Researching IP Implications on SMEs
advertisement

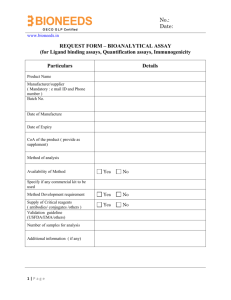
WIPO Expert Group on Internationally Agreed Scope and Methodology for Undertaking National Surveys and/Studies on IP and SMEs Researching IP Implications on SMEs A. Damodaran Indian Institute of Management Bangalore SMEs in India: A Profile In India, SME sector is the second largest manpower employer, after agriculture Nearly 13 million units, employing 31 million people The output from the SSI sector alone constitutes 40 percent share of the value added in the manufacturing sector 39% of country’s Industrial Production and 1/3rd of country’s exports Very Traditional to High Tech Source: MSME, Government of India Policy Framework GOI enacted the Micro Small and Medium Enterprise Development Act, 2006 to address issues of the sector GOI to do away with 24% ceiling prescribed for equity holdings in MSME Expected Legislation on Limited Liability Partnership to encourage corporatization of SME in India National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC) was set up to energize and sustain the growth of the manufacturing industry. New Promotional Packages for SMEs, and focus on development of clusters. Steps to enhance access to equity and other funds from the markets for SME’s Source: MSME, Government of India Promotional Schemes of MSME Revised strategy of lending and introduction of newer measures, such as the scheme to establish Small Enterprises Financial Centres (SEFC) for strategic alliance between branches of banks and SIDBI located in 388 clusters identified by ministry of SSI. SME Fund of US$ 2.27 billion operationalised. Proposal for doubling the credit flow to MSME sector in next 5 Yrs. Promotion and financial support for Credit-cum-Performance Rating in MSME sector in India, to facilitate greater and easier flow of credit from the banking sector to SMEs. Guarantee coverage under Credit Guarantee Fund for Small Enterprises expanded substantially Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme for Technological Upgradation Source: MSME, Government of India Policy NMCC has recommended a 5year programme for enhancing competitiveness in SME’s Programme aimed at improving awareness on IPR for SME’s Hopes to target 12000 units and 30 MSE clusters at a target cost of 55 crores with a private contribution of 5 crores Source: MSME, Government of India Geographical Indications 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Tea,West Bengal,Darjeeling Tea (word & logo) Handicrafts,Kerala,Aranmula Kannadi Textiles- Andhra Pradesh Pochampalli Ikat Textiles,Tamil Nadu, Salem Fabric Textiles, Madhya Pradesh, Chanderi Fabric Textiles, Maharashtra, Solapur Chaddar Textiles, Maharashtra,Solapur Terry Towel Textiles, Orrissa, Kotpad Handloom fabric Textiles,Karnataka,Mysore Silk Textiles,Rajasthan,Kota Doria Geographical Indications 11. Incense Sticks, Karnataka,Mysore Agarbathi 12. Textiles, Tamil Nadu, Kancheepuram Silk 13. Textiles, Carpets, Tamil Nadu, Bhavani Jamakkalam 14. Textiles, Himachal Pradesh, Kullu Shawl 15. Handicrafts, Karnataka, Bidriware 16. Textiles, Tamil Nadu, Madurai Sungudi 17. Textiles, Orissa, Orissa Ikat Handicrafts, Karnataka, Channapatna Toys & Dolls 19. Handicrafts, Karnataka, Mysore Rosewood Inlay 20. Tea, Himachal Pradesh, Kangra Tea 18. GIs 21. Wet Grinder, Tamil Nadu, Coimbatore Wet Grinder 22. Textiles, Andhra Pradesh, Srikalahasthi Kalamkari 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Essential Oil, Karnataka Mysore Sandalwood Oil Soap, Karnataka Mysore Sandal soap Embroidery (Textiles), Karnataka Kasuti Embroidery Paintings, Karnataka Mysore Traditional Paintings Horticulture Products, Karnataka Coorg Orange Horticulture Products, Karnataka, Mysore Betel leaf Horticulture Products, Karnataka Nanjanagud Banana Paintings, Bihar Madhubani Paintings GIs 31. Handicrafts, Andhra Pradesh, Kondapalli Bommallu 32. Paintings, Tamil Nadu, Thanjavur Paintings 33. Handicrafts, 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. Andhra Pradesh, Silver Filigree of Karimnagar Coir Products, Kerala, Alleppey Coir Textiles, Assam Muga Silk Handicrafts, Tamil Nadu, Temple Jewellery of Nagercoil