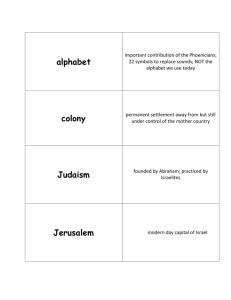
Introduction to Judaism
advertisement

Introduction to Judaism Professor Noam Pianko npianko@u.washington.edu Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 1 Class Overview • • • • Course Introduction Major Course Themes Syllabus/Expectations Start Historical Overview Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 2 Don’t Write this Down! • It will be available on the course website for download • Listen and engage in class! Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 3 Introduction • Who am I? • Who are you? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 4 What Do You Think? • How should we analyze a religion? • What topics would you want to know about? • How is studying Judaism similar/different from studying other religions? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 5 Six Areas of Investigation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Role of Scripture and Interpretation Theology and Symbolic Vocabulary Communal Forms and Religious Authority Ritual and Worship Ethical Values and the Formation of the Person 6. Ideologies of Political Life Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 6 1. Scripture and Interpretation • What are Judaism’s central texts? • How/when do certain texts become “scripture” or canonized ? • How does the process of interpretation work in Judaism? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 7 2. Theology and Symbolic Vocabulary • What are the core beliefs/symbols that orient the Jewish tradition? – – – – God Torah Israel Messiah/Redemption • How have these concepts changed over time in dialogue with surrounding cultures? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 8 Symbolic Vocabulary and Surrounding Cultures Canaanite Pantheon Christian and Islamic Mysticism Lecture 1 Greco-Roman View of the Cosmos Modern Philosophy and Ethics Introduction to Judaism 9 3. Communal Forms and Religious Authority • What is the Jewish ideal for community structure? • How are boundaries determined? Who is inside/outside of the community? • Who establishes norms in the community? • Who has authority to enforce norms? • How is authority challenged? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 10 Who Has Authority? A Nation Led By Prophets A Liturgical Community Led By Priests Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism Rabbi and Congregation The Rebbe and His Disciples 11 4. Worship and Ritual • What rituals (actions with symbolic meaning) and forms of worship does Judaism proscribe? • How is time punctuated on the Jewish calendar? • What are Jewish conceptions of worship and how have they changed? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 12 Jewish Worship: From Sacrifice to Yoga Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 13 5. Ethical Values and the Formation of the Person • What does it mean to be a good Jew? A good person? • Where do ethics come from? • How do celebrations of milestones (lifecycle events) contribute to the formation of the individual? • How have Jewish ethics/values changed over time? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 14 6. Ideologies of Political Life • How has Judaism interacted with its many majority host cultures? • What effect has life in the diaspora had on Judaism? • What is the relationship between the modern State of Israel and Judaism? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 15 A Taste of Contemporary Jewish Diversity • How do the six themes play out in this video? • What is interesting about the film? • What questions about Judaism does the film raise? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 16 Syllabus Notes • • • • • Writing and Analysis Emphasis Books in Class and Section Late Policy Introducing Jennifer Callaghan Key terms exam Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 17 Why Start Intro to Judaism with Jewish History? • Pragmatic Considerations • Past-Present-Future Blurred in Jewish Tradition – History and memory – Fact and myth Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 18 Central Themes in Jewish History 1. Fluid Boundaries Between Jew and non-Jew 2. Diaspora and “Imagined Community” 3. Persecution Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 19 Example Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 20 But First, Some Terminology • • • • • • Hebrews Israelites-Children of Jacob/Israel Judeans-Southern Kingdom Jews-Book of Esther Judaism Hebrew Bible/TaNaCh Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 21 Jewish History in Six Acts 1. Israelite Origins and the Babylonia Exile (1900 BCE-587 BCE) 2. Return to Judea and the Second Temple (515 BCE-70 CE) 3. Diaspora and Rabbinic Judaism in Babylon and Jerusalem(70 CE-632 CE) 4. Jews in the Islamic World (632 CE-1500 CE) 5. Jews in Medieval Europe (900-1500) 6. Jews in the Modern World (1500-present) Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 22 Ancient Israelite History • What do we know? • What sources are available? • What do you need to know? Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 23 The Historicity of the Bible • Nomadic group called “Habiru” • Migration from Mesopotamia into Canaan • Temple and New Capital built in Egypt in 13th century BCE • No Evidence of Exodus from Egypt • Pharaoh's Inscription (1220BCE) – “Israel is Laid to Waste, his seed is no more.” • Records of conquest Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 24 Bible Emerges from Ancient Near Eastern Setting • Bible reflects interactions with surrounding cultures • Bible culls from local traditions, narratives, rituals • Imagines community of Israelites as distinct and separate Lecture 1 Introduction to Judaism 25 Similar Divine Myths “When you [Baal] killed Litan, the fleeing serpent, finished off the twisting serpent, the mighty one with seven heads, the heavens withered and drooped” Lecture 1 “On that day, Yahweh will punish with his fierce, great, and mighty sword Leviathan, the fleeing serpent, Leviathan, the twisting serpent, he will slay the dragon of the sea.” Introduction to Judaism 26