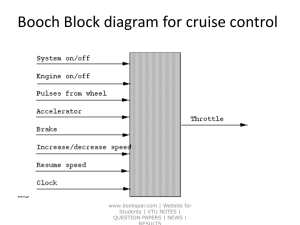
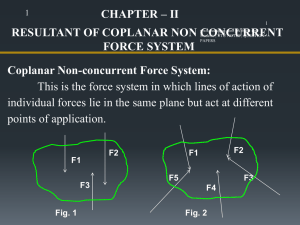
Unit-3-Organising-and-Staffing
advertisement

UNIT - 3 www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Organizing and Staffing : Nature & Purpose of Organization : Some Definitions on Organization : One Definition being “Including all the Behavior of Participants in a Group”. The other definition being “Describe the Total System of Social & Cultural Relations”. According to Amitai Etzioni “An Organization is a Social Unit or Human Grouping, deliberately structured for the purpose of attaining Specific Goals.” www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Egs: Corporations, Schools, Colleges, Hospitals, Temples etc are all Organizations. Note: But, friendship groups & families are not Organizations because they do not involve any significant amount of Conscious Planning or deliberate structuring. But for Practicing Managers, the term “Organization implies a formalized intentional structure of Roles or Positions.” By “Intentional Structure of Roles we say, People working together must fill certain Roles. The Roles that the people are asked to fill should be intentionally designed to ensure that required activities are done & that activities fit together so that people work smoothly, effectively, & efficiently in Groups. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers For an Organizational Role to exist & be meaningful to people, it must incorporate, 1) Verifiable Objectives, which are Major part of the Planning Process. 2) A clear idea of the Major duties or Activities involved & 3) An understood area of discretion or authority so that the person filling the Role knows what he can do to accomplish Goals. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers To make a Role work out more effectively, provision should be made for supplying needed information & other tools necessary for performance in that Role. Organizing is considered as : 1) The identification & classification of reqd activities. 2) The grouping of Activities necessary to attain Objectives. 3) The assignment of each Grouping to a Manager with the delegation of Authority necessary to supervise it & 4) The Provision for Co-ordination horizontally on the same or similar organizational level & vertically with corporate head quarters, division & dept etc., in the Organizational Structure. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers This should be designed to clarify who is to do what tasks & who is responsible for what results to remove hindrances caused by confusion & uncertainty of assignment & to furnish Decision Making & Communications Networks reflecting & supporting enterprise Objectives. Purpose of Planning : This is to aid in making Objectives meaningful & to contribute to enterprise Objectives : 1) Principle of Unity of Objectives : An Organization Structure is effective if it enables individuals to contribute to Enterprise Objectives. 2) Principle of Organizational Efficiency : An Organization is efficient if it is structured to aid the accomplishment of Enterprise Objectives with a minimum of unsought consequences for Costs. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Principles of Organization : This is the strength & basis of Organization Structure, the thread that makes it possible, the means by which groups of activities can be placed under a Manager & Co-ordination of Organizational Units can be promoted. It is the tool by which a Manager is able to exercise discretion & to create an environment for individual performance. Therefore, some of the most useful principles of Organizing are related to Authority. They are highlighted as follows : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 1) Scalar Principle : The clearer the line of authority from the topmost management position in an enterprise to every subordinate position, the clearer will be the responsibility for Decision Making & more effective will be the Organization Communication. 2) Principle of Delegation by Results expected : The responsibility of subordinates to their superiors for performance is absolute, & the superiors cannot escape responsibility for the Organizational activities of their subordinates. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 3) Principle of parity of Authority & Responsibility : The responsibility for actions cannot be greater than that implied by the authority delegated, nor should it be less. 4) Principle of Unity of Command : The more complete an individual’s reporting relationships to a single superior, the smaller the problem of conflicting instructions & greater the feeling of personal responsibility for results. 5) Authority – level principle : Maintenance of intended delegation requires that decisions within the authority of individual manager’s should be made by them & not be referred upward in the Organization Structure. Other principles of Organization related to achievement of Objectives are as under : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 6) Principle of Unity of Objectives : An Organization Structure is effective if it enables individuals to contribute to Enterprise Objectives. 7) Principle of Organizational Efficiency : An Organization is efficient if it is structured to aid the accomplishment of enterprise objectives with a minimum of unsought consequences or Costs. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 8) Specialization : Effective Organization must promote specialization. The activities of the enterprise should be divided according to functions & assigned to persons according to their specialization. 9) Span of Management Principle : In each Managerial Position, there is a limit to the number of persons & individual can effectively manage but the exact number will depend on the impact of underlying variables. As far as possible, the span of control should be the minimum. That means, a Manager should be asked to supervise a reasonable number of subordinates only, say six. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 10) Simplicity : The Organization Structure should be as simple as possible & the Organization levels should, as far as possible, be minimum. A large number of levels of Organization means difficulty of effective communication & coordination. 11) Flexibility : The Organization should be flexible, should be adaptable to changing circumstances & permit expansion & replacement without dislocation & disruption of the basic structure. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 12) Balance : There should be reasonable balance in the size of various depts, between Centralization & Decentralization, between the principle of span of control & short chain of command, & among all types of factors such as Human, Technical & Financial. 13) Unity of Direction : There should be one Objective & one plan for a group of activities having the same Objective. Unity of Direction facilitates unification & co-ordination of activities at various levels. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 14) Personal Ability : As people constitute an Organization, there is a need for proper selection, placement & training of Staff. Further, the Organization Structure must ensure Optimum use of Human Resources & encourage Management Development Programmes. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Process of Organizing : The various principles of Authority Delegation & of Departmentation or Segmentation of the activities on the basis of some Homogeneity & Integration are fundamental truths about the process of Organizing. They deal with phases of the three primary aspects of Organizing – a) Authority b) Delegation c) Activity Groupings & Integration. Integration is the process of achieving unity of effort among the various Departments or Subsystems to achieve the Objectives of the Enterprise. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers The Process of Organizing involves the following Six Steps : Consideration of Objectives : The first step in Organizing is to know the Objectives of the Enterprise. They determine the various activities which need to be performed & the type of Organization which needs to be built for this purpose, i.e., the Strategy of the Organization determines its Structure. For Eg: The Structure of an Educational Institution is not the same as that for a Business Enterprise. Therefore, Consideration of Objectives has the First & Foremost Role to play in the Process of Organizing. 1) www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) Grouping of Activities into Depts / Divisions/ Segments/ Subsystems : The Second Step is to identify the activities necessary to achieve them & to group the closely related & similar activities into divisions & depts or Subsystems. For Eg: The activities of a graded Cast Iron Castings Manufacturing Enterprise may be grouped into such Depts as Pattern Shop, Moulding Shop, Core Shop, Sand Plant, Melting Shop, QA Dept, Personnel Dept, etc. In addition, the activities of each Dept can be further classified & placed under the charge of different sections of that Dept. For Eg: In the Moulding Shop, separate sections may be created for Machine Moulding, Hand Moulding etc. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 3) Identification of Key Depts : They are activities essential for the fulfillment of the Goals. Such Key Depts demand utmost importance. Other Depts exist merely to serve them. If Key Depts are not identified, Top Management very often tends to focus its attention on Minor Issues leading to wastage of Time & Resources. Thus Key Depts have to be identified & placed directly under the Top Management. For Eg: An enterprise manufacturing Soaps & Detergents can identify advertising & sales promotion Depts as Key Depts which report directly to the MD of the enterprise. