Multidimensional Arrays
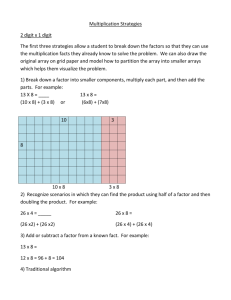
advertisement

Introduction
One
dimensional Arrays
Accessing array elements
Example 1
Example 2
Multidimensional
Arrays
Initialization of Multidimensional Arrays
Accessing Two-Dimensional Array Elements
Example
In C programming, one of the frequently arising problem is to handle similar types of data. For
example: If the user want to store marks of 100 students. This can be done by creating 100
variable individually but, this process is rather tedious and impracticable. These type of problem
can be handled in C programming using arrays.
Arrays are of two types:
One-dimensional arrays
Multidimensional arrays
One-dimensional arrays : A one-dimensional array is a type of linear array. Accessing its
elements involves a single subscript which can either represent a row or column index.
Syntax :
data type Array name[size of Array];
For example: int age[5];
Back
Here, the name of array is age. The size of array is 5,i.e., there are 5 items(elements) of
array age. All element in an array are of the same type .
Accessing array elements: In C programming, arrays can be accessed and treated like
variables in C.
For Example
scanf("%d",&age[2]);
/* statement to insert value in the third element of array age[]. */
scanf("%d",&age[i]);
/* Statement to insert value in (i+1)th element of array age[]. */
/* Because, the first element of array is age[0], second is age[1], ith is age[i-1] and
(i+1)th is age[i]. */
printf("%d",age[0]);
/* statement to print first element of an array. */
printf("%d",age[i]);
/* statement to print (i+1)th element of an array. */
Example 1.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
main()
Back
{
int i , min_value , max_value ;
int list[10] ;
for ( i=0 ; i<10 ; i++)
list[i] = rand() ;
/* Find the minimum value */
min_value = 32767 ;
for ( i=0 ; i<10; i++)
if (list[i]<min_value)
min_value=list[i] ;
printf("Minimum value generated is %d\n" , min_value) ;
/* Find the maximum value */
max_value = 0 ;
for ( i=0 ; i<10; i++)
if (list[i]<max_value)
max_value=list[i];
printf("Maximum value generated is %d\n" , max_value) ;
}
Back
Example 2.
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int i[10],j;
for ( j=0 ; j<10 ; j++)
i[j] = j ;
for ( j=0 ; j<10 ; j++)
printf("%d\n" , i[j]) ;
}
Back
Multidimensional Arrays
C programming language allows to create arrays of arrays known as
multidimensional arrays.
Syntax: type array Name [ x ][ y ];
Where type can be any valid C data type and array Name will be a valid C
identifier. A two-dimensional array can be think as a table which will have x
number of rows and y number of columns.
For example: float a[2][6];
Here, a is an array of two dimension, which is an example of multidimensional array. This array
has 2 rows and 6 columns.
Initialization of Multidimensional Arrays :
initialized in different number of ways.
In C, multidimensional arrays can be
int c[2][3]={{1,3,0}, {-1,5,9}};
OR
int c[][3]={{1,3,0}, {-1,5,9}};
OR
int c[2][3]={{1,3,0} , {-1,5,9}};
For better understanding of multidimensional arrays, array elements of
above example can be shown as:
Thus, every element in array a is identified by an element name of the form a[ i ][ j ], where a is the
name of the array, and i and j are the subscripts that uniquely identify each element in a.
Back
Accessing Two-Dimensional Array Elements : An element in 2-dimensional array is
accessed by using the subscripts, i.e., row index and column index of the array.
For example: int val = a[2][3];
The above statement will take 4th element from the 3rd row of the array.
Program 1
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
/* an array with 5 rows and 2 columns*/
int a[5][2] = { {0,0}, {1,2}, {2,4}, {3,6},{4,8}};
int i, j;
/* output each array element's value */
Back
for ( i = 0; i < 5; i++ )
{
for ( j = 0; j < 2; j++ )
{
printf("a[%d][%d] : %d\n", i,j, a[i][j] );
}
}
return 0;
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following
result:
a[0][0]: 0
a[0][1]: 0
a[1][0]: 1
a[1][1]: 2
a[2][0]: 2
a[2][1]: 4
a[3][0]: 3
a[3][1]: 6
a[4][0]: 4
a[4][1]: 8
Back
Thank You