoed Bland-Allison Act Would Have put silver money into circulation and eventually would’ve caused prices to rise. Hayes advocated the Dawes Severalty Act of 1887-Outlawed tribal ownership of land and forced 160 acres into the hands of individual indians. Goal: Assimilate Indians Outcome: Outcast of indians James Garfield & Chester Arthur(1881-1885) James Garfield became president in 1881, after just 1 year as president he was assassinated by Charles Guiteau. Garfield’s Vice President, Chester Arthur took over just one week after. These two men didn't have an eventful presidency. President arthur passed the Pendleton ActWhich created the Civil Service Commission to make sure Federal employees were being hired on merit, and that employees of the government weren't being put in government offices solely because they had money, or strong friendships with important people. Republicans Chester Arthur James Garfield Grover Cleveland(1885–1889 and 1893–1897) Democrat Grover Cleveland’s first term was uneventful, and came to an end because of his lowering tariffs policy which was beat by Benjamin Harrison’s Higher Tariff policy Grover Cleveland was the founder of the Bourbon Democrats whose platform opposed Free-Silver, Inflation, Subsidies to veterans, and High Tariffs. During Cleveland's first term he battled The Pullmen Strike and during his second term he battled the Depression 1893-During the depression gold reserves sank due to trading and Cleveland repealed the Sherman- Silver Act, during this depression the U.S treasury was at one of its lowest points 41,000,000. Cleveland was a non-interventionist, he opposed imperialism and expansion During cleveland's administration Coxey's army marched for debt relief programs. Benjamin Harrison(1889-1893)Republican Benjamin Harrison Focused on home during his presidency, he passed many pieces of legislation which bettered the United States economy, society, and political policy, these include… Sherman Silver Purchase act- Which allowed the government to buy more silver to produce currency. The Pension Act- Which gave money to civil war veterans Mckinley Tariff- Which increased duties on foreign goods to 50% Land Revision Act of 1891- Created National Forests During Harrison's administration the U.S.S Texas was Built, and advancements such as the battleship were added to the United States Military. William Mckinley(1897-1901)Republican Before president Mckinley was assassinated in September 1901, he guided the united states to win the SpanishAmerican War. Mckinly was an advocate of the Gold Standard, and protective tariffs. In 1890 he created the Mckinley tariff which increased the duty to 50%. in 1897 he created the dingley tariff which protected manufacturing companies from foreign competition. During Mckinley's presidency he annexed Hawaii as an independent republic. “Open Door Policy”- All nations would freely trade with china without trying to take over the country. Teller Amendment- Cuba would be independent as long as spain left. Mckinley was assassinated at the Pan American Association in New York. Theodore Roosevelt (1901-1909)Republican (Progressive) Theodore Roosevelt was strongly against “Trusts”, or large corporations, he became known as the trustbuster, breaking up major monopolies such as the Standard Oil Company. Roosevelt (Speak Softly And Carry a big stick) policy took advantage of smaller nations. Panama Canal- Roosevelt advocated the panama canal, but because of opposition he had to have the Hay-Bunau-varilla treaty created it gave the ownership of canal lands to the U.S. Roosevelt Corollary-The United states would collect and distribute debts to Europe because the United States is the only country allowed to get involved with latin american affairs. Gentleman's agreement- Japanese kids can go to schools in America as long as japan reduced its immigration numbers. Muckrakers caused public to demand regulations of food, and drugs with the Meat Inspection Act, and the Pure Food and Drug Act. Hepburn act- Strengthened Interstate Commerce Commission and gave it control of the Railroads. Environmental Conservation: Roosevelt set aside several million acres of forest and ore rich land. Newlands act- Sold federal lands in the west to make money for irrigation projects. “Square Deal” Roosevelt promised to focus on home policies, like organized labor, big businesses, and preserving the nation's resources such as ore, and forests. William Taft(1909-1913)Republican Dollar Diplomacy: Taft used money as leverage, he believed he could get small countries to back up the United States if we gave them money to support their economies. This eventually Failed. “Trust Busting”- taft continued Roosevelts antitrust sentiment, and filed 90 lawsuits.Taft Dissolved J.P Morgans trust, and John Rockefeller's. Payne-Aldrich Tariff- So many amendments that it didn't really change the tariff at all. Woodrow Wilson(1913-1916)Democrat Wilsons Legilation In Wilson's first 4 years he Reduced the tariff, Passed more anti-trust legislation, and Reformed the Banking system Underwood Tariff- reduced duties on foreign goods from 40% to 25%. La Foleetes Seamans Act- Protected Sailors rights and wages on merchant ships Federal Farm Loan Act- gave farmers access to easy credit Workingmen's Compensation act- Supported temporary disabled federal employees. Adamsons Act- 8 hour work day for all interstate railroad workers. 