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 4) Determining Levels at whichVarious Types of Decisions are to be made : After deciding the relative importance of various depts, the levels at which various Major & Minor Decisions have to be taken, have to be determined. Each enterprise must decide on the degree of Centralization & Decentralization of authority & responsibility it wants to have. Extreme Decentralization may lead to loss of Control, on the other hand, Extreme Centralization may lead to improper decisions, failure to take decisions at the right time, delays & complete breakdown of the morale of the employees. Therefore, Top Management must very carefully decide the levels of the enterprise at which various types of decisions can be taken in order to achieve overall Objectives of the enterprise most effectively & efficiently. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 5) Deciding the Span of Management : One has to decide on the Span of Management. i.e., the Number of Subordinates who should report directly to each Executive. The Narrower the Span, the taller would be the Structure with several levels of Management. This will complicate Communication & increase financial burden of Salaries. For these reasons, a Flat Structure is generally desirable. However, the Span of Management, of each Executive Position must be tailored to meet the satisfactory working environment of the enterprise. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 6) Setting up a Coordination Mechanism : Proper Coordination among various depts & its individuals is very important for the successful & smooth running of the enterprise. As individuals & depts carry out their specialized activities, the overall goals of the Organization may become submerged or conflicts among Organization members may develop. Therefore, effective Coordination Mechanisms are reqd to enable members of the Organization to keep sight of the Organization Goals & reduce inefficiencies & conflicts. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Peter F Drucker’s Process of Organizing : Activities Analysis : A thorough & careful activities analysis clarifies as to what work has to be performed, what kinds of work belong together, & what emphasis each activity is to be given in the Organization Structure. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Decision Analysis : Second Step involves Decision Analysis. Although, it is important for any one to anticipate the contents of the future decisions, one can predict their kind & decide their places so that when they arise in future, they need no “go looking for a Home.” www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Relations Analysis : In the final step, an analysis should be made of various relationships between the tasks of a Manager & those of his subordinates, peers & superiors. Traditionally, only downward relationships of a Manager are analyzed. But, this done not give a complete picture of his contribution to the total Organization. This can be obtained only by analyzing his Horizontal & upward relations also. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Types of Organization : Organizations can be of 2 Types as given below : 1) 2) Formal Organization. Informal Organization. Both types are found in the Organization shown below : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 1) Formal Organization : There are various Levels in any Organization, right from President or Chairman or Managing Director or Chief Executive Officer at the top to Foremen/Supervisors down the line. Formal means the Intentional Structure of Roles in a Formally Organized Enterprise. This doesn’t mean there is anything inherently inflexible. If a Manager is to organize well, the structure must furnish an environment in which individual performance, both present & future contributes most effectively to Group Goals. Formal Organizations should be flexible, there should be room for advantageous utilization of creative talents for recognition of individual likes & capacities in the most formal of Organizations.Yet, individual efforts in a Group situation should be directed towards Group & Organization Goals. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) Informal Organization : Such an Organization is a Joint Personal Activity without conscious joint purpose, even though contributing to joint results. Thus, the Informal Relationships established in the Group of people during morning Tea Break or Playing Cricket in the Evening etc., may aid in the achievement of Organization Goals. It may be easier to ask for help in an Organization Problem from someone you know personally, even if he may be in a different section, than by passing thro the Organization Structure. Definition : “ A Network of Personal & Social Relations not established or required by the formal organization but arising spontaneously as people associate with one another. Thus, relationships not appearing on the Organization Chart might include Evening Cricket Team & Morning Tea Regulars. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Organizational Division – The Department. The Word Dept indicates a distinct area, division or branch of an Organization over which a Manager has authority for the performance of specified activities. Dept could be the Manufacturing Division, Sales Division, R&D division etc. Each Division is generally headed by a VP or a Manager. These designations may change from one Organization to the other. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Organization levels & Span of Management : Span Of Control : Meaning of Span of Control & its importance : The term “Span of Management” is also referred to as “Span of Control, Span of Supervision, Span of Authority, Span of Responsibility.” This indicates the Number of Subordinates who report directly to a Manager. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers While the purpose of Management is to make Human Cooperation more effective, the Reasons for levels of Management is the Limitations of the Span of Management. In other words, the Organization Levels exist because there is a limit to the number of persons a Manager can supervise effectively. This limit to the Number of Persons a Manager can supervise effectively varies depending on the Situations & Types of Organization. This is called as Span of Control or Span of Management. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Reasons for deciding an Appropriate Span of Control in an Organization : There are 2 Possible Reasons : 1) This affects the efficient utilization of Managers & the effective performance of their Subordinates. When the Span of Control is too Wide, Managers are overstraining themselves & also, their Subordinates are receiving very little guidance from their Managers. This also means Managers have very little Control on their Subordinates. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) There is a Relationship between Span of Control & Organizational Structure. A Narrow Span of Control results in a “Tall” Organization” with many Levels of Supervision between Top Level Management & Lowest Organizational Level. This creates Ineffective Communication Problems & also increases the Financial Burden on the Organization. There is also a Burden of finding suitable experienced personnel at different levels. On the other hand, a Wide Span of Control for the same number of Employees, means a “Flat Organization” with fewer Management Levels between Top & Bottom Levels. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Relationships between Span of Control & Organizational Levels : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers In the figure shown above, the Relationships between Span of Control & Organization Levels are shown. A Wide Span of Control is associated with Few Organization Levels; a Narrow Span contains Many Levels. Advantages & Disadvantages of Narrow & Wide Spans of Control : Advantages of Organizations with Narrow Spans : 1) Managers have Close Supervision on their Subordinates. 2) Therefore, Close & effective Control on them. 3) There is a Clear Cut Fast Communication between Subordinates & their Superiors & therefore Communication is not diluted. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Disadvantages of Narrow Organization Spans : 1) Superiors tend to get too involved in Subordinates Work. 2) There are many Levels of Management. 3) Financial Burden of the Organization increases due to high costs because of many levels in the Organization. 4) There is an Excessive Distance between Lowest Level & Top Level. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages of Organizations with Wide Spans : Superiors are forced to delegate authority & responsibility to their Subordinates. Organization makes clear policies. Subordinates are very carefully selected. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Disadvantages of Wide Span Organizations : There is a tendency of Overloaded & Stressed Superiors to become Decision Bottlenecks. There is a tendency of Superiors loss of Control on his Subordinates. This requires Managers with Superior & Exceptional Qualities. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Deciding on the Span : In every Organization, it must be decided how many subordinates a Superior can manage effectively & efficiently. According to Research, the Number is usually about, 4 to 8 Subordinates at the Upper levels, & 8 to 15 or more at the Lower Levels. According to another Study, “the ideal number of Subordinates for all Superior Authorities is to be 4”, while at Lowest Levels in the Organization, what is delegated is Responsibility for the Performance of Specific Tasks & not for the Supervision of Others, the Max Number being 8 to 12. Other Management Experts find that Manager may be able to manage as many as 20 to 30 Subordinates. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Summary : Studies on several Well Managed Companies have shown widely varying Spans & that merely counting the Numbers in the existing Spans is not enough to establish what a Span ought to be. This is true even if it could be assumed that each Company has reached the best Number thro Trial & Error. That might prove only that underlying conditions vary for different Companies. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Factors Governing Effective Span of Control : The Number of Subordinates a Manager can effectively depends on Various factors discussed below : Apart from such personal capacities as Comprehending Quickly, getting along with people & commanding Loyalty & Respect, the most important determinant is a Manager’s ability to reduce the time he spends with his Subordinates. This ability naturally varies with Manager’s & their jobs, but several factors materially influence the number & frequency of such contacts & therefore the Span of Control. The appropriate Span of Control, therefore, must be determined by the Specifics of the Manager’s particular situation. They are given below : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 1) Subordinate Training. 2) Competency of the Manager. 3) Competency of the employees. 4) Nature of Work. 5) Delegation of Authority & Responsibility. 6) Communication Technique. 7) Clarity of Plans. 8) Use of Objective Standards. 9) Geographic Location. 10) Levels of Management. 11) Economic Considerations & 12) Other Factors. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 1) Subordinate Training : Proper Training of Subordinates for their job leads to the fewer number of necessary Superior Subordinate Relationships. Also, well trained Subordinates require not only less of Manager’s time but also less contact with their Manager’s , thus allowing a Larger Span of Control. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) Competency of the Manager : A Manager who is Competent & Well trained can effectively Supervise more Subordinates than one who is not ! Therefore, in Planning an Organization, the Span of Control should be based on Manager’s Average Competency Level. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 3) Competency of the Employees : If the Employees are Competent, & possess necessary skill & Motivation to perform the Task assigned, Less Control & Supervision from the Manager is reqd & a wider Span of Control can be employed. If, Incompetent Employees are there, they demand more of the Manager’s time in Supervision & Control, a Narrow Span of Control will have to be forced in. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 4) Nature of Work : If Employees are carrying out, similar repetitive jobs, the Span of Control can be widened. However, if their Jobs keep changing frequently, more of Manager’s time is reqd in Supervision & Control, & hence again forcing Narrow Span of Control. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 5) Delegation of Authority & Responsibility : If the Authority & Responsibility of each employee are properly defined & delegated, they need not meet their Superiors very often for guidance & Instructions. This helps the Superior to manage a large number of Subordinates. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 6) Communication Techniques : The effectiveness with which communication Techniques are used also influences the Span of Control. An Ability to communicate plans & instructions clearly & concisely tends to increase a Manager’s Span. The Subordinates Job is greatly facilitated by Superiors who can express themselves. On the Other Hand, if clarity is lacking in Communication about what is reqd to be carried out, Subordinates will make frequent visits to the Superiors for seeking Clarifications, therefore a Narrow Span of Control becomes necessary. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 7) Clarity of Plans : Much of the Character of a Subordinate’s Job is defined by the plans to be put into effect. If Plans are well defined & if the Authority to undertake them has been delegated, & if the Subordinate understands what is expected of him, little of Supervisors time is reqd & hence, Span of Control is much larger. Such is the case with a Production Supervisor responsible for largely Repetitive Jobs. On the other hand, if plans cannot be accurately drawn, & subordinates do much of their own Planning, they may require considerable guidance from their Superiors, thereby, requiring a Narrow Span of Control. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 8) Use of Objective Standards : A Manager must find out, either by personal observation or thro use of Objective Standards, whether, Subordinates are following Plans. Obviously, good Objective Standards, revealing with ease, any deviations from Plans, enables Managers to avoid many time consuming contacts. But, Direct Attention under exceptional cases will be reqd, which may be Critical to the Organization’s Success. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 9) Geographic Location : An Office Manager who has 30 Employees, all located in One Place ,may be able to Supervise them very well. On the Other Hand, a VP – Marketing who has 30 Marketing Managers located at different places in the Country would find direct supervision difficult. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 10) Levels of Management : Span of Management also varies with each level in the Organization. Gerald G. Fisch has divided the Management Hierarchy for this purpose into 4 Basic Groups : 1) Super Managers 2) General Managers 3) Middle Managers 4) Supervisors. The Max Span of Management of Super Managers, whose functions involve only Broad Policy Control rather than Direct Supervision, can be 50 Subordinates. Contd …… www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers But, for General Managers who are more closely involved with their Subordinates, than Super Manager’s, the Span of Control has to be comparatively narrow, say 9 to 10 Subordinates only. For Middle Level Managers, the appropriate Span of Control depends on the precise mix of Executive & Operative Supervision than their specific Jobs require. It can be 40 to 50 Subordinates. For Supervisory Level whose Job is of a Routine Nature, the Span of Control is normally quite Wide, say up to 100 Subordinates. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 11) Economic Considerations : Economic Considerations also affect choice of Span. Smaller Spans means a Large No of Managers with added Salaries & other Costs they entail. But Wide Spans also involve extra costs due to inefficiencies that result from decreased Managerial Leadership. Hence, an Economic Balance has to be struck between Costs Saving that result from the largest possible Span & the added Costs that an Organization begins to incur as the Span grows too Wide. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 12) Other Factors : Simple Tasks may allow for a Wider Span than Tasks which are Complex & include a Great Variety of Activities. A Wider Span of Control can also result from the +ve attitude of Subordinates toward assumption of responsibility, as well as their willingness to take reasonable risks. Similarly, with more mature Subordinates, the Superior may delegate more Authority thus Widening the Span. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Departmentation : The Horizontal Differentiation of Tasks or Activities into discrete segments is called Departmentation. The limitation on the Number of Subordinates that can be directly managed would restrict the size of the enterprises if it were not for the tool of Departmentation. Grouping of activities & people into depts makes it possible to expand Organization & to manage it effectively & efficiently. Departmentation is thus the Key in building up an effective & efficient Organization. The basic aim is to take advantage of the division of Labor & Specialization. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Depts however differ with respect to the basic patterns used to group the activities. There are several bases for Departmentation, each of which is suitable for particular Organizations, strategies & purposes. It can be emphasized “there is no single best way of Departmentizing that is applicable to all Organizations or to all situations”. The pattern used will depend on given situations & on what Managers believe will give the best results for them in the situation they face. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers The various bases of Departmentation : 1) Departmentation by Enterprise Functions : Functional Departmentation is the most widely employed basis for Organizing Activities & is present in almost every Enterprise at some level in the Organization Structure. Each Major function of the enterprise is grouped into a Dept. For Eg : A typical Manufacturing Company will have Production, Engineering, Marketing, Finance & Personnel Depts. A typical Manufacturing Unit representing such Functional Depts is shown below : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages : ( Function based Departmentation) It is logical & time proven. The Power & prestige of the basic activities of the enterprise are maintained by the Top Managers. The identity of various functions is maintained. Functional Departmentation follows the principle of Occupational Specialization & thereby facilitates efficiency in utilization of people. It simplifies training. It furnishes a means of tight control at the Top, as the Top Managers are responsible for end results. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Disadvantages : This may tend to de-emphasize over all Enterprise Objectives. Over specializes & narrows view points of Key Personnel. People develop attitudes & other behavioral patterns involving loyalty to their Functional Depts & not to the enterprise as a whole & this tends to reduce Co-ordination between Functions. Responsibility for profits is at the Top only. In small Enterprises, this may be acceptable, but in large Enterprises the burden becomes too heavy for the person to bear. Functional Departmentation makes it difficult to adapt quickly to environmental changes. It limits development of General Managers. