Description
advertisement

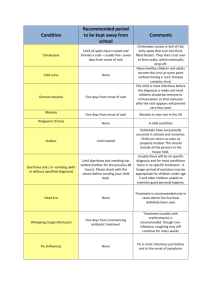
CHICKEN POX&SMALL POX Edited by: Dr: HALA ALI ABED Lecturer of public health Definition of the disease( bacterial ,viral, zoonotic ……….etc). Magnitude of the problem. Epidemiology of the disease: Agent. Reservoir: man only, animal only or man& animal. Mode of transmission. Incubation period. Susceptibility: Distribution of the disease according to time , place person. * Immunity: natural( active& passive) and acquired (active& passive). * Herd Immunity. Diagnosis : - Clinical picture, complication and investigation. Prevention Control CHICKEN POX Epidemiology • Acute viral disease of children characterized by skin rash (centripetal and pleomorphic). Chicken pox is also called varicella. • Causative agent: Varicella Zoster (V-Z) virus • Reservoir:(man only) • Cases of varicella or herpes zoster: (V-Z) virus in the respiratory secretions and fluid of skin rash. • Mode of transmission: Direct droplet infection (cough spray). Droplet nuclei (air-borne). Contact infection (fluid of vesicles). Articles and fomites (by fluid of vesicles or respiratory tract discharge). Exposure to a case of herpes zoster • Incubation period: 2-3 weeks. • Communicability period: • Throughout the disease “1” day before and “7” days after appearance of skin rash. • Clinical picture Prodroma: Fever, headache and malaise. Skin rash: Centripetal: more on the abdomen. Pleomorphic: all stages of rash present, macules, papules, vesicles, pustule, crusts and scabs that fall off within one week • Complications Secondary infection of vesicles. Pneumonia. Encephalitis, rare. Fatality: rare • Diagnosis: • Clinical picture. • Lab-isolation of virus by tissue culture of vesicles – fluid. “To exclude small when suspected”. pox • Susceptibility : • Infant born to immune mothers have passive immunity. • Children (sporadic cases or outbreaks). • Adults may be affected (severe disease). • Vaicella zoster IgG modify or preventing disease if given withen 4days after exposure. • Durable immunity( virus remain latent, and disease may recure years later as herpes zoster in 15% of older adult. Prevention: 1- general prevention measures: for prevention of respiratory diseases. • 2- specific: A.Vaccine: • Type: live attenuated vaccine. • Adminsteration: 0.5 ml s.c • Immunity: 85%-90% for prevention of disease . 100%for prevention of severity. • Target group: • -children aged 18 months and up to 12 y who have not varicella before • -contact of cases: if given within 3 days of exposure. • Susceptible persons ˃ 13y e.g: health worker(2 doses ,4-8 weeks apart. B. Seroprohylaxis: by specific immunoglobulin, to high risk close contacts (prematures and debilitated children). Control: • a- Cases • Notification, Isolation(isolate children from school for 1 week after 1st appearance of the rash or until vesicles become dry). • , & Disinfection ( concurrent an terminal). • Symptomatic treatment: to relieve irritation of skin and prevent infection • Release: one week after appearance of rash (when rash disappears). • b- Contacts: • -Enlistment, surveillance( for maximum i.p) • - vaccine is given 3days after exposure if they are not vaccinated. • Seroprophylaxis for high- risk contacts. • And for newborns of mothers who develop chicken pox around delivery. SMALL POX VARIOLA • Acute infectious disease characterized by generalized skin rash, it has been eradicated from the world (1978). • Causative agent: • Variola virus. • Resistant to glycerol. • Destroyed by heat, potassium permanganate. • Survives several months in crusts of eruption • Reservoir • Cases: Virus in respiratory discharges and skin rash. • Incubation period: • About 14 days (international) • Mode of transmission: Direct droplet infection. Droplet nuclei and crusts (air-borne). Contact infection. Contaminated articles & fomites. • Communicability • From onset of disease till disappearance of rash (2-3 weeks). • Clinical picture: • 1- Prodroma: Fever, headache and backache (sudden). • 2- Skin rash: • Appears at the end of 3rd day of disease. • First on the face and then covers the body in 2-3 days. • Characterized by being: • - Centrifugal : more on face and extremities. • - More on extensor than flexor surfaces (maxillae free). • - More at areas of pressure. • - Monomorphic: only one stage present, the Stages of rash are macules & papules. Vesicles, pustules, crusts, Fall off at the end of 3rd w causing scar (permanent scar) • - Enanthema: Eruption of mucous membranes of mouth, tongue, nose, pharynx, larynx and other parts may be present. Types • 1- Variola major: with different forms of rash and severity • - Discrete. • - Confluent: extensive, severe rash fatal. • - Hemorrhagic: very high fatality. • 2- Variola minor (alastrim): Mild fever may simulate chickenpox but it is centrifugal and monomorphic. • 3- Varioloid: A mild form. In vaccinated cases, conjunctivitis and corneal ulcer, bronchopneumonia. mucosal ulcers, pneumonia and • Diagnosis: • Clinical: Prodroma and typical skin rash. • Laboratory: - Stained smears from vesicles and pustules. •- Chick embryo culture (from blood and fluid of eruption). •- Paul’s test on rabbit cornea fluid of vesicles on scarified rabbit cornea produces vesicles on rabbit cornea. • Prevention: By: (I) immunization. • (II) International measures. • Control: • a-Case: * Notification: even in suspected cases. • * Isolation in hospital. • * Disinfection. • * Treatment. • * Release: after all scabs disappear. • b- Contacts: • - Vaccination. • - Surveillance for 2 weeks. • c- Epidemic measures: • ► Trace source and channels of infection. • ► Mass vaccination of the area.