Answer: b
advertisement

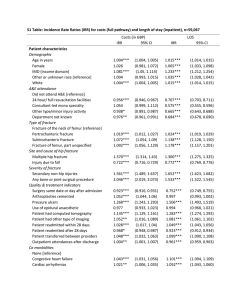
بسم هللا الرمحن الرحيم Promotion Exam 2014 All answers are personal opinion, please review it << Central Region >> 1. Male patient post MVA with 0/5 supraspinatus, infraspinatus & 4/5 rhomboids. What is his level in Brachial plexus? a) Post-ganglionic b) Pre-ganglionic c) C5 avulsion root d) Answer: a 2. Os Acromiale is failure of fusion between: a) Meso-acromion and pre-acromion b) Meso-acromion and meta-acromion c) Preacromion & meta-acromion d) Answer: b 3. Tibia Vara in pediatric is define as: a) 20-degree deviation from mechanical axis. b) Metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle (Drennan) of 11 degree c) Langenskiold Classification type 1 d) Answer: ? b 4. A 33-year-old man requires a transfemoral amputation because of a mangling injury to his leg. Six months after the amputation he has persistent difficulty with ambulation because his femur bone moves into a subcutaneous position in his lateral thigh. It persists despite a well-fitted prosthesis. What technical error is the most likely cause of his dysfunction? a) b) c) d) Inadequate anterior skin flap failure to bevel the distal femur lack of abductor myodesis to femur lack of adductor myodesis to femur Answer: d 5. During a Lisfranc (tarsometatarsal) amputation of the foot, which of the following is crucial to prevent the patient from having a supinated foot during gait. a) Releasing the posterior tibialis tendon b) Preserving the soft-tissue envelope (peroneus brevis, tertius and plantar fascia) around the fifth metatarsal base c) Myodesis of the anterior tibialis to the medial and middle cuneiforms d) Lengthening of the gastrocsoleus (achilles tendon) Answer: b 6. A 35-year-old man fell from a scaffold. This resulted in pain in his shoulder & neck with no radiographic findings. Four weeks later, he present with weakness in abduction of his shoulder, numbness of the lateral aspect of the arm & winging of the scapula. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? a) b) c) d) Rotator cuff pathology. C6 nerve root avulsion Upper trunk injury Axillar nerve palsy. Answer: c 7. Shoulder abduction movement from 0 – 180 involved all the following structures except: a) b) c) d) Deltiod. Thoracodorsal. Spine cranial nerve. Suprascapular nerve. Answer: b 8. A 44-year-old male presents with a 2-month history of posterior shoulder pain. He is noted to have normal forward flexion and abduction strength and isolated weakness on shoulder external rotation. He has slight atrophy of his periscapular area. He has no numbness or paresthesia. Which pathology would best explain his symptoms? a) b) c) d) Brachial plexus injury Spinoglenoid notch cyst Axillary nerve palsy Suprascapular notch cyst Answer: b 9. In proximal humerus fracture, Loss of greater tuberosity will affect which movement of shoulder: a) b) c) d) Abduction & Internal Rotation. Abduction & External Rotation. Adduction & Internal Rotation. Adduction & External Rotation. Answer: b 10. Q about proximal humerus fracture & AVN: a) Risk increase with comminution in metaphysis Answer: ?? 11. 80 year old male with chronic shoulder dislocation, ROM from 0 – 80. Complaining of mild shoulder pain. Treatment consist of: b) c) d) e) Hemiarthroplasty. Conservative therapy & pain medication Open reduction & subscapularis advancement. Close reduction & sling. Answer: ??? 12. Patient with mid shaft humerus fracture. Treated with retrograde IM nail. What is the most common complication compared to plating: a) b) c) d) Elbow pain. Reoperation rate. Higher nonunion Iatrogenic fracture Answer: a or d 13. 25 year old male involve in accident & sustain injury shown in X-ray with Terrible Triad & comminuted radial head, Treatment should include: a) b) c) d) Radial fixation, Coronoid fixation & MCL repair. Closed reduction & sling Radial Replacement, Coronoid fixation & LCL repair. Radial excision & Coronoid fixation. Answer: c 14. A 30-year-old female presents with the Galeazzi fracture after falling on her outstretched arm. During operative treatment of the fracture, anatomic reduction of the radius is achieved. However, the surgeon is unable to reduce the distal radioulnar joint. What structure is most likely impeding the reduction: a) b) c) d) Flexor carpi radialis Pronator quadratus Extensor carpi ulnaris. Flexor carpi ulnaris. Answer: c 15. A female patient fell in out stretched hand present to ER with dinner fork deformity. Underwent closed reduction that was successful. Which of following parameter in will indicate risk of redisplacement in future: a) b) c) d) 1 mm articular step Dorsal angulation of 10 degree 3 mm +ve ulnar variance age Answer: ??? 