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) Departmentation by Products : This method is ideally suited for Large Organizations manufacturing various different Products. In this method, a separate Semi Autonomous Dept is created for each Product & is put under the Charge of a VP or, a Manager is made responsible for achieving Set Goals. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Within each Dept, all the needed Production, Engineering, Personnel, Marketing & other facilities are grouped. This method is ideal when an Organization grows to a very Large Size & the usual method of Functional Departmentation creates Operational Problems. For Eg: An Automobiles Manufacturing Company has 3 Products say : 1) Tractors 2) LCV & 3) Luxury Cars etc. The Company may create 3 Different for these Products, each headed by a VP for efficient & effective running of the Organization. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages : It facilitates use of specialized Capital (eg : A person may be extremely good in Marketing Luxury Cars or LCV & his Services may be used in these areas.) Relieves Top Management of Operating Task Responsibility, therefore it can better concentrate on such centralized activities like Finance, R & D, & Control. This enables the Top Management to Compare the performance of different Products & take the Policy Decisions about those Products which are not performing at expected levels. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers In this form, since Responsibility for Performance of each Product is entrusted to a particular Dept Head, he is well stimulated for improving his performance. Here, those who Work within the Dept derive greater satisfaction from identification with a recognizable Goal. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Disadvantages : This form results in Duplication of Facilities & Staff. Extra expenditure is incurred in maintaining a Sales Force for each Product Line. Employment of a Large No of Management Personnel is reqd. Plant & Machineries in each Dept may not be used fully. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 3) Customer Departmentation : An enterprise may be divided into a Number of Depts on the basis of the Customer that it serves. In this form, the Customers are the Key to the way the activities are grouped when each of the different things an enterprise does for them is managed by one Dept Head for that particular activity/thing. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages : Encourages Concentration on Customer Needs. Gives Customers feeling that they have an understanding Supplier. This form helps to develop Expertise in Customer Area. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Disadvantages : It may result in Under Utilization of resources & facilities in some Depts. There may be duplication of Services. Requires Manager’s & Staff Experts in Customer’s Problems. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 4) Departmentation by Territory or Geography or Regions : It is based on Territory or Region which is Very Common in Enterprises that operate over Wide Geographic Areas. For Eg: Used widely in Automobile Assembling, Chain Retailing, Wholesaling & Oil Retailing. i.e., “Big Bazaar”, “Wal Mart in USA”, departments based on Region “Western Railways, Southern Railways etc”. Here, it is important that activities in a given area or region be grouped & assigned to a GM, when this type of Departmentation is adapted. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages : It motivates each regional head to achieve high performance. Places responsibility at a Lower Level. Places emphasis on Local Markets & problems. It improves Coordination in a Region. It enables better face to face communication with the local interests. Takes advantage of economics of Local Operations such as Raw Materials availability, Cheap Labor, Market etc. It enables Organization to compare Regional Performances & invest more in Profitable Areas & withdraw Resources from Unprofitable Ones.This promotes spirit of healthy competition between the Regions. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Disadvantages : It requires more people with GM capabilities. It increases problem of Top Management Control. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 5) Departmentation by Time : One of the Oldest form of Departmentation generally used at Lower Levels of Organization, i.e., Grouping based on Time. The use of Shifts is Common in many enterprises where for Economic, Technological or other reasons, the normal day will not suffice. Egs: Hospitals, Machine Shops, Forging Shops, Press Shops working in 3 Shifts for Economic Reasons. This is also true for Chemical Industries, Blast Furnaces, Steel Melting Furnaces etc where processes cannot be interrupted. These industries work in 3 Shifts. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages : Services may be rendered that go beyond the typical 8 Hours a Day, often extending to 24 Hours a Day. It is possible to use processes that cannot be interrupted, those that require a Continuous Cycle. Expensive Capital Investment on Plant & Machinery can be used more than 8 Hours a Day when Workers in all the 3 Shifts use the same Machines. This is a very important Economic Consideration. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Disadvantages : Supervision may lack during Night Shift. There is a fatigue factor ; it is difficult for most people to switch, for instance, from a Day Shift to a Night Shift & Vice Versa. Having Several Shifts may cause problems in Communication & Coordination. In a factory, the night shift people may not clean up the machines to be used by the day shift people. Efficiency of the people have generally been found to be quite low between 12:00 AM to 8:00 AM. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 6) Process or Equipment Departmentation : This is done on the basis of several discrete processes or technologies involved in the manufacture of a Product. In this kind of Departmentation, the necessary Resources are brought in to do the particular Job. Eg: This can be explained by means of a Cast Iron Foundry manufacturing Graded cast Iron Castings. There are so many processes involved such as Moulding, Core Making, Melting, Sand Preparation, Fettling etc. The Block Diagram of a Typical Enterprise is shown below : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages : It achieves Economic Advantages. Follows principle of Specialization – each Dept is engaged in doing a special type of work, therefore utilizing special skills of the people & increases Operational Efficiency. Ideally suited for manufacturing enterprises using a Number of Intermediate Processes to manufacture their Products. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Disadvantages : It does not provide a good training ground for overall development of Managerial Talent. Coordination of different Depts is difficult & some times, it may lead to Production Bottle Necks. Responsibility for Profit is at the Top. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 7) Matrix Organization or Combined Base : It is quite typical to find an enterprise having a different base of Departmentation at different levels. For Eg: An enterprise Manufacturing Consumer Durables viz., Refrigerators, Washing Machines & TV ‘s may follow “Product” as the Base at the Top level, “Region” as the base at the Intermediate level & “Function” as the base at the Bottom Level. This is represented in Block Diagram given below : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Matrix Organization in an Engineering Dept : Another kind of Departmentation is Matrix or Grid Organization or Project or Product Management. The essence of Matrix Organization normally is the combining of Functional & Product Patterns of Departmentation in the same Organization Structure. In the figure given below, there are Functional Managers In Charge of Engineering Functions & an Overlay of Project Managers responsible for the end products. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Functional Depts are a permanent feature of the Matrix Organization. They retain Authority for Overall Operation of their Respective Depts. Product Depts or Project Teams, on the other hand, are created as the need for them arises. Members of a Project Team are grouped from the various functional depts & are placed under the direction of a Project Manager. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers The Manager for each Project is responsible & accountable for its success; thus, he has the authority over the other team members for the duration of the Project. This temporary authority is shown by the dotted lines as shown in fig. above. On Completion of the Project, the members of the Team including the Project Manager revert back to their respective Depts until the next assignment to a New Project. This type of Organization is frequently found in Construction Projects, Designing & Launching Weather Satellites, in Management Consulting Firms, where Experts work together on a Specific Project for a fixed period. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages : Oriented towards End Result. In this Organization, Professional Identification of the Individuals are maintained. It pinpoints Product Profit Responsibility. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Disadvantages : Conflict in Organization Authority exists. Possibility of disunity of Command exists. Requires Manager to be good at Human Relations. Matrix Organization requires many Time Consuming Meetings. