21.2 Protist Structure and Function
advertisement

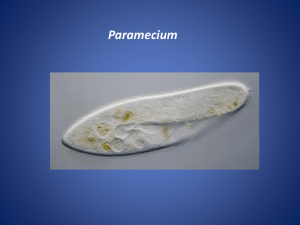
1. 2. 3. Explain How does conjugation produce genetic diversity in a population of Paramecium Compare and Contrast How does a macronucleus differ in function from a micronucleus Compare and Contrast Compare asexual and sexual processes in paramecium- include the terms mitosis and meiosis CH 21 PROTISTS AND FUNGI 21.2 Protist Structure and Function How Protists Move Change their cell shape Specialized organelles Do not actively move. Amoeboid Movement Move by changing their shape Pseudopods Use of cytoplasmic projections Powered by a cytoskeletal protein- actin. Cilia and Flagella Cilia Short and numerous Move like oars on a boat Ciliates. Cilia and Flagella Flagella Long and usually one or two long Spin or a wavelike motion from base to tip Flagellates. Passive Movement Depend on air or water currents and other organisms to carry them around Spores Reproductive cells that can enter the cells of other organisms and live as parasites. Protist Reproduction Asexually by mitosis Combine asexual and sexual forms of reproduction. Cell Division Many use mitosis Allows rapid reproduction Produces genetically identical cell, which limits the genetic diversity. Conjugation Two organisms exchange genetic material Not a type of reproduction because no new individuals are formed Sexual process because new combinations of genetic information are produced. Macronucleus Multiple copies of genes the cell uses in its day-today activities Micronucleus “Reserve copy” of every gene in the cell. Alternation of Generations Alternate between a diploid and a haploid phase. Water molds grow into long branching filaments. Sporangium Structure that produces spores asexually. Reproduce sexually by meiosis and form male and female structures Haploid nuclei fuse during fertilization, forms a zygote and begins a new life cycle.