Metal + Nonmetal
advertisement

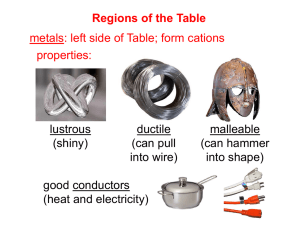
7.6 Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids By: Monique Briones, Marie Leibfreid, Bryanne Vollmer, Richard Wang In the Periodic Table ncrease Increase • No elements exist naturally as individual atoms EXCEPT noble gases • Metals—left and middle • Nonmetals—top right • Metalloids—between metals and nonmetals • Hydrogen nonmetal Characteristic Properties Metals • Luster, various colors (silver) • Solids malleable and ductile • Good conductors heat and electricity • Oxides are basic ionic solids • Form cations aqueous solution • Corrode • Dense • High melting point Nonmetals • • • • No luster, various colors Solids brittle, hard and soft Poor conductors heat and electricity Oxides molecular substances form acidic solutions • Anions or oxyanions in aqueous solution • Cannot change shape without breaking • Low melting point • Metallic Character—the extent to which an element exhibits the physical and chemical properties of metals • Nonmetallic Character— “the extent…” nonmetals Metals • Solids room temp. (except Hg, Cs 28.4C, Ga 29.8C) • Low ionization energies • Oxidized • Form positive ions easily • Noble Gas Electron Configuration (Alkali 1+, Alkaline Earth 2+) • Transition metals more than one positive ion • Alkali, Alkaline Earth, Transition, and Other Metals Cont. • Compounds with nonmetals are ionic (Ex: oxides) • Metal oxides basic, dissolve in water to form metal hydroxides (due to oxide ion) • React with acids to form salt and water • High melting point Alkali • Group 1A • Reactive • Do not occur naturally on their own • Bond with other elements since there is only one e- in outer shell • Soft • Explode in water Alkaline Earth • Oxidation number: +2 • Reactive • Not naturally found uncombined in nature • I.E. – Beryllium – Calcium – Radium Transition • Groups 3-12 • Valence e- in more than shell • Several oxidation states • I.E. – Titanium – Iron – Cobalt Other Metals • • • • Groups 13-15 Solid High density Opaque (light cannot get through) • Oxidation numbers: +3,+/- 4, -3 • I.E. – Aluminum – Tin – Lead Metal Chemical Reactions • Metal + Nonmetal ––––> Ionic substance – Ex: 2Ni(s) + O2(g) ––––> 2NiO(s) • Metal Oxide + Water ––––> Metal Hydroxide – Ex: Na2O(s) + H20(l) ––––> 2NaOH(aq) – Ex: CaO(s) + H20(l) ––––> Ca(OH) 2(aq) • Basicity Due to Oxide Ion – Ex: O2-(aq) + H2O(l) ––––> 2OH-(aq) • Metal Oxide + Acid ––––> Salt + Water – Ex: NiO(s)+ 2HCl(aq)––––> NiCl2 (aq) + H2O(l) Nonmetals • Vary greatly in appearance • 7 Diatomic (Gas: H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2; Liquid: Br2; Solid: I2) • Gain electrons when react with metals to form noble gas electron configuration • Completely nonmetal compounds are molecular substances • Oxides acidic, dissolve in water to form acids (acid rain) • Dissolve in basic solution to form salts Nonmetal Chemical Reactions • Tend to gain electrons when react with metals – Ex: 2Al(s) + 3Br2(l) ––––> 2AlBr3(s) • Nonmetal Oxide + Water ––––> Acid – Ex: CO2(g) + H2O(l) ––––> H2CO3(aq) – Ex: P4O10(s) + 6H2O(l) ––––> 4H3PO4(aq) • Nonmetal Oxide + Base ––––> Salt + Water – Ex: CO2 (g) + 2NaOH(aq) ––––> Na2CO3(aq)+ H20(l) Metalloids • Have metal and nonmetal properties • Found in stair shaped section of periodic table • Used in computers & calculators • Shiny or dull depending on element • Shape can be changed easily • Ex: Silicon – Looks like metal – Brittle – Poorer conductor of heat and electricity than metal • Electrical semiconductors Additional Research Chemical Behavior Metals Nonmetals • Reducing Agents • Form oxides that react with water to give hydroxides • Form basic hydroxides • React with O, F, H, and other nonmetals, giving ionic compounds • React with other metals, giving metallic compounds • Lower electronegativities • Have 1-5 electrons in valence, usually not more than 3 • Low ionization potentials, form cations by loss of electrons • Oxidizing agents (except noble gases) • Form oxides that react with water to give acids • Form acidic hydroxides • React with O, F, H, and other nonmetals, giving covalent compounds • React with metals, giving ionic compounds • Higher electronegativities • Usually have 4-8 electrons in valence • High electron affinities, form anions by accepting electrons in valence (except noble gases) Physical Behavior • • • • • • • Metals Good conductors of heat and electricity Malleable and ductile in solid state Metallic luster Opaque High density Mostly solids Crystal structure in which each atom surrounded by 812 nearest neighbors (metallic bonds between atoms) • • • • • • • Nonmetals Poor conductors Brittle and nonductile in solid state Show no metallic luster May be transparent or translucent Low density Gases, liquids, or solids Form molecules that consist of atoms covalently bonded; noble gases monatomic Metalloids • Has both properties • Has appearance of metal, but behaves chemically like nonmetal • Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Tellurium (Te), Polonium (Po), Astatine (At) • Not Aluminum • Semiconductors of electricity • Conductivity increases with temp. (metals decrease) • Ex: Silicon – Metallic luster – Forms weak acid Periodic Trends • Consistent with trends of ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity • Effective nuclear charge increase across period (left to right) and decrease down group (top to bottom) • Atomic Radius (decrease) • Ionization Energy (increase) • Electron affinity (general increase) • Electronegativity (increase) • Polarizability (Decrease) Dependence Oxidation Number • As oxidation number of element increases, metallic behavior decreases, nonmetallic behavior increases • HOCl (+1) is weak acid, HClO4 (+7) is strong acid • TlCl (+1) is ionic, TlCl3 (+3) is covalent Acidic and Basic Properties • Basic oxide—oxide that reacts with acids • Acidic oxide—oxide that reacts with bases • Amphoteric oxide—oxide with both basic and acidic properties • • • • MgO(s)+ 2HCl(aq) ––––> MgCl2 (aq) + H2O(l) CO2 (g) + NaOH(aq) ––––> NaHCO3(aq) Al2O3(s) + 6HCl(aq) ––––> 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H20(l) Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) ––––> 2Na[Al(OH)4](aq) Helpful Websites: • http://www.gordonengland.co.uk/elements/n on%20metals.htm • http://www.cstephenmurray.com/onlinequize s/chemistry/readingperiodictable/metalnonm etal.htm *** • http://www.mikeblaber.org/oldwine/chm1045 /notes/Periodic/Metals/Period06.htm • http://www.webelements.com/