16. In chronic scaphoid nonunion: a) Define as if no union seen more than 8 weeks of injury b) Should be fixed even if asymptomatic c) No need to use bone grafting during fixation d) Answer: b 17. A male patient fell in out streaked hand & complaining of radial wrist pain with initial X-ray was normal. 3 weeks in the clinic X-ray showed 5 mm scapholunate gap. Treatment consist of: a) Reduction, Pinnig & Repair b) First row corpectomy c) immobilization d) Answer: a 18. Picture showing the cross section of wrist. Which of the following structure indicate 5: a) b) c) d) Extensor Extensor Extensor Extensor Pollicis Longus Indicis Digiti Minimi Carpi Ulnaris Answer: c 19. Which of the following structure limit hyperextension of hip: a) b) c) d) Obturator internus muscle Ischiofemoral ligament Iliotibial band Tensor Facia Lata Answer: b 20. What type of injury is associated with injury shown in the X-ray ( ? anterior shoulder dislocation ): a) b) c) d) Impression fracture. Axillary nerve. Lesser tuberosity fracture. Proximal humerus fracture. Answer: a 21. 65-year-old female known case of rheumatoid arthritis fell at home & present to emergency department complaining of right hip pain. X-ray showed neck of femur fracture. Patient report right hip pain for 3 years prior of injury. Treatment should be: a) b) c) d) Cannulated screw fixation. Total hip arthroplasty. Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty. Conservative Treatment. Answer: b 22. A young patient involved in road traffic accident & sustained neck of femur fracture with ipsilateral comminuted femur shaft fracture. which surgical option & sequence will provide the best outcome for him: a) b) c) d) Closed reduction & screw fixation for NOF + antegrade IM nail for shaft. Open reduction & screw fixation for NOF + antegrade IM nail for shaft. Open reduction & screw fixation for NOF + retrograde IM nail for shaft. Open reduction & screw fixation for NOF + plating for shaft. Answer: c 23. A male patient known case of Paget disease underwent total hip arthroplasty utilizing posterior approach. Preoperative he received 700 rad & postoperatively he developed heterotropic ossification. What is the cause for developing HO? a) b) c) d) Disease itself. Approach utilized. Low radiation dose. No diphosphate prophylaxis. Answer: ? a 24. What is the best view to be used for percutaneous antegrade screw fixation of superior ramus fracture to prevent posterior penetration of cortex: a) b) c) d) Inlet iliac oblique view. AP pelvis. Outlet iliac oblique view. Obturator view. Answer: a 25. A young patient sustain neck of femur fracture with medial wall comminution. He underwent closed reduction & Gamma nail insertion with Tip-Apex distance was 22.5 mm & screw was inserted in centroinferior configuration. Few weeks later, he present with hip pain which showed failure of fixation. What is the reason for failure in this patient: a) b) c) d) Tip-Apex distance. Screw in centroinferior location. Using Gamma nail. Medial wall comminution Answer: d 26. Patient with femur fracture, which of the following ipsilateral injury is contraindication to use retrograde femur IM nail: a) b) c) d) Neck of femur fracture. Patella fracture. Acetabulum fracture. Patella baja. Answer: d 27. What is the best treatment for fracture shown in X-ray: a) b) c) d) Cannulated screw. Cephalomedullary nail. Dynamic hip screw. Dynamic condylar screw. Answer: b 28. Regarding imaging: a) b) c) d) Meniscal tear is best to be evaluated with MRI T1 weighted image. CT ...??? Fat fluid level in patellar bursa indicate intraarticular fracture. Bone scan TC99 is ?? sensitive or specific for pathology. Answer: c 29. A 35-year-old-male sustains the subtrochanteric fracture. Which of the following reduction forces must be applied to the proximal fragment to correct the deformity commonly seen in these fractures? a) b) c) d) Flexion and Lateral rotation Flexion and medial rotation Extension and Lateral rotation Extension and medial rotation Answer: d 30. Acetabular labrum received blood supply from: a) b) c) d) Superior gluteal artery Inferior gluteal artery Obturator artery Medial circumflex femoral artery Answer: ?? c 31. Regarding gait cycle: a) b) c) d) Swing phase is occupy most of gait cycle Stance phase start when the leg cross contralateral limb Central of gravity is posterior to S2 vertebral body During the push off the foot become rigid Answer: ?? d 32. An athlete sustains a traumatic patellar dislocation. The MRI shows a hemarthrosis with a floating osteochondral fragment. Which of the following is the most likely site of origin for the loose fragment: a) b) c) d) Lateral patellar facet Medial patellar facet Medial condyle Lateral condyle Answer: b 33. A 53-year-old man sustains tibial Plateau fracture and later undergoes open reduction and internal fixation. What variable will most significantly increase his rate of degenerative arthritis in the long-term? a) b) c) d) Joint step-off Fracture type Malalignment Ligament instability Answer: c or d 34. 