Electric Field Lines
advertisement

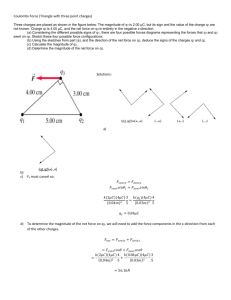
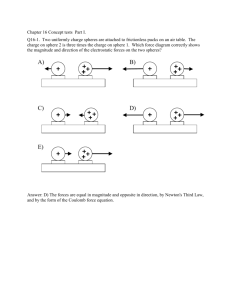
January 14-15 2016 What is a “force” field anyway? In physics, a ‘force’ field describes an area where objects experience a force-at-a-distance such as gravity, electrostatic force, or magnetism. In each case, the field is generated by a certain type of particle: • Gravity by a mass • Electrostatic by a charge • Magnetism by a moving charge Watch me! Electric Fields Let's take a single electric charge, Q, and put it somewhere. The space around Q is altered – it has the ability to cause a force on any other charge that approaches it. This space contains an electric field. Q An electric field is an area where another charge could feel a force. To actually experience the force, we need to introduce a second charge, q. An electric field can be measured by the force it exerts on another charge. E has units of N / C Magnitude and Direction of Electric Field The strength (magnitude) of electric fields depends just on distance from the charge Q and on the value of the charge. It does NOT depend on the test charge. Magnitude and Direction of Electric Field The strength (magnitude) of electric fields depend just on distance from the charge Q and on the value of the charge. It does NOT depend on the test charge. 𝐹 𝑘𝑞𝑄 𝑘𝑄 E= = 2 = 2 𝑞 𝑟𝑞 𝑟 E= 𝑘𝑄 𝑟2 Magnitude and Direction of Electric Field The strength (magnitude) of electric fields depend just on distance from the charge Q and on the value of the charge. It does NOT depend on the test charge. 𝐹 𝑘𝑞𝑄 𝑘𝑄 E= = 2 = 2 𝑞 𝑟𝑞 𝑟 E= 𝑘𝑄 𝑟2 Electric field is defined as having the same direction as the force that would occur on a positive test charge. Check for Understanding 1) How might you define electric field? an area around a charge that can exert a force on other charges / the force per unit charge 2) Which has a stronger electric field? A -4.0 μC charge or a 2.0 μC charge? -4.0 μC charge b/c E is proportional to charge 3)The electric field of a charge has a value E at 1 m away from the charge. What will be the strength of the electric field at 2 m away from the charge? ¼E 4) What is the value of the electric field 0.1 m away from an electron? (HINT: 1 electron has a charge of 1.6 X 10-19 C) E= 9109 1.610-19 = 1.4 X 10-7 N/C (10-1)2 5) A 5 X 10-5 C charge experiences a 15 N force when it is 0.5 m away from a charged sphere. What is the strength of the electric force at that location? What is the charge on the sphere? E = 3 X 106 N/C Q = 8 μC Electric Field Lines Electric field lines show the direction of the force on a positive test charge Electric field lines point towards negative charges Electric field lines point away from positive charges Electric Field Lines The density of lines shows the relative strength of the electric field This has two implications: 1) larger charges have more field lines radiating 2) As you move farther away from the charge, the strength of the field (density of lines) decreases Net Electric Field Lines If we have two or more charges creating an electric field, we add the vectors from each charge. NOTE: Electric field lines can never cross! That would mean that a test charge would go in two directions at once. Play with me! Question 1 - show with fingers B a) What is the charge of q1? Thumbs up for +, down for - b) What is the charge of q2? Thumbs up for +, down for - A c) Which charge is larger? d) Where will a positive charge at position A move? e) Where will an electron at position B move? Question 1 - show with fingers B A a) What is the charge of q1? Thumbs up for +, down for negative b/c field lines going towards the charge b) What is the charge of q2? Thumbs up for +, down for negative b/c field lines going towards the charge c) Which charge is larger? 2 – field lines are denser d) Where will a positive charge at position A move? Up e) Where will an electron at position B move? Up Question 4 What is the direction of the electric field at point C? 1) Left 2) Right 3) Zero Away from positive charge (right) Towards negative charge (right) y Net E field is to right. C x Question 5 What is the direction of the electric field at point A? 1) Up 2) Down 3) Left 4) Right 5) Zero A x Question 6 What is the direction of the electric field at point B? 1) Up 2) Down 3) Left 4) Right 5) Zero y B x Question7 What is the direction of the electric field at point A, if the two positive charges have equal magnitude? 1) Up 2) Down 3) Left 4) Right 5) Zero A x