2 Lecture #1 Programming Language Overview
advertisement

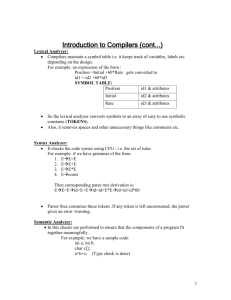
1.3 Executing Programs How is Computer Code Transformed into an Executable? • Interpreters • Compilers • Hybrid systems Language Implementation Methods • Compilation – Programs translated into machine language code that is directly executable • Pure Interpretation – Programs are interpreted by an "interpreter" – Intermediate machine code is not produced. • Hybrid Implementation Systems – A compromise between compilers and pure interpreters Layered View of a Computer System (hardware and software) The operating system and language implementation are layered over the Machine interface of a computer © Addison-Wesley Compiler Implementation • Compiler - program that – Reads a program written in one language (the source language) – Translates it into an equivalent program in another language (the target language) • Checks for the presence of errors in the source program source program compiler target program error messages 8 Phases of a Compiler • 4. 5. 6. • Lexical analyzer 6 main phases 1. 2. 3. Lexical analyzer Syntax analyzer Semantic analyzer Intermediate code generator Code optimizer Code generator Two more activities (in parallel with 6 phases above) A. Symbol table manager B. Error handler Source program Lexical units Syntax analyzer Parse trees Symbol table Intermediat Code generator (and semantic analyzer) Optimization Intermediate code Code generator Machine language Input data Computer Results (optional) A. Symbol Table Manager • Keeps track of the source program's identifiers and their attributes – Attributes: storage allocated, type, scope, arguments, return type, etc. – Uses a symbol table • Data structure (array, linked list, hash table, etc.) with a record for each identifier where fields are the identifier's attributes B. Error Detection and Reporting • When an error is detected, the compiler must somehow deal with that error, then proceed to find more possible errors – Lexical analysis phase detects errors where the characters in the source file do not form any token of the language • Example: s p a c es in var – Syntax analysis phase detects violations to the rules of the language • Example: var1 = var2 + – Semantic analysis phase detects constructs that have no meaning • Example: var1 = array1 + procedure1 1. Lexical (Linear) Analysis • Lexical = of or relating to words or vocabulary of a language as distinguished from its grammar and construction • Identifies tokens (keywords, identifier names, integers, etc.) of the programming language • Token – sequences of characters that have a collective meaning 2. Syntax (Hierarchical) Analysis • Syntax - the way linguistic elements (e.g. words) are put together to form constituents (e.g. sentence, phrase, clause) • Also called "parsing" • Groups tokens into grammatical phrases • Usually the grammatical phrases are represented by a "parse tree" 3. Semantic Analysis • Semantic - of or relating to meaning in language • Checks for semantic errors – gathers type information for the subsequent code generation phase • Uses hierarchical structure (determined by the parser) to identify the operators and operands of expressions and statements 4. Intermediate Code Generator • Generates an intermediate representation of the source program • Not all compilers perform this • An intermediate representation can be thought of as a program for an abstract machine • Should be – easy to produce – easy to translate into the target program 5. Code Optimization • Improve the intermediate code to produce a faster running machine code in the final translation • Optional - not all compilers include the code optimization step, which can be time (and space) intensive 6. Code Generation • Generate the target code, usually relocatable machine code – Relocatable code can be loaded at any location R in memory – In other words, if the number R is added to all the addresses in the code, then all references will be the actual memory address • The relocatable code is contained in the object file – .obj • It contains machine language instructions – only bits – 1's and 0’s Post-Compilation - Linking • Linker (link-editor) connects: – Object files (.obj) from the program modules – Additional library files – Creates the executable (.exe file) program • Usually uses relocatable addresses within the program – Allows the program to run in different memory locations – Allows time-sharing and virtual memory Post-Compilation - Loading • Loading the executable (.exe file) program • Also called load module or executable image • The loader – Identifies a memory location to load the program – Alters the relocatable machine code addresses to run in the designated memory location • A program must be in (loaded) memory each time it executes Implementation Methods - Interpretation • Pure interpretation - high-level language statements are immediately decoded into machine code & executed – Fast to write, modify, experiment and try different solutions – Easy to debug – Decoding is slower than execution of compiled code, however the need to compile is eliminated – May require more space for symbol table & source program Implementation Methods - Hybrid • Hybrid – combination of compilers and interpreters – High-level language programs are translated to an intermediate language, which is easily interpreted • E.g. Java – compiled and interpreted – Intermediate “byte code” is created by the compiler, – Then the byte code is interpreted • Lisp – interpreted, or compiled, or both – Compilation not required - increases speed 10 X or more – Interpreted and compiled code can run together! – Saves compiling an entire project when only one or two files have been changed! – Can be compiled after debugging - make it work, then make it fast! • Perl – seems interpreted – Partially compiled to detect errors, then interpreted Hybrid Implementation System Summary • Programming language study is valuable – Adds problem-solving methods and paradigms – Increases capacity to use different features/tools in all languages – Ability to choose implementation languages intelligently to increase productivity – Makes learning new languages (thus new tools) easier • Most important criteria for evaluating programming languages include: – Readability, writability, reliability, cost • Major influences on language design have been machine architecture and software development methodologies • The major methods of implementing programming languages are: compilation, pure interpretation, and hybrid implementation