16th Amendment- Income tax Clayton- Anti-trust Act- Gave congress power to punish trusts. Banking Reform Federal Reserve act-created a decentralized national bank that has 12 branches, all private banks were owned and run by the branch of its region. The Federal Reserve Board had final say on setting interest rates and currency issuance. This reform helped stabilize the nation's finances. 17th amendment- Direct election of senators Jones act- Made philippines an official U.S territory and promised the filipinos independence after they created a stable government. Wars- Causes and Effects • Indian Wars: between Americans and Native Americans ◆ Cause: as white settlers pushed further westward and continued to push Indians from their lands ◆ Sand Creek Massacre 1864; Fetterman Massacre; Sioux Wars 1860’s and ‘70’s; Battle of Little Bighorn; Battle of Wounded Knee, Nez Percé ◆ Effects: contained and controlled Indians, contributed to the integration of Indians into regular American society Wars- Causes and Effects • Spanish-American War: 1898-1901 o Causes: USS Maine explodes in Havana Harbor, AM believes Spanish navy is in wretched condition o Dewey (AM) attacks Manila harbor in Philippines against Spanish; AM wins without fatalities o Effects: War was quick, decisive and crumbled the Spanish Empire; Hawaii annexed July 7th, 1898; AM now a full-fledged Far East Power; increased AM patriotism; AM gain European respect; AM assume dangerous commitments and caught up in imperialism; AM get a false sense of readiness Treaties • • • Compromise of 1877- Democrats place at presidential patronage trough and support for a bill subsidizing Texas and withdraw federal troops from Louisiana and South Carolina; Pacific Railroad of a South transcontinental line; Hayes receives remainder of votes Native Americans- Ft. Laramie 1851(Sioux Reservation) and Ft. Atkinson 1853: marked beginnings of reservation system Treaty of Paris 1898- Cuba free, Pacific island of Guam, Puerto Rico, and Philippians go to AM Treaties • Panama Canal o Hay-Pauncefote Treaty 1901 gave AM free hand to build canal and right to fortify it o Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty 1903 $40 million for canal strip of 10 miles Foreign Policy Issues and Ideology • • • Indians o Dawes Severalty Act 1877: herd natives onto reservations; outlawed tribal ownership of land and forced 160-acre homesteads into the hands of individual indians and their families with the promise of future citizenship o Goals: to assimilate Indians into white culture Expansionism Blaine’s “Big Sister” Diplomacy to Latin AM Foreign Policy Issues and Ideology • • AM new willingness to risk war over such distant and minor disputes demonstrated the new aggressive national mood Monroe’s Doctrine and the Venezuelan Squall o Border dispute between BR and Venezuela o AM claims BR is breaching Monroe Doctrine and that London should submit- London claimed that US should mind own business o Impact on BR-AM relations: LA friendlier to US; BR anger deflected to GR- “great recollection” between BR and US Foreign Policy Issues and Ideology • • • Teller Amendment: AM proclaims that when they overthrow the Spanish misrule, they would give Cuba their freedom AM occupation of the Philippines o Philippines hate compulsory Americanization and preferred liberty Portsmouth Conference, 1905 o Roosevelt intervenes in Russian and Japanese war in 1904 Foreign Policy Issues and Ideology • • • Roosevelt’s Big Stick Diplomacy: 1899-1908 o 1904: Roosevelt Corollary to Monroe Doctrine Dollar Diplomacy o How supposed to work: Washington encourages bankers to invest money into foreign areas of strategic AM concern Honduras and Haiti o AM feels obligated to take place of foreign countries in Latin AM to prevent economic and political instability Foreign Policy Issues and Ideology • Wilson comes into office o Hates imperialism o Impact on foreign investments: decrease and AM pull out of a loan to China o Jones Acts o Haiti and other imperialist actions (in Dominican Republic and Virgin Islands): US marines sent to protect AM lives and property Social issues The main social issues during the Gilded age and Progressive era, regarded the working conditions due to urbanization, poor quality living, child labor, immigration, womens suffrage, civil rights and treatment of the native americans. • • • • (1874) Woman’s Christian Temperance Union- promoted the idea