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Useful Tips for making Matrix Organization Effective : 1) Define clearly the Objectives of the Project or Task. 2) Clarify the Roles, Authorities & Responsibilities of Managers & Team Members. 3) Ensure that influence is based on Knowledge & Information than on Rank. 4) Balance Power of Functional & Project Managers. 5) Select experienced Manager for the Project who can provide leadership. 6) Reward Project Managers & Team Members fairly etc. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Choosing Pattern of Departmentation : Departmentation is not an End in Itself, but it is simply a Method of arranging activities to facilitate the accomplishment of Organization Objectives. There is no one best way of Departmentising applicable to all Organizations & all situations. They must decide what is Best Looking at the situation they face - Jobs to be done, the way they should be done, the people involved & their personalities, the Technology employed in the Dept, whether the Users are being served, the other Internal & External Factors in the situation. However, some factors are given below : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 1) Specialization : The base of Departmentation should ensure Maximum Specialization of Skill & Effort. The points to be considered for this purpose are : a) Which approach permits the max use of Special Technical Knowledge. b) How will the Choice affect the differentiation among Specialists. c) Will it allow necessary differences in View Points to develop so that specialized Tasks can be performed effectively. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) Coordination : The base of Departmentation should ensure Proper Coordination & Control of the Activities of Different Depts. The Points to be considered for this purpose are : a) Which base provides the best hope of achieving reqd Control & Coordination. b) Will a particular base increase problems of achieving integration or reduce them. c) How will the Decision affect the ability of Organization Members to communicate with each other, resolve conflicts & reach necessary Joint Decisions. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 3) Economy : The expenditure involved in introducing Departmentation is also an important point to be considered. Benefits of Departmentation should always be higher than the Costs. Points to be considered here are : a) Which base provides the most efficient utilization of Plant & Machinery. b) What is the financial burden involved in following a particular base etc. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 4) Whole Task : The Organization should be so divided that each Dept has a Whole Task, this “Wholeness” may be achieved either by Technological Departmentation or by Regional Departmentation or by Time Departmentation or by Combination of these. Thus, in each Case, Managers of Different Depts have a realistic accountability & those who work within the Depts derive satisfaction from identification with a Recognizable Goal. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Committees : It is a Group of People who have been formally assigned some specific task or some problem for their decision & or implementation. In Modern Business Enterprises, use of Committees is very common in all areas of Management & Administration. The use of Committees is due not only to the Democratic Tradition but also to a growing emphasis on Group Management & Group Participation in Organizations. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Committees are broadly classified into 2 Groups as under : 1) Advisory Committees & 2) Executive Committees. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 1) Advisory Committees : When Committees are vested with Staff Authority, they are known as Advisory Committee. They have only a Recommendatory Role & cannot enforce implementation of their advice. Some of the usual advisory committees formed in Business Enterprises are : a) Works Committees b) Sales Committees c) Finance Committees d) Workers Welfare Committees etc. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) Executive Committees : Whenever Committees are vested with Line Authority, they are called as Executive Committees. These Committees not only take Decisions but also enforce Decisions & thus perform a Double Role of taking a Decision & its implementation. The Board of Directors of a Company is an Example of an Executive Committee. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages of a Committee : When Committees consist of all Departmental Heads as Members, people get an Opportunity to have a better understanding of the Problems of each other & Coordinate effectively to achieve Organizational Goals. It is a forum for the Pooling of Knowledge & experience of many persons of different skills, ages, & backgrounds. This leads to taking improved Quality Decisions. Committees provide an Opportunity for many persons to participate in the Decision Making Process. Contd …. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers More appropriate decisions or solutions are likely to emerge for a given problem by a group of people, (group decision making) rather than individuals. They are an excellent means of transmitting information & ideas, both Upward & Downward. By exposing members to different issues & view points. They contribute indirectly to their Training & Development. They are impersonal in action & hence their decisions are generally unbiased & are based on facts. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Drawbacks of Committees : One of the best administrative procedures to delay action is to refer the matter to a Committee. Almost without exception, it takes longer time to get action from a Committee than from an individual Manager. For wrong Decisions, no members of the Committee can be individually held responsible & members therefore may no apply their mind seriously. A huge amount of time & money is spent in convening such meetings & giving allowance to the members. Therefore, Committees increase the Financial Burden on the Organization. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Members of Coordinating Committees frequently regard themselves as appointed to protect the interests of their Depts rather than to find the most appropriate solution to the problem in Question. Decisions are generally arrived at on the Basis of some Compromise among members. Hence, not always the Best Decisions. As Committees consist of a large number of persons, it is difficult to maintain secrecy regarding the Decisions taken at the Committee Meetings. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Guidelines for making Committees more effective : Some of the disadvantages of Committees can be overcome by applying the following guidelines for more effective working of the Committee. They are as given below : a) Authority. b) Size. c) Membership. d) Subject Matters. e) Chairperson. f) Minutes & g) Cost effectiveness. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers They are as explained below : 1) Authority : The Committee’s Authority should be spelled out so that members know whether their responsibility is to make decisions, make recommendations, or merely deliberate & give the Chairperson some insights into the problem under discussion. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) Size : Size of the Committee is very important. As a general rule, a Committee should be large enough to promote deliberation & include the breadth of expertise reqd for the Job. It should not be too large so as to waste time or foster indecision. The Optimum Size is 5 to 6 members & the members chosen should possess adequate skills & knowledge to deal with the problem referred to the Committee. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 3) Membership : It must be selected carefully. If a Committee is to be successful, the members must be representative of the interests they are intended to serve. They must also possess the reqd authority & be able to perform well in a Group. Finally, members should have the capacity to communicate well & reach Group Decisions by integrated Group Thinking rather than inappropriate Compromise. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 4) Subject Matter : This should be carefully selected. Committee work should be limited to Subject Matter than can be handled in a GD. It could be more effective if an Agenda & relevant information are circulated well in Advance so that the members can study the Subject & come prepared for the Meeting. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 5) Chairperson : The selection of this person is extremely important for Effective Communication. Such a person can avoid the Wastes & Drawbacks of Committees by planning the Meeting, preparing the Agenda, seeing the results of Research are made available to the members in Advance, formulating definite proposals for discussion or action & conducting the meeting efficiently. He sets the tone of the Meeting, integrates the ideas & keeps the discussion from Wandering. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 6) Minutes : Sometimes, individuals leave the meeting with varying interpretations as to what was discussed & agreed upon. This can be avoided by taking careful minutes of the meeting & circulating them in Draft form for correction or modification before the final copy is approved by the Committee. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 7) Cost Effectiveness : The Committee must be worth its Costs. It may be difficult to count the benefits, especially such Intangible Factors such as Morale, enhanced status of Committee members, & the Committee’s value as a training device to enhance Team Work. But the Committee can be justified only if the Costs are Offset by Tangible & Intangible Benefits. