cs1428_11_2DArrays
advertisement

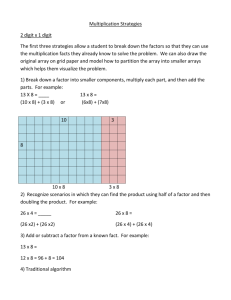
Two-dimensional Arrays Suppose you need to write a program that stores the student ID numbers of 20 students and then the grades for each of them on three different tests. You could create 4 parallel arrays to hold this data; but, it would be nice to put the test grades all into one storage structure. Something like the table below: ids[20] test_grades[20][3] 12345 89 90 92 23456 78 85 73 34567 100 98 91 ‘’ 45678 … … 65 71 … … 50 test_grades has two indexes: leftmost (20) = row index/size rightmost (3) = column index/size C - Strings The ‘string’ type we have been using is really something called a class. We have used them without really knowing what they are. You will get to classes in the next course. The ‘string’ C++ class was not always a part of the C++ language. Before that strings were always implemented as an array of char. Literals (as we have previously discussed) are stored this way. So – for now to have an array of strings, we will implement them as two-dimensional arrays of char. String: An array of char (C-Strings) C-Strings are actually single dimensional arrays of char char name[6] = “Trish”; Name is stored as an array of char with size 6 T r i s h null So, an array of c-strings is really a two-dimensional array of char names[3][10]; could store 3 names with a maximum length of 9 characters Each string in the array can be referenced by referring to its row number. Visual Look at names[5][11] E s p r e M o c h a C o l u m b D e c a f null H o u s e null names[0] == “Espresso” names[1] == “Mocha Java” names[2] == “Columbian” names[3] == “Decaf” names[4] == “House” s s o null J a v a i a n null null
![char[] name - Purdue University](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009372567_1-1dcf9c35e4c7b83b043aa8c848d641be-300x300.png)