File - Eaglet Preschool
advertisement

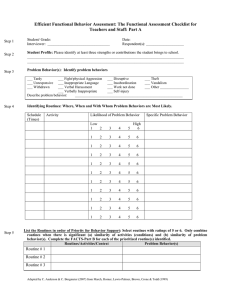
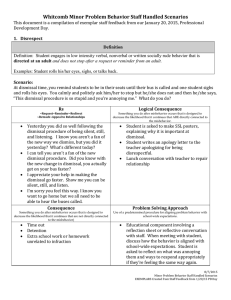
Positive Guidance Techniques Common Reasons Why Children Misbehave Normal behavior for their age Natural curiosity Don’t know better Attention Power Revenge Feeling inadequate at the task The need to feel they belong Positive Behavior and Choices In order to maintain control in a group setting, consider the amount of children with the space, safety, traffic patterns, and supervision within the room. When a child is misbehaving, the support teacher can sit beside a child and encourage them to participate. When a child habitually throws a tantrum at circle time because they do not get attention, remove the child from the group setting until they choose to calm down. Positive Behavior and Choices Schedules and routines are important because they provide structure and security for children which promotes positive behavior & choices. This reduces tension and fears due to the “unknown” thus reducing misbehavior. Misbehavior is the result of no consistency, schedule, or routines. Consistency is key to smooth schedules and routines. Guidance and Modeling To model appropriate behavior and actions. It is continually done, a caregivers daily job. Discipline Fair firm and consistent training so children know what is expected. Punishment A penalty inflicted for wrong doing through intimidation & fear. Self-Discipline The ability to control one’s own behavior by personal choice. Positive Guidance Techniques 8 Positive Techniques Natural Consequence Define Things that naturally happen without parental interference. Example Child doesn’t come home in time for dinner, goes hungry Limited Choices Define Giving a child 2-3 options so they can learn autonomy and decision making. Example Would you like apple juice, orange juice or milk? Logical Consequence Define Consequence that the caregiver sets as a result of the child’s choice or action. Should match the offense. Example If gaming longer than told minutes, the consequence is no gaming for the rest of the week. Time Out Define Child regains emotions in a quiet spot. Use sparingly. Example A child hit another child over dress up, time out for 4 minutes (age of child) Positive Statements Define Child is told what they can do rather than what they can’t do Example Instead of saying, “Don’t throw sand at your sister,” say: “Keep the sand in the sand box.” Reverse Attention/Positive Reinforcement Define Focusing on the child’s accomplishments and good choices through praise and ignore the negative behavior when possible. Example “I really like how Brody is sitting so quiet at circle time.” Redirection Define If a child is doing something you do not want them to do, direct them with another option. Example If children are fighting over dressup, “time to paint on the easel.” Modeling Define Used to show how children can solve their own problems. Used to show how children can solve their own problems. Example I can hang up my coat and find my name on the rug, can you? APPLICATION: Provide appropriate management solutions for dealing with problem behaviors. Be sure to list what positive guidance technique you are using FIRST, then proceed to explain what you will do.