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Centralization versus Decentralization of Authority & Responsibility : Meaning of Decentralization : Organization Authority is merely the discretion conferred on people to use their judgement to make decisions & issue instructions. It is the tendency to disperse decision making authority in an Organized Structure. It is a fundamental aspect of delegation, to the extent the authority is not delegated ; it is Centralized. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Delegation of Authority & hence Decentralization is necessary for an Organization to exist. Just as no one person in an enterprise, can do all the tasks necessary for accomplishing a group purpose, so it is impossible, as an enterprise grows, for one person to exercise all the authority for making decisions. There is a limit to the No of Persons Managers can effectively supervise & make decisions for. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Once this limit exceeds, Authority must be delegated to Subordinates, who will take decisions within the area of the assigned duties. Decentralization implies more than delegation. It reflects the philosophy of the Organization & Management. It requires careful selection of which decisions to be taken at lower levels of the Organization Structure & which to be taken at the Top levels. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers It also requires specific policy making to guide the decision making, proper selection & training of people & adequate control. A policy of Decentralization affects all areas of Management & can be seen as an essential element of a Managerial System. In fact, without it, Managers wouldn’t be able to use their discretion to handle the ever - changing situations they face. Every enterprise has to decide as to how much decision making authority should be centralized in the hands of the President & theVP (Top Levels) & how much should be delegated to the Managers at the Lower Levels. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers In a Centralized set up, the Decision making Authority is concentrated in a few people at the Top, in a Decentralized Set up, it is delegated to the Lower Levels where the actual work is performed. Following are the criteria to measure the extent of Decentralization in an Enterprise. Decentralization is greater : 1) When, the greater is the number of decisions made at Lower Levels. 2) When the more important are the decisions made at Lower Levels. 3) When more is the number of areas in which decisions can be made at Lower Levels & www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 4) When fewer are the people to be consulted & less is the checking reqd from the Top Levels on the Decisions made at the Lower Levels. Definition on Decentralization : “ Everything that goes to increase the importance of the Subordinate’s Role is Decentralization & everything that goes to reduce it is Centralization.” The terms “Centralization” & “Decentralization” are not absolute but are relative. Absolute Centralization is not possible, except in a One – Man Enterprise. Consequently, we can say that Decentralization Characterizes all Organizations. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Similarly, there cannot be absolute Decentralization of Authority because the Manager cannot delegate all his authority without surrendering his position as a Manager. Meaning of Centralization : It has several meanings : 1) Centralization of Performance : Pertains to Geographic Concentration ; it characterizes, for Eg : a Company operating in a single location. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) Departmental Centralization : Refers to Concentration of specalized activities in one Dept. For Eg : Repairs & Maintenance for an entire plant may be carried out by a Single Dept. 3) Centralization as an aspect of Management : It is the tendency to Restrict Delegation of decision making. A high degree of authority is held at or near the Top by Managers in the Organizational Hierarchy. We are concerned with this aspect of Centralization & Decentralization of Authority & Responsibility. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Delegation of Authority : Authority is delegated when a Superior gives a Subordinate discretion to make Decisions. The process of delegation involves : 1) Determining the results expected from a position. 2) Assigning Tasks to a position. 3) Delegating Authority for accomplishing these tasks. 4) holding the person in that position responsible for the accomplishment of tasks. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers In practice, it is impossible to split this process, since expecting a person to accomplish goals without giving him the Authority to achieve them is unfair, as is delegating authority without knowing the end results for which it is used. Moreover, since the superior’s responsibility cannot be delegated, a Superior has no practical alternative but to hold subordinates responsible for completing their tasks. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Distinction between Delegation & Decentralization : They appear to be the same, but in reality they mean different things. The Major differences are given below : 1) Delegation is a process, while Decentralization is the end result (Outcome) of the Delegation & Dispersal of Authority. Delegation mainly refers to granting of Authority & the creation of responsibility as between one individual & another; Decentralization is the situation which exists as a result of the systematic delegation of Authority throughout the Organization. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) In Delegation, a Superior continues to be responsible for the work delegated to his Subordinates, while in Decentralization, the Superior is relieved from his responsibility for the work Decentralized & Subordinate becomes liable (responsible) for that. 3) Delegation is Vital & essential to the Management Process. Only thro Delegation, Subordinates can be involved in the Organization & the Management can get things done. Decentralization is Optional, in the sense, that it may or may not be done as a Systematic policy. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages of Decentralization : Relieves Top Management of some burden of Decision Making & forces upper level managers to let go. (giving freedom to the Lower Level Mgrs to take independent Decisions.) Reduces problems of Communication & hence enables Top Managers to take timely decisions on all important issues, thus, enhancing the efficiency of the Organization. Encourages Decision Making & assumption of Authority & responsibility. Gives Managers more freedom & independence in Decision Making. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Promotes establishment & use of broad controls which may increase Motivation. Makes comparison of performance of different Organizational units possible. Facilitates setting up of Profit Centers. Facilitates Product Diversification. Promotes development of more capable Managers. Because, Managers in a Decentralized structure often have to adapt to & deal with difficult situations, they are assumed to be excellently trained for Promotions into positions of greater authority & responsibility. Decentralization aids in adaptation to fast changing environment. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Limitations of Decentralization : Makes it more difficult to have a Uniform Policy. Increases Complexity of Coordination of Decentralized Organizational Units. May result in loss of some control by Upper-Level Managers. May be limited by inadequate Control Techniques. May be constrained by inadequate Planning & control systems. Can be limited by the availability of qualified & capable Managers. Involves considerable expenses for Training Managers. May not be favored by Economics of Scale of some Operations. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers The Extent of Decentralization : To avoid problems, any program for decentralization of Authority & Responsibility must consider thoroughly the Advantages & the Limitations of Decentralization. Strong forces in the Organization favor the practice of Decentralization. But, at the same time, extensive Decentralization is not to be blindly undertaken. Perhaps, One Major Problem of Decentralization is loss of Control. No enterprise can Decentralize to the extent that its very existence is threatened & the achievement of its Goals is frustrated. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers If Organizational Disintegration is to be avoided, Decentralization must be tempered with selective Centralization in certain major policy areas. An enterprise with well balanced Decentralization will probably centralize decisions at the Top on such things as given below : 1) Financing. 2) Overall Profit Goals & Budgeting. 3) Major Facilities & other Capital Expenditures. 4) Important New Product Programs. 5) Major Marketing Strategies. 6) Basic Personnel Policies. 7) Development & Compensation of Managerial Personnel. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers A Well Organized enterprise always tries to balance between Centralization & Decentralization. In, such an Organization, Authority is retained at the very Top for Major Policy & Program Decisions on matters affecting the Soundness & Success of the entire Company. Thro Decentralization, however, once the Major Programs & Policy Decisions have been made at the Top, many Decisions involving their execution are made at the Lower Levels in Various Depts of the Organization. