WORKSHEET 10: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
advertisement
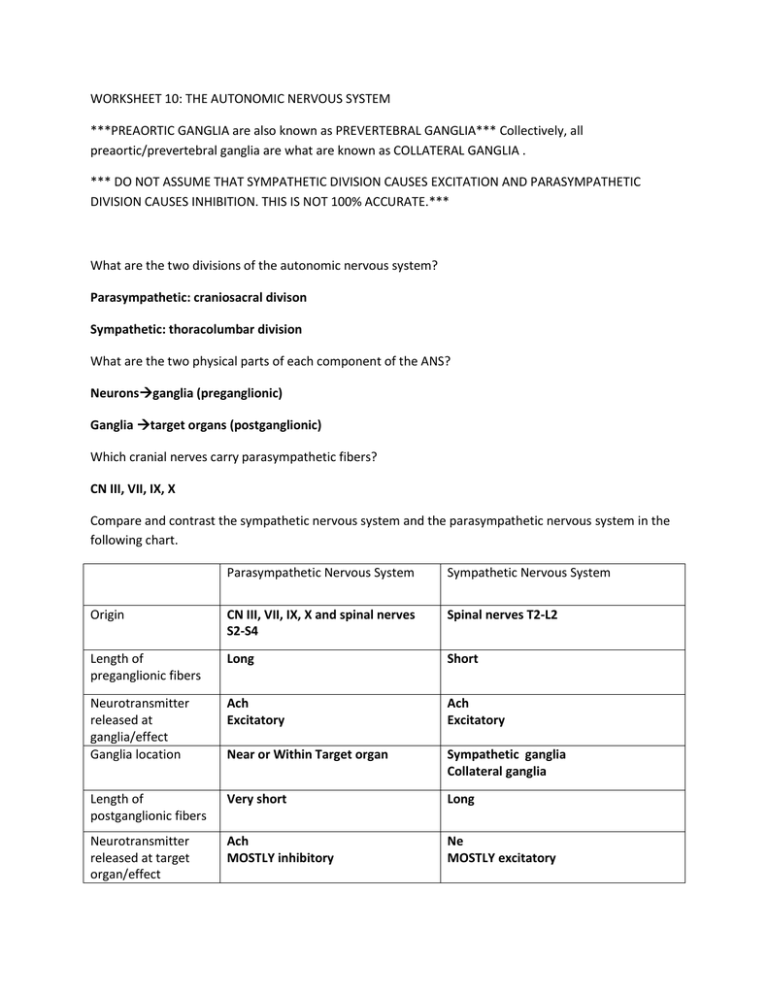
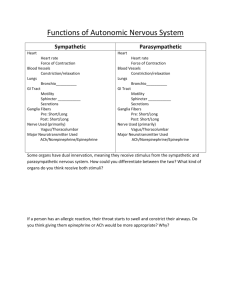
WORKSHEET 10: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ***PREAORTIC GANGLIA are also known as PREVERTEBRAL GANGLIA*** Collectively, all preaortic/prevertebral ganglia are what are known as COLLATERAL GANGLIA . *** DO NOT ASSUME THAT SYMPATHETIC DIVISION CAUSES EXCITATION AND PARASYMPATHETIC DIVISION CAUSES INHIBITION. THIS IS NOT 100% ACCURATE.*** What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system? Parasympathetic: craniosacral divison Sympathetic: thoracolumbar division What are the two physical parts of each component of the ANS? Neuronsganglia (preganglionic) Ganglia target organs (postganglionic) Which cranial nerves carry parasympathetic fibers? CN III, VII, IX, X Compare and contrast the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system in the following chart. Parasympathetic Nervous System Sympathetic Nervous System Origin CN III, VII, IX, X and spinal nerves S2-S4 Spinal nerves T2-L2 Length of preganglionic fibers Long Short Neurotransmitter released at ganglia/effect Ganglia location Ach Excitatory Ach Excitatory Near or Within Target organ Sympathetic ganglia Collateral ganglia Length of postganglionic fibers Very short Long Neurotransmitter released at target organ/effect Ach MOSTLY inhibitory Ne MOSTLY excitatory Target organs Glands and organs of head and neck, thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic organs Arrector pilli muscle, sweat glands, skin, blood vessels, thoracic and abdominal and pelvic visceral organs What are the effects of sympathetic stimulation? Increased energy Increased HR, BP, breathing rate Increased muscle tone Increased use of energy reserves (breakdown of glycogen from liver and fat from adipose tissue) What are the effects of parasympathetic stimulation? Increased activity in salivary glands Increased contractions in GI tract Stimulation of defecation and micturition Decreased HR, BP, breathing rate Sexual arousal What is the main difference between the synapse of sympathetic nerves going to heart and lungs and the ones going to abdominal organs? The difference is the location of synapse. Sympathetic nerves going to thoracic organs and the head and neck will go synapse at the sympathetic chain ganglia. After that synapse, postganglionic fibers will go to head, neck, and thoracic organs. Sympathetic nerves going to abdominal organs will bypass the sympathetic ganglia and unite to form several splanchnic nerves that will then synapse at collateral ganglia (celiac ganglion, superior mesenteric ganglion and inferior mesenteric ganglion). List the GANGLIA where preganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system synapse and the organs/structures where postganglionic fibers head to after that synapse. CN IIIciliary ganglionintrinsic muscles of the eye CN VIIpterygopalantine ganglion & submandibular ganglionlacrimal glands and salivary glands CN IXotic ganglionparotid gland CN Xintramural gangliathoracic and abdominal viscera Spinal nerves S2-S4intramural gangliapelvic viscera List the GANGLIA where preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system synapse and the organs/structures where postganglionic fibers head to after that synapse. Sympathetic chain ganglia organs of head and neck, thoracic viscera like the heart and lungs Collateral ganglia Celiac ganglionstomach, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, duodenum Superior mesenteric ganglionSmall intestine, part of large intestine Inferior mesenteric ganglionrest of large intestine, kidneys, gonads (pelvic viscera) ***Parasympathetic fibers are not distributed in all peripheral nerves. These DON’T go to sweat glands or blood vessels or arrector pilli muscle. Parasympathetic fibers have LIMITED distribution.