6 year old male sustain tibial shaft fracture. Which of the following parameter acceptable to treat him conservatively? a) 10 degree Valgus b) 10 degree posterior angulation c) 10 mm shortening d) Answer: ??? 35. Patient with midshaft tibia fracture and an intact fibula. If treated with closed reduction and casting, which of the following is associated maluinion? a) b) c) d) Shortening Valgus Varus Rotational Answer: c 36. Patient sustain ankle fracture with open medial wound & tibials posterior tendon laceration. After irrigation & fixation of fracture, you should do: a) b) c) d) Tenodesis to FDL. End to end repair. Leave it & close the wound. . Answer: b 37. Type of bone ossification seen with type of treatment in the following X-ray is: a) b) c) d) Endochondral. Intramembranous. creep. . Answer: b 38. The flexor hallucis longus tendon is at greatest risk of injury with a lateral-tomedial drill or screw during fixation of what structure: a) b) c) d) Lisfranc fracture-dislocation. Navicular body fracture. Intra-articular calcaneus fracture. Talar neck fracture. Answer: c 39. MRI cut for patient with low back pain, diagnosis is: Not exactly the same what we have in exam a) b) c) d) Synovial cyst. Intradural lipoma. Subdural abscess. . Answer: a 40. In surgical management of spine fracture, Which of the following scenario need urgent surgical intervention: a) b) c) d) Neurologically intact & unstable surgically. Complete neurological & unstable surgically. Incomplete neurological injury & stable surgically. Incomplete neurological injury & unstable surgically. Answer: d 41. In rheumatoid arthritis patients, which of the following spinal problem can lead to death: a) b) c) d) Atlantoaxial instability. Basilar invagination. Jump facet. subaxial subluxation Answer: b 42. Regarding Odontoid fracture type II: a) b) c) d) Most common anterior displacement. Most common posterior displacement. Have better chance to heal compare to type III. ??? Usually asymptomatic. Answer: b 43. Pediatric patient sustain mid-thoracic fracture with complete spinal cord injury. What do you expect after 10 years: a) b) c) d) Recurrent chest infection. Normal bowl function. Electronic wheelchair. Need spinal surgery for scoliosis. Answer: d 44. The most sensitive test for diagnosing discitis in its early stages is: a) b) c) d) MRI. CT. Gallium scan. Technetium bone scan. Answer: a 45. The male osteoporosis risk estimation score include: a) b) c) d) Weight over Height. Previous fragility fracture. . . Answer: ??? 46. Most common fracture seen in type I osteoporosis: a) b) c) d) Vertebral body. Hip. Distal radius. . Answer: c 47. Which of the following antibiotic need liver function monitor: a) b) c) d) Ampicillin. Gentamycin. Flagyl. Ciprofloxacin. Answer: d 48. Dilantin is used in epilepsy patients & cause vitamin D deficiency through: a) b) c) d) Decrease renal absorption. GI irritation. Prevent hydroxylation of 24,25 hyrdoxyvitamin D3. Prevent hydroxylation of 25 hyrdoxyvitamin D3. Answer: d 49. 35-year-old male underwent discectomy for herniated lumbar disc 6 months ago. Present to the clinic complaining of low back pain radiating to right leg with numbness over medial aspect of leg. What is the reason: a) b) c) d) Recurrence of herniated disc. Infection. Muscle spasm. Fibrosis at surgical site. Answer: a 50. A female patient underwent posterior spinal fusion & instrumentation for adult scoliosis 1 year ago. She is complaining of low back pain when start to stand & no rest pain. What is the cause of her complain: a) b) c) d) Adjacent level disease. Pseudoarthrosis. Positive sagittal imbalance. Positive coronal imbalance. Answer: c 51. A 16-year-old gymnast diagnosed as L5-S1 isthmic spondylolisthesis with translation of 60 %. Complaining of intermittent low back pain. She did not with conservative treatment & does not have any neurological symptom. X-ray showed normal sagittal balance. Treament should be: a) b) c) d) Reduction & L5 – S1fixaton. In-situ L4 – S1 fixation. Bracing. Epidural injection. Answer: b 52. Patient with foraminal disc at L5 – S1 will have: a) b) c) d) Decrease sensation over medial aspect of leg. Decrease sensation over dorsum of foot. Abnormal patellar reflex. Decease big toe dorsiflexion. Answer: d 53. X-linked autosomal dominant inheritance seen in: a) b) c) d) Morquio syndrome. Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Vitamin D-resistant rickets Hemophilia. Answer: c 54. Regarding osteogenesis imperfecta, which of the following is not involve: a) b) c) d) Normal X linking collagen. High parathyroid & calcium. Dental Cavities. . Answer: a 55. A 16-year-old swimmer has pain and weakness in her dominant shoulder with overhead use. Her physical examination demonstrates a +2 anterior and posterior load and shift test. There is 1.5 cm of sulcus sign evident with the arm at adduction and 30 degrees of external rotation. Her radiographs are normal. What is the most appropriate next step in management: a) Arthroscopic anterior and posterior labral repair with rotator interval closure. b) Home stretching program with emphasis on posterior capsular stretching. c) Dynamic stabilization therapy. d) Sport specific bracing. Answer: c 56. A 25-year-old male injured his left knee in a motor cycle accident. During examination, noted to have a positive reverse pivot shift test and a negative posterior drawer. What other examination finding is this patient expected to have: a) Positive anterior drawer test. b) Increased opening to valgus stress at 30 degrees of knee flexion. c) A 10 degree increased external tibial rotation at 30 degrees of knee flexion. d) A 10 degree increased external tibial rotation at 90 degrees of knee flexion. Answer: c 57. Internal rotation of femur component during total knee arthroplast will cause: a) b) c) d) Increase patellofemoral instability. Decrease patellofemoral instability. Increase patellofemoral arthritis. Decrease patellofemoral arthritis. Answer: a 58. Regarding MRI with arthrogram: a) b) c) d) 90 % sensitivity for labral tear. . . . Answer: a 59. A 42-year-old male has a suspected distal biceps rupture with a tendon that can be palpated but is painful during the hook test examination. The next appropriate step is: a) b) c) d) CT scan. MRI scan. Immobilization for three weeks followed by repeat physical examination. Operative exploration of distal biceps tendon. Answer: b 60. Most common sign seen in Femoroacetabular Impingement is: a) b) c) d) A bump at head-to-neck junction. Shallow acetabulum. Femur antiversion. . Answer: a 61. 30-year-old woman with progressive and severe right hip pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs no longer control her pain. What is the next most appropriate step in management? a) b) c) d) Total hip arthroplasty Single innominate (Salter) osteotomy Chiari osteotomy Ganz osteotomy Answer: d 62. A 35-year-old male patient who had ACL reconstruction with hamstring autograft 5 days ago. He reports his knee pain and swelling have significantly increased in the last day, and now it is difficult for him to raise his leg off the bed and is having more difficulty tolerating the CPM machine. Upon questioning he denies fever, chills, or any new trauma to the knee. What is the next step in management: a) Ice, NSAIDS, elevation, compression wrap and restart therapy once symptoms improve. b) Increase CPM use to 10 hours a day. c) Immediate knee aspiration for gram stain and cultures. d) Start physical therapy visits once daily. Answer: c 63. Pattern of ossification in the distal tibial physis in the following order : a) b) c) d) Medial then lateral then central. Lateral then medial then central. Central then Medial then lateral. Central then lateral then medial. Answer: c 64. Most common residual deformity of club foot after posteromedial release is: a) b) c) d) Mild cavus & dorsally rotated navicular. Intoning gait Dorsal bunion. Dynamic supination. Answer: a 65. A 30-year old female present to the clinic complaining of progressive left foot deformity that failed with conservative management. On Physical examination, she have cavus midfoot, varus hindfoot, which was corrected with coleman block test. She have weak tibialis anterior & peroneus brevis. Which procedure is associated with improved clinical outcomes in patients with the above described condition: a) b) c) d) Lateral forefoot orthosis. Triple