CHAPTER IV Organization of business relations in trade
advertisement

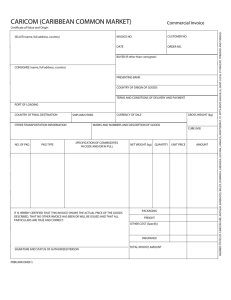
CHAPTER IV Organization of business relations in trade Chapter outline: 1. 2. 3. 4. Business relations in trade Procedure of trade regulations Conclusion and termination of a contract Content of necessary documentation Preface Every company which leads commercial activity enters into economic and legal relationships with their customers, suppliers and partners. In the economic literature, these relationships are usually characterized by the term “business relations.“ The concept of business relations - rather broad and includes a set of economic, institutional, commercial, legal, administrative, financial and other relations developing between manufacturers, consumers and commercial organizations in the supply of goods on the purchases or sales. Business relations of trade and industry - the most important part of the economic mechanism of the country, which is a set of forms, methods and instruments of interaction between enterprises, associations, firms, other sectors of the economy with consumers. Rational business relations contribute to the orderly development of the economy, the balance of supply and demand, timely delivery of industrial products and consumer goods to buyers. Business relations includes, in particular, participation of trade organizations in the development of industrial enterprises plans for the production of goods through the submission of applications and orders; economic contracts; monitoring compliance with contractual obligations; the use of economic sanctions; participate in the commodity exchanges and wholesale trade fairs; quality control (examination) of the supplied goods; the establishment of financial relationships; the use of administrative law and others. The administrative-command system of commercial companies’ management of business relations in trade subjected to detailed state control and regulation. State regulation of business relations between suppliers and buyers was introduced from the beginning of the centralized administrative system of the economy. In the 26th, (THE CONCEPT and TERMS of CONTRACT) 27th, (FORMATION of CONTRACT) ,28th (MODIFICATION and TERMINATION of CONTRACT) and 29th (Buying and Selling) Chapters of Civil Code of RT has brought the concept and basic terms of business relations. Articles of current Code includes norms and regulations of all scope of business relations (terms and conditions of contract, price terms, formation and termination of contract, trade procedure regulation, regulation in auction trade etc.) The legal basis for our businessmen in transactions of purchase and sale is the Civil Code of the RT. Contracts for the sale of goods in the domestic and international business are the most common type of business relations between buyers and sellers. What is a Contract? A contract is an agreement between two parties that creates an obligation to perform (or not perform) a particular duty. A legally enforceable contract requires: An Offer (I’ll mow your lawn this weekend if you pay me $30) An Acceptance (You’ve got a deal) Consideration (the value received and given – the money and the lawn mowed) Mutual Assent: A "Meeting of the Minds" A legally recognized offer and an acceptance create a "meeting of the minds", or mutual assent, between the parties. The law requires the parties to a contract to demonstrate mutual assent to the contracts' terms The Offer The Offer is the key element that defines the relevant issues in the contract. To be a legally valid offer, the offer must be effectively communicated so that the receiving party has the ability to accept or reject the offer. Whether or not the receiving party reads the contract has no bearing in determining the clarity of the offer. The offer must only provide the recipient with a clear opportunity to accept or reject the contract. Someone who signs a contract without reading it does so at his/her own risk. In addition, a valid offer must contain certain and definite terms. In determining whether the terms are definite, courts will review the clarity within four primary elements: the parties; the length of time for performance (term or service schedule) the price; and the subject matter or scope of services; The Acceptance For acceptance of an offer to be valid, the acceptance must be unequivocal (without any doubt) and unconditional. In other words, the acceptance must conform to the exact terms of the offer. If the acceptance is conditional on another event or stipulation, it creates a counteroffer and the roles of the parties become reversed. The conditional acceptance becomes a new offer. Types of commercial contracts: Types of contracts Contract of purchase and sale Rent contract Lease contract License contract Franchise contract Forms of contracts of purchase and sell Contract of purchase and sell Contract of Retail purchase And sell Delivery contract Agreement in Government procurement Contracting Procedure of purchase and sale 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Quotation Pro forma Invoice Contract of purchase and sale Invoice Commercial invoice QUOTATION VS PRO FORMA INVOICE A quotation is simply that, a written confirmation of the price of a product or service. A price quotation prepared in the form of an invoice, a pro forma invoice, is different from commercial invoices. It is used to create a sale and is sent in advance of the commercial invoice. The content of a pro forma invoice is almost identical to a commercial invoice and is usually considered a binding agreement although the price might change in advance of the final sale. Contract of purchase and sale An agreement of sale constitutes the terms and conditions of sale of a property by the seller to the buyer. These terms and conditions include the amount at which it is to be sold and the future date of full payment. Being an important document in the sale transaction, it enables the process of sale to go through without any hurdles. All the terms and conditions included in the agreement of sale must be understood thoroughly by both the parties and obeyed throughout the sale process till the time the sale deed is made. Agreement of sale is the base document on which the sale deed is drafted. INVOICE A commercial document that itemizes a transaction between a buyer and a seller. An invoice will usually include the quantity of purchase, price of goods and/or services, date, parties involved, unique invoice number, and tax information. If goods or services were purchased on credit, the invoice will usually specify the terms of the deal, and provide information on the available methods of payment. Commercial invoice A commercial invoice is a document used in foreign trade. It is used as a customs declaration provided by the person or corporation that is exporting an item across international borders. A commercial invoice must also include a statement certifying that the invoice is true, and a signature. A commercial invoice is used to calculate tariffs, international commercial terms and is commonly used for customs purposes. The definitive invoice for payment usually has only the words "invoice". This invoice can also be used as a commercial invoice if additional information is disclosed. 1. What kind of relations we can engage with business relations? 2. Definition and nature of a contract and types of contract? 3. Distinguish the terms quotation with pro-forma invoice? 4. Full content of the invoice