Variable Cost - Binus Repository

Matakuliah : <<AKUNTANSI BIAYA II>>
Tahun : <<2009>>
DIRECT COSTING
Pertemuan Ke -1 dan 2
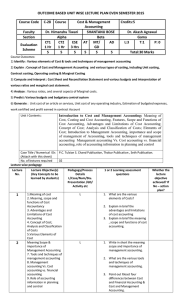
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Distinguish between direct costing and absorption costing.
Calculate income by direct costing and reconcile it with absorption costing.
State the uses of direct costing
State arguments for and against direct costing
Bina Nusantara University 3
DEFINITION
• Direct Costing also referred to as Variable Costing or
Marginal Costing, charges to products only those manufacturing cost that vary directly with volume.
• Materials, Labor and Variable FOH are assigned to
Work In Process, Finished Goods and Cost of Goods
Sold.
• All Fixed Manufacturing Cost are treated as period expenses.
Bina Nusantara University 4
CONTRIBUTION MARGIN
• Contribution Margin or Marginal Income is the difference between sales revenue all variable cost.
• C/M can be computed in total entire firm or separately for each product line, sales territory, operation division, etc
•
• Example :
Per unit Total % of Sales
Sales(10,000 units) $ 70 $ 700,000 100
Less variable cost 42 420,000 60
Contribution margin 28 280,000 40
Bina Nusantara University 5
INTERNAL USES OF DIRECT COSTING
• Direct Costing as a Profit-Planning Tool
• Direct Costing as a Guide to Product Pricing
• Direct Costing for Evaluating Profitability of Multiple
Products
• Direct Costing for Managerial Decision Making
• Direct Costing for Cost Control
Bina Nusantara University 6
EXTERNAL USES OF DIRECT COSTING
• Separating fixed and variable cost and accounting for each by direct costing will simplify both the understand of the income statement and assignment of cost to inventories.
• To keep fixed overhead out of reported product cost, variable and fixed cost should be recorded in separate account.
Bina Nusantara University 7
EXTERNAL USES
• For accounting of external activity is used two accounts for Factory Overhead : Applied FOH and FOH Control
• FOH Applied : predetermined
• FOH Control : actual
• Do adjusting to Income Statement about variance
Bina Nusantara University 8
DIRECT VS ABSORPTION COSTING
• DIRECT COSTING :
• Including Manufacturing Cost based on this Cost
Concept are Material, Labor and Variable Factory
Overhead.
• All Product Cost are Variable Cost , include Material and
Labor, although not be mentioned as Variable Cost.
• Approach : based on cost behavior
Bina Nusantara University 9
DIRECT VS ABSORPTION COSTING
• ABSORPTION COSTING
• Including Manufacturing Cost based on this Cost
Concept are Material, Labor, Fixed Factory Overhead and Variable Factory Overhead.
• All Product Cost are Fixed Cost and Variable Cost
• Approach : based on classifying of cost
Bina Nusantara University 10
INFLUENCES TO NET INCOME
• Production = Sales , so Net Income (NI) Direct Costing
(DC) = Net Income Absorption Costing (AC).
• Production > Sales , so Net Income (NI) Direct Costing
(DC) < Net Income Absorption Costing (AC).
• Production < Sales , so Net Income (NI) Direct Costing
(DC) > Net Income Absorption Costing (AC).
• Total Inventory determine differences on Net Income
Bina Nusantara University 11
FORMAT OF INCOME STATEMENT
• Format of I/S for Direct Costing use cost behavior concept.
• Margin Contribution will be obtained with subtracting
Sales to Variable Cost.
• Net Income will be obtained with subtracting Margin
Contribution to Fixed Cost.
• Format of Contribution (Margin)
Bina Nusantara University 12
Format of Contribution
• Format of I/S for Direct Costing
• Sales …………………………………… xxx
• Variable Cost …………..……………… xxx -
• Margin Contribution …………………… xxx
• Fixed Cost ……………………………… xxx -
• Net Income (Loss) …………………….. xxx
Bina Nusantara University 13
• Format of I/S for Absorption Costing use base on classifying of cost-related production cost.
• Gross Profit on Sales will be obtained with subtracting
Sales to Cost of Goods Sold.
• Net Income will be obtained with subtracting Gross
Profit to Operating Expenses.
• Format of Traditional or Conventional
Bina Nusantara University 14
Format of Traditional or Conventional
• Format of I/S for Absorption Costing
• Sales …………………………………… xxx
• Cost Of Goods Sold …...……………… xxx -
• Gross Profit …………………………… xxx
• Operating Expenses ……….………… xxx -
• Net Income (Loss) …………………….. xxx
Bina Nusantara University 15
CONCLUSION
• Direct Costing makes I/S for Internal User with using
Format of Contribution Margin .
• Direct Costing makes I/S for External User with including many variances to I/S.
• For External User can be used other I/S format : Format of Traditional/Conventional, its performance is same as direct costing with adjusting above.
Bina Nusantara University 16