Horticulture, Karnataka Mysore Jasmine Horticulture, Karnataka, Udupi Jasmine Horticulture, Karnataka, Hadagali Jasmine Agricultural Products,Kerala Navara Rice GIs 41. Agricultural Products, Kerala Palakkadan Matta Rice 42. Handicrafts,Tamil Nadu,Thanjavur Art Plate 43. Textiles, Karnataka Ilkal Sarees 44. Handicrafts, Bihar Applique - Khatwa Patch Work of 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. Bihar Handicrafts, Bihar, Sujini Embroidery Work of Bihar Handicrafts, Bihar, Sikki Grass Work of Bihar Agricultural Products, Kerala Malabar Pepper Guava,Uttar Pradesh, Allahabad Surkha Textiles, New Delhi, Nakshi Kantha Handicrafts, Karnataka, Ganjifa cards of Mysore (Karnataka) GIs 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. Textiles, Karnataka, Navalgund Durries Handicrafts,Karnataka,Karnataka Bronze Ware Textiles,Karnataka,Molakalmuru Sarees Coffee, Karnataka Monsooned Malabar Arabica Coffee Coffee Karnataka Monsooned Malabar Robusta Coffee Agricultural Products, Kerala Spices - Alleppey Green Cardamom Agricultural Products, Karnataka Coorg Green Cardamom E. I. Leather, Tamil Nadu, E. I. Leather Textiles and Textile Goods, Tamil Nadu, Salem Silk Textiles and Textile Goods, Tamil Nadu, Kovai Cora Cotton Textiles and Textile Goods, Tamil Nadu, Arani Silk Darjeeling Tea The first attempt on the part of the Tea Board of India towards protection of the ‘Darjeeling’ brand was undertaken way back in 1983, when the ‘Darjeeling’ logo was created. The Tea Board obtained home protection for the Darjeeling logo as a certification trade mark under the Indian Trade and Merchandise Marks Act 1958 (now the Trade Marks Act, 1999). The registration was granted in class 30 in the name of the Tea Board in 1986. In the same year, the logo was registered as a trademark in several other countries In the absence of a separate law dedicated exclusively to GI’s in India during that time, the word ‘Darjeeling’ was also registered under the Trade and Merchandise Marks Act 1958 in class 30 in the name of Tea Board in 1998. Source: Government of India Knowledge Intensive Sectors Biotech including plant biotech , traditional medicines and bioinformatics IT Software Agri-enterprises associated with export based products Innovation Systems Informal – Protected as Trade Secrets or Confidential Information Formal – IPRs Filed Well Springs of Innovation Start up Innovation Firms: Vendor of Innovations : Bioinformatics Innovations by Learning by doing Firms Cluster Generated Joint Innovations Public-Private Innovations Typology of Innovations Designs New Processes Products Devices Access To Patents: Transaction Costs Prior Art Data Base is Difficult to Access Patent processes are too costly for SMEs to access Transaction Costs of Filing and Getting Patents high PCT applications are excessively costly Defending Patents Probability of Infringement Assessment Cost of Defending Damage Compensation Self Assessment Capacity for Self Assessment of Innovation Quality not there Self Assessment involves: - Determination of Quality of Innovation in terms of Prior Art - The Depth of the Inventive Step - IPR-ability of the Innovation - Ramification of the Innovations in terms of Applicability and Multiplier Effects Assessment of Competitive Advantage afforded by innovations Standards and SMEs SMEs role in Standard setting very limited Costs of Compliance with Standards high This in turn affects Competitiveness Business Models for Technology Transfer Business Models that are appropriate to SMEs can facilitate transfer of technology and enable optimum revenue realization This in turn can facilitate iinovation Such Models have not been designed Cluster Innovations Cluster based Innovations are economically viable (by promising external economies) and achieve innovations that give greater leverage power to companies concerned Cases to be documented Research Issues New IP laws – like Petty Patents Transaction Costs of filing and defending Patents and other IPs Cluster Innovations Economic Analysis of Business Models Finance early bird innovations that are promising Facilitate Self Assessments through Capacity Building Financial Mechanisms Thank You