of abstinence from alcohol. (1882) Chinese Exclusion Act- congress passed, completely banning Chinese immigrants (1889) Jane Addams found Hull House in Chicago- first settlement house that aided immigrants and also became a meeting place for women to discuss politics. (1896) Plessy vs Ferguson- Supreme Court issues, which facilitated segregation. Social Issues • • • • • • (1916) Adamson Act- establishes an eight-hour workday for railroad workers. (1916) Workingmen’s Compensation Act- Seeking a measure of Progressive support in an election year, President Woodrow Wilson signed it to extend financial help to federal employees who are injured on the job. (1919) Eighteenth Amendment ratified- prohibiting the sale and manufacture of alcoholic beverages. The measure was advocated by temperance groups such as the Womans Christian Temperance Movement and Progressives. (1920) Nineteenth Amendment ratified- Women are given the right to vote in the amendment passed by both houses of Congress. (1916) Federal Farm Loan Act- allowed farmers to borrow money at favorable rates of interest. (1916) Keating-Owen Child Labor Act- limits how many hours children are allowed to work, and bans interstate transport of goods produced by child labor. Publications Writing at the time of the Gilded Age to Progressive Era, turned from the romanticism of pre-civil war to post-war realism . Most writers wrote about the struggles of a post war society and depicted the terrible conditions of the economy, society and overall well-being of the nation. ● ● ● ● 1890- Jacob Riis publishes, How the Other Half Lives, depicting the living conditions of the New York slums. Riis’s exposé supports the accusation by many Progressives and Socialists that American capitalism fosters inequality. The expose also contained detailed pictures. 1885- Mark Twain, who wrote Huckleberry Finn, reproduced the everyday speech of unschooled whites and blacks, acknowledged social pretensions of the day, made fun of the Old South, and challenged racially biased attitudes toward African-Americans. 1889- Kate Chopin used feminist ideals in The Awakening, dealing with repression of a woman's desires. 1893- Stephen Crane’s Maggie: A Girl of the Streets depicted how urban life could turn a young woman to prostitution. Supreme Court Decisions o Wabash vs. Illinois (1886) – Denial of state power to regulate interstate rates for railroads and led to ICC o US vs. Wong Kim Ark (1896) – Wong Kim Ark denied re-entrance to US after visiting China due to Chinese Exclusion acts, even though he was born in the US o Munn vs. Illinois (1877) – Allowed states to regulate certain businesses within their borders, including railroads. o Muller vs. Oregon (1907) – Law that limited women to ten hours of work in factories and laundries. o Hammer vs. Dagenhart (1917) – prohibited the interstate shipment of goods produced by child labour o Adkins vs. Children’s Hospital (1922) – guaranteed minimum wage to women and children employed in District of Columbia Acts • • • • Bland-Allison Act (1878) – required Treasury to buy certain amount of silver and putting it into circulation as silver dollars (free coinage) Pendleton Act (1883) – stipulated government jobs that should be awarded merit; provided selection of government employees competitive exams (civil service commission) Interstate Commerce Act (1887) – railroads first industry subject to federal regulation; response to demand that railroads’ conduct be constrained Sherman Anti-trust Act (1890) – prohibits trusts (arrangement by which stockholders in several companies transferred shares into single trustees) Acts • • • • Corollary to Monroe Doctrine (1904) – made us “regional police” for all Americas, offering military aid to keep foreign influences out of the western hemisphere Hepburn Act (1906) – formally gave Interstate Commerce Commission authority to establish max railroad rates (enable government to discontinue free passes to loyal shippers) Pure Food and Drug/Meat Inspection Acts (1906) – First series of consumer protection laws; ban foreign interstate traffic in adulterated or mislabeled food or drug products Clayton Anti-trust Act (1914) – addition to Sherman antitrust act Amendments • 16th - Allowed federal government to collect • • • • income tax 17th - Direct election of Senators 18th -Prohibition of manufacturing, selling, or transfer of alcohol (temperance and Prohibition) 19th - Gave women the right to vote Platt (1901) – 8 conditions to which Cuban government had to agree to before US withdrew Tariffs • • • • McKinley Tariff (1890) – raised protective tariff rate to nearly 50% on average Wilson-Gorman Tariff (1894) – first peacetime income tax (2% on income over $88,100 (2010 dollars)) Payne-Aldrich Tariff (1909) – lowered certain tariffs on goods entering the US Underwood Tariff (1913) – First reduction of all the existing tariffs, but introduced graduated income tax