Translating Production to Profits
advertisement

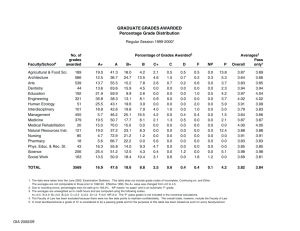
Market Regulation Food is most highly regulated of all consumer product industries Differences of opinion on the appropriate level of regulation Regulate Competition US founded on private enterprise Concerns about market power – 1890 Sherman Anti-trust Act – 1914 Clayton and FTC Acts set rules – 1936 Robinson-Patman Act »Price discrimination illegal unless economically justified Regulations of Monopolies Recognized natural monopolies and dealing with monopolies Capper-Volsted Act 1922 – Right of farmers to collectively bargain Agricultural Marketing Act 1937 – Established marketing orders for dairy and fruit and vegetables Facilitate Trade and Service PSA 1921 – Set standards for trade – Assured prompt payment Grades, weights, & standards Promotion and research 1980s – Checkoff activity Mandatory Price Reporting Federal initiative Midwest state regulations Currently – AMS collects, reports, doesn’t keep – GIPSA can demand all records but can report Consumer Health and Safety. Food and Drug Act – 1906, 1938 – 1958 Delaney Clause Food Quality Protection Act – 1996 replaced the Delaney Clause Wheeler-Lea Act 1935 – Truth in advertising – Labeling laws, 1973, 1990 Regulations on Food Prices Price control or freezes – Typically war time and/or rapid inflation – Retail price freeze -> farm price impact – WWI 1917-18 – WWII 1941-1946 also rationing – Korean conflict 1950-1953 – 1971-1973 inflation Economic and Social Progress 1862 Department of Agriculture 1862 Morrill Land Grant Act 1987 Hatch Act, experiment station 1914 Smith-Lever Act, extension Currently over 10,000 agricultural researchers employed by gov’t Standardization and Grading Reduces marketing costs – Improves communication – Possible to trade on description rather than inspection – Grading sorts commodities by defined quality standards – Quality grades typically optional Public or Private Use differs by industry – Cattle use USDA grades and graders »Moving to private grades – Hogs use private grading »Grading done by employee of buyer – Grain use USDA standards but grading by the buyer Examples of Grades Beef Quality Grades Prime 3-4% Choice 60-65% Select 30-35% Standard --- Yield Grades 1 11-12% 2 48-50% 3 33-40% 4 1-2% 5 <1% NATIONAL CARCASS PREMIUMS AND DISCOUNTS FOR SLAUGHTER STEERS AND HEIFERS For the Week of: April 20, 1998 Value Adjustments Quality Range Simple Avg Change Prime 3.00 - 10.00 5.71 0.00 Choice 0.00 - 0.00 0.00 0.00 Select -2.00 -4.00 -2.72 -0.30 Standard -12.00- -23.00 -16.43 -0.15 Examples of Grades Hogs – Barrows and Gilts »U.S. 1-2, 230-250 pounds »U.S. 1-3, 230-250 pounds – Sows »U.S. 1-2, 400-500 pounds W estern Cornbelt Lean Value Direct Hog Trade (close) Hot Carcass Value Information Based On Individual Packers Lean Value Programs and W eight Differentials - Plant Delivered 47-48 49-50 51-52 53-54 41.32 47.61 42.57 49.30 44.62 50.30 46.00 51.11 170191 45.31 49.14 45.31 49.30 47.15 52.50 48.50 54.50 192199 45.37 49.38 46.00 49.38 47.94 52.50 48.88 54.50 200207 45.37 50.17 46.00 52.17 47.94 54.17 48.88 54.50 pct Lean Car W t 163169 Examples of Grades #2 Yellow Corn #1 HRW Wheat ordinary protein #1 HRW Wheat 13% protein #2 SRW Wheat #1 Yellow Soybeans Mandatory v. Optional Grades Few precedents for compulsory Cost may increase if mandatory Industry may already have grades Grades may inhibit innovation Criteria for Grades and Standards Based on characteristics that – Are important to users – Are easily recognizable – Can be measured and interpreted by graders to reduce variation within a grade – Have common terminology – Represent the distribution of production – Make it cost effective to operate Problems of Grades and Standards Subjective nature of “quality” Made for industry not consumers Designing grades and grading methods – Accurate, fast, cheap, meaningful – Number of grades Implementing grades Farmers and Grades Not always used – Trust of grades or grader – Risk - reward Beef industry transition – Selling on average – Strategic alliances Marketing Agencies & Grades May add value to commodity Role of private brands Larger firms may develop own Specification contracts with more detail may replace grades Consumers and Food Grades Grades often confusing and offer little differentiation Consumers often do not understand grades Brand loyalty may replace uniform grades