Cycloalkanes
advertisement

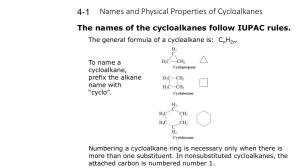
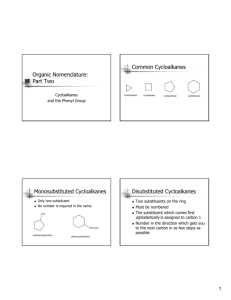
Cycloalkanes Cycloalkanes • Compounds that contain rings of carbon atoms • Have the general formula CnH2n • Represented by polygons in skeletal drawings cyclopropane cyclobutane cyclopentane Naming cycloalkanes 1. Count the number of carbon atoms in the ring and the number in the largest substituent. – If the number of carbon atoms in the ring is equal to or greater than the number in the largest substituent, the compound is named as alkyl-substituted cycloalkane. Substituted cycloalkane Cycloalkyl-substituted alkane Methylcyclopentane 3 carbons 4 carbons 1-cyclopropylbutane 2. For alkyl-substituted cycloalkanes, start at a point of attachment and number the substituents on the ring so as to arrive at the lowest sum. 2 6 1 1 3 5 6 2 4 4 5 3 1,3-dimethylcyclohexane NOT 1,5-dimethylcyclohexane 3. When two or more different alkyl groups or halogens are present, number them by alphabetical priority. CH3 CH2CH3 1-ethyl-2-methylcyclopentane NOT 2-ethyl-1-methylcyclopentane Cis-trans isomers • Because there is not free rotation in cycloalkanes, geometric isomers called stereoisomers are formed. • Cis (L. “on the same side”) • Trans (L. “across from”) • Geometric isomers do not convert back and forth. H H H H H H H Cl Cl H H H Cl H H H H H H H Cl H H H trans-1,4-dichlorocyclohexane cis-1,4-dichlorocyclohexane Chair Conformation Homework Page 320: 39-43