Name: Period:______ Unit 2: Changing Earth Study Guide
advertisement

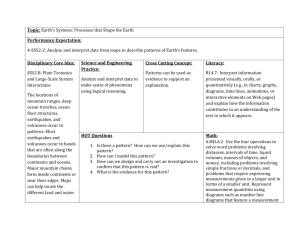
Name:________________________________________________________ Period:__________ Unit 2: Changing Earth Study Guide Benchmark: MARCH 10th Learning Targets I can describe the structure of Earth’s interior. I can analyze surface features of the Earth to infer the processes that shape them. I can examine a rock and tell its story. I can compare and contrast renewable and non-renewable sources of energy. Earthquakes 1. Where do earthquakes typically occur? 2. How are earthquakes measured? 3. How does measuring earthquakes help scientists understand more about Earth’s interior? 4. What is the difference between p-waves and s-waves? 5. How do earthquakes affect the surface features on Earth? Earth’s Interior Directions: Label the diagram of Earth’s interior below. 6. In which layer of Earth are convection currents taking place? ______________________________ 7. Which layer is broken up into the Earth’s plates? _______________________________ 8. Compare and contrast continental and oceanic crust. Plate Tectonics (convection in the mantle) Directions: Use the diagrams below to answer the questions 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. What kind of boundary is picture A? ________________________________ What is happening to the crust in picture A? _____________________________ What kind of boundary is picture B? ________________________________ What is happening to the crust in picture B? _____________________________ What kind of boundary is picture C? ________________________________ What is happening to the crust in picture C? _____________________________ 15. What kind of plate boundary is pictured above? ____________________________ 16. Why does the oceanic plate slide under the continental plate? 17. Explain how convection currents form in the mantle and how they affect the earth’s crust. 18. On the diagram below, draw arrows to show the direction the plates could be moving at the plate boundary. Volcanoes 19. Name the three types of volcanoes. 20. How do volcanoes get their shape? (*Think about the viscosity of the lava associated with each type of volcano) 21. How do scientists study and predict volcanoes? 22. How do volcanoes affect the surface features of the earth? Rocks and Minerals 23. What are the properties used to identify rocks and minerals? 24. Name the three types of rocks. 25. Name two characteristics of igneous rocks. 26. Name two characteristics of sedimentary rocks. 27. Name two characteristics of metamorphic rocks. 28. Directions: Fill in the rock cycle diagram with the types of rock and the processes that creates each type. Weathering, erosion, deposition 29. What is the difference between weathering, erosion, and deposition? Directions: Label the examples below as erosion, weathering, OR deposition. 30. Waves dropping sand on the beach. ____________________________ 31. Wind blowing sand from one location to another. _____________________ 32. Glaciers that drop rock, sand, and other debris forming landforms called moraines. _____________________ 33. Landforms called deltas that form where rivers flow into other bodies of water such as the sea. ______________ 34. Flood water pounding against a canyon wall and wearing it down. _______________________ Glaciers 35. What are the three requirements for something to be labeled a glacier? 36. Name two landforms formed by glaciers. 37. How do glaciers affect the surface features of the Earth? Renewable/Nonrenewable Resources 38. Define renewable resource and give an example. 39. Define nonrenewable resource and give an example. 40. How is coal formed? Constructive vs. Destructive Processes Directions: Label each example below as constructive OR destructive process. 41. Volcanoes? _____________________________ 42. Weathering? ___________________________ 43. Erosion? _______________________________ 44. Convergent plate boundary? __________________________ 45. Deposition? ____________________________