arthrodesis. Peroneus longus tendon transfer & first metatarsal dorsiflexion osteotomy. Peroneus longus tendon transfer & first metatarsal dorsiflexion osteotomy + Dwyer osteotomy. Answer: c 66. You are called to assess a 4 year old child who suffered a severe head injury one week ago, You assess him in ICU where he is extubated but semiconscious. You determine that both feet have spastic equinus deformities. What is the most appropriate treatment at this pain? a) b) c) d) Bilateral tendoachiles lengthening. Bilateral posterior medial releases. Splinting, continue nonoperative treatment. Bilateral above knee casts. Answer: c 67. A 6-year-old boy with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy has a crouched gait. Examination reveals hip flexion contractures of 15° and popliteal angles of 70°. Equinus contractures measure 10° with the knees extended. Which of the following surgical procedures, if performed alone, will worsen the crouching? a) b) c) d) Iliopsoas release at the pelvic brim Hamstring lengthening Heel cord lengthening Split posterior tibial tendon transfer Answer: c 68. A 34 year old female present to the clinic complaining of bilateral feet progressive deformity & medial feet pain. Left more than right. On examination, valgus left hindfoot which is correctable & decrease in the medial longitudinal arch. She is able to perform single-leg heel raise. She also able to dorsiflexed her foot about 5 degree with knee extension & 10 degree with knee is flexed. Her picture showing her foot from posterior. Most likely the cause for her condition is: a) Tendon Achilles contracture. b) Gastrocnemius contracture. c) Tarsal Coalition. d) Posterior tibial tendon incompetent. Answer: d 69. Development of a valgus deformity in children after a fracture of the proximal tibial metaphysis most likely results from: a) b) c) d) Lateral physeal arrest. Asymmetric physeal growth. Tethering by the fibula. Periosteal interposition. Answer: b 70. What is not true regarding pediatric ankle radiograph? a) b) c) d) Conventional radiograph recommended as first evaluation. Stress view recommended. CT scan need it if for fracture displacement more than 2 mm. MRI will not add new information more than conventional radiograph. Answer: d 71. Mixed tumor is differentiated from chondrosarcoma in: a) b) c) d) Interosseous location. Myxiod stroma. Chondroid stroma. Squamous cell. Answer: ? b 72. What is the diagnosis for lesion seen in X-ray: a) b) c) d) ABC. UBC. Fibrous dysplasia. Nonossefying fibroma. Answer: ??? a 73. What is the treatment for acetabulum giant cell tumor with size more than 5 cm? a) b) c) d) Radiation alone. Bisphosphonates. Radiation, Intralesion curettage & bone graft. Radiation & curettage. Answer: c 74. Patient with enchondroma of middle phalanx, which was treated with intralesional curettage and bone grafting one year ago. Present now with more aggressive lesion & soft tissue involvement. Treatment should include: a) b) c) d) Amputation from PIP joint. Ray amputation. . . Answer: ??? 75. A young patient twisted his knee 2 days ago & diagnosed with ACL tear. On examination, moderate swelling, ROM 0 – 80 & Lachman positive. What is the appropriate treatment at this stage? a) b) c) d) Knee immobilization. Immediate Physiotherapy. Arthrocentasis. Arthroscopic reconstruction. Answer: a or b 76. A prospective study for Tendon Achilles rupture. A 16 patients in every group. Randomized disruption of patient between tow treatment & blinded observers. First group received primary repair of rupture with suture & the other group just end to end repair without suturing. Both group received the same protocol postoperatively. The investigator was looking for rerupture rate, which was not significant. What is the type of this study & what is the level of evidence? a) b) c) d) Prognostic study, level 1. Therapeutic study, level 1. Therapeutic study, level 2. Therapeutic study, level 3. Answer: a 77. You review all RCT about a treatment for specific disease & found that all the articles are supported from the medical companies. Which of the following best describes the bias that is present in these studies? a) b) c) d) Selection bias. Systemic bias. Conflict of interest. . Answer: c 78. An 8-year-old girl comes to the office with increasing thigh pain mostly at night. Radiograph and biopsy specimen are shown. The patients WBC and ESR are both elevated. What is the most likely diagnosis? What is the most likely diagnosis? a) b) c) d) Osteomyelitis Ewing's sarcoma Osteosarcoma Eosinophilic granuloma Answer: b 79. Patient with Low back pain, what is the benefit of Bed rest for him? a) b) c) d) Strongest pain relief. It’s better to return him to previous functional level in longterm Better than Brace. . Answer: b 80. The most common complication of bilateral total knee replacement in compare to unilateral is: a) b) c) d) Deep vein thrombosis. Death. Infection. Cardiac event. Answer: d 81. 