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Management by Objectives (MBO) : Introduction : They are the End Points, towards which enterprises activities are aimed. MBO is the philosophy of Management that emphasizes the Development of Mutual Objectives by Managers & their Subordinates & the use of these Objectives as the primary bases of Motivation, Evaluation & Control Efforts. The Management process begins with a Mission Statement & Setting up of Organizational Objectives. Objectives give meaning & purpose to the Organization. Without Objectives, without something to achieve, Organization would be Purposeless & Chaotic. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Good Management, therefore, is always Management by Objectives. Objectives determine the Scope of Future Events. They provide the Spotlight on the Routes over which activities, are Organized.They serve as Reference Points to Concentrate Resources & Efforts.They determine what Action to take today to obtain Results Tomorrow. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Mission : Very Reason & Justification for the existence of the enterprise. It is usually expressed in terms of the benefits the Firm provides to its Customers. An Organization’s Mission Statement states what it is, why it exists, & the unique contribution it can make. Mission Statements are characterized by the following (given below) : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 1) Customer Oriented : The purpose of a Business according to Peter F Drucker is “to create a Customer” . Mission Statements, therefore, are directed at serving the Customers in useful way. 2) Future Oriented : Mission Statements must be indicative of what the Business is going to be in the years to come. The Statement must be Valid for at least some years to come. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 3) Dynamic : The Concept of Mission is Dynamic & not a Static One. It must strike a Happy Balance between the Narrow & Broad Ways of doing things in the Years ahead ; between the present requirements & future expectations. It is worth remembering that the future of a Business is usually determined by the way it defines its Business Today. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Example of a Mission Statement : Name of the Company : The Tata Group Mission Statement : “ At the Tata Group, our purpose is to improve the quality of life of the communities we serve. We do this thro Leadership, in Sectors of Leadership, in Sectors of National Economic Significance to which the Group brings in a Unique Set of Capabilities. This requires us to grow aggressively in focused areas of Business.” www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers “Our Heritage of returning to Society what we earn, evokes confidence & trust among Consumers, Employees, Shareholders & the Community. This heritage will be continuously enriched by formalizing the high standards of behavior expected from employees & the company” etc. Objectives & Goals : The terms “Objective” & “Goal” indicate end results to be sought & accomplished. Both of them have Value Orientations & indicate conditions considered necessary to improve the Overall Performance of the Organization. Three important definitions of Objectives are given below : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 1) Objectives are Goals established to guide the efforts of the Company & each of its Components. 2) An Organizational Goal is a desired state of affairs which the Organization attempts to realize. 3) They indicate the “End Point of a Management Programme”. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers MBO MBO also called “Appraisal by Result”, “Planning by Objectives”, “Goal Management”, “Work Planning & Review”, “Joint Target Setting” etc is an overall philosophy of management that concentrates on measurable goals & end results. It provides Systematic & Rational Approach to Management & helps prevent Management by Crisis. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers MBO is based on the assumption that people perform better when they know what is expected of them & can relate their Personal Goals to the Organizational Objectives. It also assumes that people are interested in the Goal Setting Process & in evaluating their own performance against the Target. MBO is a “Process where the Superior & Subordinate Managers of an Organization jointly identify its Common Goals, define each Individual’s Major areas of Responsibility in terms of results expected of him, & use these measures as Guides for operating the Unit & assessing the Contribution of each of its Members.” www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Features of MBO : It emphasizes participation in Setting Goals that are Tangible,Verifiable & Measurable. It focuses attention on what must be accomplished (Goals) rather than how to accomplish it ! MBO, by concentrating on Key Result Areas translates the abstract philosophy of Management in an attempt to concretize it. Further, it is “ A Dynamic System which seeks to integrate the Company’s need to achieve its Profit & Sales Growth with the Manager’s need to contribute & develop himself. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers MBO is a Systematic & Rational Technique that allows Management to attain Maximum Results from available Resources by focusing on Achievable Goals. It allows the Subordinates with plenty of room to be more creative in their Decision Making. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Management by Exception (MBE): Introduction : Control is an essential part of every Organization. It is a Process of Comparing Actual Performance with established Standards, for the purpose of taking Action to Correct Deviations. It is only thro this Process of Control, that Management is able to maintain the “Equilibrium between Ends & Means, Output & Effort”. In a Large, Multi - Product, Multi -Plant & Multi – Location Organization, it is impossible to check everything & initiate timely, remedial steps whenever things go off the track. Manager’s therefore, focus attention on Key or Critical Areas which have a Significant Bearing on the performance of Various Depts in an Organization. One of the Ways that have been found to be relevant in this regard is Management by Exception (MBE). www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers MBE MBE tries to focus attention on exceptionally serious deviations from the Plans & Standards. According to this principle, a Manager should give more attention to unusual or exceptional items only. Only very important deviations from Established Standards should be brought to the Notice of Management. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers If the Actual Performance is within an acceptable range of deviation from the Standard (Say 5%), it need not be reported to Management, as no Remedial Action is reqd. However, in Case of Major Deviation from the Standard, the Matter has to receive the immediate attention of the Management on priority basis. The principle highlights the importance of the Statement that, if you want to Control everything, you will end up Controlling Nothing. So better focus on Key Deviations & leave the minor ones to be taken care of by the Lower Levels. That is, the Top Management must focus on Important issues & leave the routine things to people at Lower Levels. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers The importance of MBE stems from the enormous size of Business & the Consequences of Complexity in Operations. It is a Very Effective Approach in Controlling Modern Organizations. 1) 2) 3) 4) MBE offers the Following Benefits : It saves Time. It identifies Critical Problem Areas. It stimulates Communication. Reduces Frequency of Decision Making. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 5) It leads to Concentration of efforts on Important things. 6) Makes use of more Knowledge & Data. 7) It is necessary in Big Organizations. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Nature & Importance of Staffing : Introduction : People are very Vital for the effective Operation of an Enterprise. All managers often say, “Our people are our most important Asset.” The Managerial function of Staffing is defined as filling & keeping filled, various positions, in the Organization Structure. This includes identifying Work Force requirements, inventorying the People available, & Recruiting, Selecting, Placing, Promoting, Appraising, Planning the Careers of, Compensating & Training or otherwise developing both Candidates & Current Job Holders to accomplish their tasks effectively & efficiently etc. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers It is therefore, clear that Staffing must be closely linked to Organizing, that is, to the setting up of Intentional Structures of Roles & Positions. All Managers have a Responsibility for Staffing. The board of Directors performs the Staffing Function by selecting the Chief Executive. The Chief Executive in turn, discharges this Function by selecting Managers for different Depts, viz; Production, Marketing, Finance etc. The Managers do likewise when they select their Subordinates. Even the Foremen or Supervisors have a Staffing Responsibility when they Recruit & Select Workers. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Importance & Need for Proper Staffing : Direct Labor Costs account for nearly 15 to 20 % Cost of Production in a Manufacturing Enterprise. Therefore, a Business Enterprise needs Right Kind of People at Various Important Positions in the Organization Structure to manage the affairs of the enterprise efficiently & successfully. There are a Number of Advantages of Proper & efficient Staffing. They are described below : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Advantages of Staffing : Helps in choosing the right kind of Personnel for different important positions in the Organizational Structure. Helps in identifying Talented & Competent People, grooming them, develop them to help move up the Organization Ladder. Ensures higher Productivity by placing the Right Man in the Right Job. