File - Are You Reaching Your Students?
advertisement

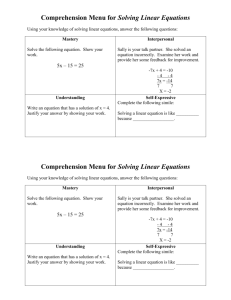
Are You Reaching Your Students? Using Learning Styles to Reach Your Students Tonya, Todd, Ashley, Cheri, Melisa What is a Learning Style? • Learning styles are simply different approaches or ways of learning. • In this presentation we will address the different ways that students learn, and give you an idea of how to incorporate these learning styles into your lessons. 3 Learning Styles • Kinesthetic or Tactile Learners are learners who learn by doing. • Auditory Learners are learners who learn by hearing. • Visual Learners are learners who learn by seeing. • (See Teaching Strategies Powerpoint) ASSESSMENT • In order to learn what learning style your student is you can give them an inventory that will help you name their strengths. Source: http://people.usd.edu/~bwjames/t ut/learning-style/stylest.html ASSESSMENT • A Learning Styles Assessment will be given at this time. • For these questions, choose the first answer that comes to mind. Don't spend too much time thinking about any one question. Source: Biology Junction http://www.biologyjunction.com/#just for teacher Multiple Intelligence- Linguistic • Linguistic Intelligence: the ability to produce and use language • Mastery: Uses language to describe events. Jobs: journalist, technical writer, administrator • Understanding: Uses logical arguments and rhetoric. Jobs: lawyer, professor, philosopher • Self-Expressive: Uses metaphoric and expressive language. Jobs: playwright, poet, ad writer, novelist • Interpersonal: Uses language to build trust and rapport. Jobs: salesperson, counselor, member of the clergy • Multiple Intelligence-Logical Mathmatical • Logical-Mathematical Intelligence: Ability to solve problems and think scientifically • Mastery: Uses numbers to compute and document. Jobs: accountant, bookkeeper, statistician • Understanding: Uses mathematical concepts for conjectures, proofs, and other applications. Jobs: computer programmer, scientist, logician • Self-Expressive: Sensitive to the patterns, symmetry, logic, and aesthetics of mathematics. Solves problems in design and modeling. Jobs: composer, engineer, inventor, designer • Interpersonal: Uses mathematics in everyday life. Jobs: tradesperson, homemaker Multiple Intelligence- Bodily • Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence: Ability to use parts or the whole body to solve problems, to construct products or displays • Mastery: Uses the body and tools to act, construct or repair effectively. Jobs: mechanic, trainer, craftsperson • Understanding: Develops strategic plans and critiques the actions of the body. Jobs: physical educator, sports analyst, professional athlete, theater or dance critic • Self-Expressive: Appreciates and uses the aesthetics of the body to create new forms of expression. Jobs: sculptor, choreographer, actor, dancer, puppeteer • Interpersonal: Uses the body to build rapport, console, persuade and support others. Jobs: coach, counselor, salesperson, trainer Multiple Intelligence-Spacial • Spacial Intelligence: Uses visual and spatial configurations • Mastery: Views the visual-spacial world accurately. Jobs: artist, guide, photographer • Understanding: Interprets and graphically represents visual or spacial ideas. Jobs: architect, icongrapher, computer graphics designer, art critic • Self-Expressive: Uses visual and spacial ideas creatively. Jobs: artist, inventor, model builder, cinematographer • Interpersonal: Uses color, space, line, form and space to meet the needs of others. Jobs: illustrator, artist, guide, photographer Multiple Intelligence- Musical • Musical Intelligence: Uses skills involving music • Mastery: Understands and develops musical technique. Jobs: technician, music teacher, instrument maker • Understanding: Interprets musical forms and ideas. Jobs: music critic, aficionado, music collector • Self-Expressive: Creates expressive and imaginative performances and compositions. Jobs: composer, conductor, individual/small group performer • Interpersonal: Works with others and uses music to serve others. Jobs: choral, band, and orchestral performer or conductor Multiple Intelligence- Interpersonal • Interpersonal Intelligence: Interacts with others, sensitive to their moods, temperament, motivations, and intentions • Mastery: Effective communicator and organizer of people. Jobs: consultant, politician, evangelist • Understanding: Interprets differences in interpersonal clues. Jobs: sociologist, psychologist, psychotherapist • Self-expressive: Creates imaginative and expressive performances and compositions. Jobs: composer, individual or small-group performer • Interpersonal: Works with others to use music to meet the needs of others. Jobs: coach, counselor, salesperson, or trainer Multiple Intelligence- Intrapersonal • Intrapersonal Intelligence: Understands one's own feelings and emotions • Mastery: Accesses and uses one's own weaknesses, strengths, talents, and interests to set goals. Jobs: planner, small business owner • Understanding: Develops concepts and theories based on self-examination. Jobs: psychologist • Self-expressive: Creates and expresses a personal vision based on inner moods, intuitions, and temperament. Jobs: artist, religious leader, writer • Interpersonal: Uses understanding of self to serve others. Jobs: counselor, social worker Interest Inventory • • • • • • • • Principles of Creating Student Interest Thinking is interesting. Interest is contagious. Interest is strengthened by a sense of progress. Interest is sustained by a state of suspense. Goals become interest centers. The novel and unexpected are interesting. Humor creates interest. Assessment- Interest Inventory • Interest Inventories will be given out at this time. • First day interest inventory to help you get to know your students. http://www.saskschools.ca/curr_content/adapthandbook/l earner/interest.html How to maintain student interest • Techniques for Creating and Maintaining Interest • • • • • • • • • • • • Arouse a feeling of need. Use illustrations and personal experiences. Use multiple sensory teaching and learning aids. Use a variety of teaching techniques. Base teaching on thinking. Create doubt and suspense. Build genuine interests in your students. Create a "felt need" for learning. Be enthusiastic. Use "real world" examples and situations. Expect quality from your students. Be professional.