Magnitude and Phase Measurements
advertisement

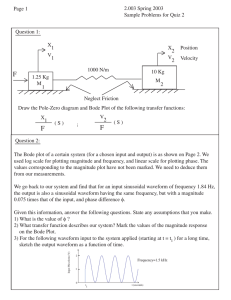
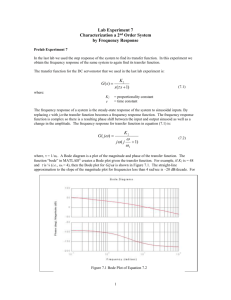
Magnitude and Phase Measurements Analog Discovery Set up the oscilloscope to measure the signal of the reference voltage (the input voltage from the arbitrary function generator, in this case) and the output signal from the operational amplifier. Set the Source of the trigger signal , located on the toolbar directly above the graph of the signals, to be equal to the channel of your reference signal, which is Channel 1 in this example). The Condition can be either Falling or Rising and the Level can remain at 0 V. Set the time division for the two channels to a value that is reasonably small to maximize the measurement accuracy. In this example, the Base selected is 200 us/div as the signals have a frequency of 1 kHz. Slightly less than two periods of the signals on the two channels is displayed. A smaller Base could be selected. Move one of the X cursors on to the plot by click-anddragging on the X in the lower left corner of the graph. Since the voltage of the reference signal should be 0 V at time is equal to 0 s, as set by the trigger function, you only have to measure the time when the second signal crosses the xaxis (i.e., has a value of 0 V). Note that this may be impossible to position the cursor to exactly the point where the value is equal to 0 V due to digitizing errors. This is one reason why you should select the smallest possible Base when performing this measurement. Record the time displayed with the cursor. Make sure that you have positioned your cursor to the point that is closest to time equal 0 s. Time = 0 ms is in the middle of the graph in this example. • Before you can determine the phase angle of the signal measured on Channel 2, you must also determine the period of the two signals. The period of both signals must be the same when calculating phase angles and when determining which signal leads or lags the other. – The period can be measured by moving the cursor to an appropriate position on the sine wave on Channel 1 (e.g., first time when the signal of Channel 1 is its maximum value after time = 0 s is equal to ¼ of T, the period of the signal). – Or, you can use the Measurement option on the upper toolbar of the scope program to determine the period of each signal. The steps to perform to use the Measurement option are described on Slides 19-20 in Intro_AnalogDiscovery_Scope.pdf, which was posted in Module 7. • The phase angle of the signal on Channel 2 using the signal on Channel 1 as the reference can then be calculated using the technique described in Phase Delay.pdf, which is posted in this week’s module (-61.2o in this example). • The amplitude of the two signals may be measured using the Y cursors. Or, you can use the Measurement option on the upper toolbar of the scope program. Measurements vs. Frequency It is often more interesting to measure the amplitude of one signal and the phase angle of that signal with respect to another over a range of frequencies. A plot of the amplitude and phase angle as a function of frequency is known as a Bode plot. To set up the oscilloscope to make a Bode plot, go back to the main window of the program. Select Bode Transfer Function from the pull-down menu at the lower right of the window. Channel 1 is assumed to be the reference signal in the Analog Discovery Bode plot. The magnitude of Channel 1 is referenced to the magnitude of the output of the arbitrary waveform generator, which you specify on the upper toolbar of the Bode Transfer Function GUI. The magnitude of the signal on Channel 2 is referenced to the magnitude of Channel 1. The magnitudes are plotted in dB as a function of frequency. Select the Start and Stop frequencies for the measurement using either the dropdown menu or by typing in a value into the box or by using the sliders to the right. The Steps and Max-Gain should be chosen to obtain a reasonably noise free plot in a relatively short period of time. A single set of measurements (Single) or repeating set of measurements (Run) can be made. The option is located in the upper left side of the toolbar. The cursor on the Bode plot is activated by right clicking in the graph and selecting Hot Track. A black line will appear of the graph, which you can drag to the frequency at which you want to make a measurement. Labels on the cursor will display the frequency at which the amplitude and phase measurements are shown. Or, you can click on File/Export. A pop-up window will open that contains a list of the data measured at each of the frequency steps used to form the Bode plot. Note that the number of data points that will be collected is set by the value of Steps in the upper toolbar of the Bode Transfer Function. You can either find the values of interest from the list displayed or export the list as well as the image of the Bode plot.