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Helps to avoid disruption of Production Schedules due to shortage of personnel by proper indication in Advance. Helps to prevent Under Utilization of personnel thro Over manning & the Resultant High Labor Costs & Low Profit Margins. It provides Information to Management for the Internal Promotion of Managerial Personnel in the event of an Unanticipated Staff Turn over. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers The Function of Staffing : The Function of Staffing involves Proper Manpower Planning . Manpower Planning includes Forecasting, Developing & Controlling is the Process by which an Enterprise ensures that it has the Right Number of People & the Right Kind of People at the Right Time doing work for which they are Economically most useful. The Managerial Function of Staffing & in turn Manpower Planning relates to the Total Management System as depicted in Figure Given Below : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers As Shown in the Figure, Enterprise Plans become the basis for Organization Plans. The Present & Projected Organization Structure determines the Number & Kinds of Managers reqd. These demand for Managers are compared with the available talent thro the Management Inventory. On the basis of this Analysis, External & Internal Sources are utilized in the process of Recruitment, Selection, Placement, Promotion & Separation. Other essential aspects of Staffing are Appraisal, Career Strategy & Training & Development of Managers. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Important Points in Staffing : 1) Staffing affects Leading & Controlling. 2) Well trained Managers creates an environment in which people, working together in Groups, can Achieve enterprise Objectives, at the same time accomplish Personal Goals. It facilitates Leading. 3) Similarly selecting Quality Managers affects Controlling ( it assists Controlling ) by preventing any undesirable deviation from becoming Major Problems. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 4) Staffing requires an Open System Approach. It is carried within the Enterprise, which in turn is linked to the External Environment. 5) Therefore, Internal Factors of the Enterprise, such as Personnel Policies, the Organizational Climate, & the Reward System must be taken into Account. 6) It is certain that without adequate Rewards, it is not possible to attract & keep Quality Managers. 7) The External Fast Changing Environment is also equally important. High Technology demands Well Trained, Well Educated & Highly Skilled Managers. Inability to meet this Demand for such Managers may prevent an Enterprise from growing at the Desired Rate. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Process of Selection & Recruitment : What is Recruitment : The Process of Recruitment starts after Estimating the Manpower Requirements for Various Positions in the Organization Structure. It can be defined as the Process of Identifying the Sources for Prospective Candidates & to Stimulate them to Apply for the Jobs. In other words, Recruitment is the Process of Attracting Potential Employees to the Company. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers The Management should have a Proper Plan of Recruiting the Number & Qualification of Personnel required & also the Time Frame when it is needed. The Process of Recruitment & the Cost involved in it depends on the Size of the Enterprise & the Type of the Persons to be recruited. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Sources of Recruitment : They can be both Internal & External. Internal Sources refer to Present Working Force of the Company. Vacancies other than at the Lowest Level may be filled by selecting Competent Individuals from amongst the Existing Employees of the Organization. External Sources of Recruitment are as Follows : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers Re-Employing Former Employees. Friends & Relatives of Present Employees. Applicants at the Gate. Educational Institutions – Tech, Management & the Others. Employment Exchanges. Advertising for Vacancies in Leading Newspapers. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 1) Re-Employing Former Employees : Those Employees who have been laid off or have left for Personal Reasons may be employed. Such Employees may require very Less Training compared to the New People to the Company. 2) Friends & Relatives of Present Employees : Some Companies encourage their Existing Employees to recommend their Friends & Relatives for appointment to fill the Existing Vacancies. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 3) Applicants at the Gate : Unemployed Persons who call at the Gate of the Enterprise are considered, after Proper Selection Process, for filling up different Vacancies in the Organization. 4) Educational Institutions – Technical, Management & Others : Many Big Enterprises remain in touch with Leading Technical, Management, & Other Colleges & Young, Talented Candidates are Recruited from Campus Selection Process. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 5) Employment Exchanges : They also serve as an Important Source of Recruitment for a Number of Business Enterprises. 6) Advertising forVacancies in Leading News Papers : This is a Very Important Source for many of the Bigger Enterprises requiring the Services of Persons possessing Certain Special Skills & Qualifications. Small Enterprises generally resort to Advertising for Vacancies in Classified Columns in Leading Newspapers. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers SELECTION : Under Recruitment, the enterprise identifies the Sources for prospective candidates & encourages them to apply for Various Openings in the Organization Structure. Under Selection, Candidates are evaluated with respect to their qualifications & the Job requirements & those who do not satisfy the requirements are Rejected. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers There are some Variations of the Specific Steps in the Selection Process. For Eg : The Interview of a Candidate for a First Level Supervisory Position may be relatively simple when compared with the Rigorous Interviews for Top Level Managers. However, the Following Steps are indicative of the Typical Selection Process : 1) The Selection Criteria : They are usually established on the Basis of Current & Sometimes Future Job Requirements. These Criteria include Educational Qualification, Knowledge, Skills & Experience. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 2) Application Form : Candidates are reqd to complete an Application Form. In this form, the Applicant gives relevant Personal Data such as his Qualification, Specialization, Experience, Firms in which they have worked etc. The Application Forms are carefully scrutinized to decide the suitable applicants to be called for Interview. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 3) Screening Interview : Those who are selected for Interview on the basis of particulars furnished in the application form are called for initial screening interview to identify the more promising candidates. The Interview is the most important means of evaluating the poise or appearance of the Candidate. It is also used for obtaining additional information or clarification given in the Application Form & also to Check References. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 4) Employment Tests : For Further Assessment of Candidates Nature & Abilities, some Tests are conducted in the Selection Process. The Primary aim of Testing is to obtain Data about Applicants that help predict their Probable Success as Managers. Some of the Advantages from Testing include finding the Best Person for the Job, obtaining a High Degree of Job Satisfaction for the Applicant & reducing Staff Turnover. The most Commonly used Tests can be classified as follows : www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers i) Intelligence Tests : They are designed to measure Mental Capacity & to Test Memory, Speed of Thought, & Ability to see Relationships in Complex Problem Situations. ii) Proficiency & Aptitude Tests : They are designed to Discover interests, Existing Skills & Potential for Acquiring Skills. iii) Vocational Tests : They are designed to show a Candidate’s most suitable Occupation or the areas in which the Candidate’s Interests match the interests of the People working in that Occupation. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers iv) Personality Tests : They are designed to reveal Candidate’s Personal Characteristics & the way Candidates may interact with others, thereby giving a measure of Leadership Potential. 5) Group Discussion : Candidates found satisfactory in the Screening Interview & Employment Tests are further short listed for GD Test. Many Companies conduct this test to assess the Candidates Communication & Presentation Skills, Interpersonal Skills, Leadership Qualities & ability to pull on in Team Work. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers 6) Checking References : If a Candidate has been found satisfactory in the GD, the Employer would like to get some important Personal Data about the Candidate, such as his Character, Past History, Background etc., verified from the people referred to in the Application Form. 7) Physical or Medical Examination : A Physical Examination of the Candidate is carried out to check the Physical Fitness of the Applicant for the Position/Job applied for. 8) Final Interview : This is conducted for those who are ultimately selected for Employment. In this Interview, the selected candidates are given idea about their future prospects within the Organization. 9) Appointment Order : Appointment Orders are given to the finally Selected Candidates giving the Position Offered, Scale of Pay and, Terms & Conditions of Employment. www.Bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU - Notes - Question Papers