65-year-old male sustain neck of femur fracture. He was treated with hemiarthroplasty. In compare to total hip arthroplasty, hemiarthoplasy have: a) b) c) d) Better functional outcome. Better pain relief. Less dislocation rate. . Answer: c 82. A "double PCL sign" seen on a sagittal MRI image of a knee is indicative of which of the following conditions? a) b) c) d) ACL tear. Combined ACL & PCL tears. PCL & PLC tears. Bucket-handle meniscal tear. Answer: d 83. Varus intertrochatric osteotomy for coxa valga will produce which of the following results? a) b) c) d) Decreased Abductor leaver arm. Increased hip joint reaction force. Abductor lag & lurch. Lengthening of the leg. Answer: c 84. When the surgeon position the total hip implant, he put the acetabulum component 40 degree in horizontal plane, 30-degree antiversion & femoral component 10-degree antiversion. What type of instability patient will have? a) b) c) d) Anterior dislocation. Posterior dislocation. Inferior dislocation. Superior dislocation. Answer: a 85. When performing a total hip in developmental dysplasia patients. The most common acetabulum abnormality encounter is: a) b) c) d) Superiolateral deficiency. Superiomedial deficiency. Acetabulum protrusion. . Answer: a 86. During primary total knee arthroplasty, what is the maximum distance the joint line can be raised or lowered before poor motion, joint instability, and increased chance of revision occur? a) b) c) d) 4 mm 8 mm 10 mm 12 mm Answer: b 87. During primary total knee arthroplasty, If you put the extramedullay guide too medial in the tibial platue. What deformity will be seen postoperatevly? a) b) c) d) Varus. Valgus. Patella baja. No effect. Answer: a or b 88. Best method to minimized osteolysis after TKR is: a) b) c) d) Gamma Irradiation PE insert steralization. Metal-backed tibial components. . . Answer: ??? 89. Nerve regeneration occur from: a) b) c) d) 1 cm proximal to injury. Just at injury. Schwann cell. . Answer: ? c 90. High failure rate of ceramic-on-ceramic THA due to: a) b) c) d) Acetabulum cup fracture. Femoral head fracture. Acetabulum cup loosening. Femoral head loosening. Answer: b 91. In normal aging process of bone, Red marrow is replaced by yellow marrow in which pattern: a) b) c) d) Start with axial bone then peripheral. Start with peripheral bone then axial. Same rate. No change Answer: b 92. Which of the following a vascular sequel of proximal femur first to be encounter during treatment developmental dysplasia of hip: a) b) c) d) Kalamchi type 1. Kalamchi type 2. Kalamchi type 3. Kalamchi type 4. Answer: a 93. Which of the following joint is not involve in forearm supination / pronation movement: a) b) c) d) Radiohumeral joint. Ulnoheumeral joint. Radiocarpal joint. Midcarpal joint. Answer: d 94. 65-year-old active patient present to the emergency department complaining of severe left knee pain after falling down the stairs. He had bilateral TKA 10 years ago that was uncomplicated & he has been pain free since surgery. Examination revels a closed injury. A radiograph is shown. What is the best treatment option for this patient? a) b) c) d) Antegrade femoral IM nail. Distal femoral locking plate. Tow stage revision with antibiotic spacer between stages. Revision TKA using distal femoral tumor prosthesis. Answer: ??? 95. A 34-year-old woman presents with right foot pain and and a callus over the 1st metatarsalphalangeal joint. Accomodative shoewear has failed to relieve symptoms. Her radiographic measurements were: Hallux valgus angle (HVA) 40 degree Intermetatarsal angle (IMA) 16 Distal metatarsal articular angle (DMAA) 15 Which of the following operative procedures is most appropriate for this deformity? a) Proximal Chevron osteotomy + proximal Akine osteotomy. b) Proximal Lapidus osteotomy + distal soft tissue release. c) Proximal dome osteotomy + distal soft tissue release. d) Answer: ??? 96. : a) b) c) d) . . . . Answer: ??? 97. : a) b) c) d) . . . . Answer: ??? 98. : a) b) c) d) . . . . Answer: ??? 99. : a) b) c) d) . . . . Answer: ??? 100. a) b) c) d) : . . . . Answer: ??? ^_^ Good luck ^_^