Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift
advertisement

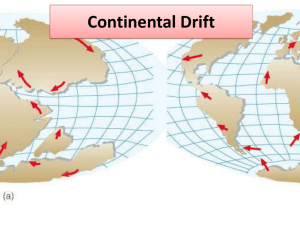
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift TEKS Objectives: • (8.3) Scientific processes. The student uses critical thinking and scientific problem solving to make informed decisions. The student is expected to: – (A) Analyze, review, and critique scientific explanations, including hypotheses and theories, as to their strengths and weaknesses using scientific evidence and information; – (E) Connect Grade 8 science concepts with the history of science and contributions of scientists. • (8.14) Science concepts. The student knows that natural events and human activities can alter Earth systems. The student is expected to: – Predict land features resulting from gradual changes such as mountain building, beach erosion, land subsidence, and continental drift; Earth Systems Alfred Wagner 1910-1920 • Introduced The Theory of Continental Drift • Based theory on: – S. America & Africa – paleontology (the study of fossils) How do such large continents move? Arthur Holmes 1930’s • Introduced supportive theory: Currents of heat and thermal expansion in the Earth's mantle move continental plates. Convection! Great Global Rift Discovered! • After WW1 – Germany found a mountain-like ridge that ran through the Atlantic to the southwest of Africa. • Today it is call MidAtlantic Ridge Harry Hess 1950-1960 • Introduced supportive theory: sea-floor spreading! • Different plate movements gave us different land forms: – Divergent = divide (Mid-Atlantic Ridge) – Convergent = come together (Himalaya Mt. Range or Appalachian Mt. Range) – Transform = sliding (San Andres Fault) Seismology • Seismology is the study of earthquakes. • Check out the data below that shows where most earthquakes occur. Volcanology • The Pacific Ring of Fire is an area of frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Plate Tectonics Theory • Developed from – Puzzle piecing of the continents – Paleontology (the study of fossils) – Convection (movement of heat) – Great Global Rift (aka Mid-Atlantic ridge) – Sea-Floor Spreading – Seismology (the study of earthquakes) – Volcanology (the study of volcanoes) But…. • What if everything I told you was old and scientists have created a new theory? • This new theory is not completely accepted, but how easily do people accept change? • Keep in mind that our Earth is a celestial body and star characteristics might not be to far off. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VjgidAICoQI&feature=related http://www.newgeology.us/