File
advertisement

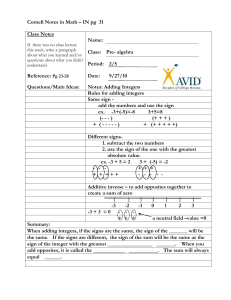
Open your book to page 4 Complete 1-6 on the Are You Ready? section in your book. Remember to turn your vocabulary into your class bin. LG 702: Students will be able to apply and extend previous understandings of operations to add and subtract rational numbers. LG 703: Apply and extend previous understandings of operations to multiply and divide rational numbers. Today I am working with integers. So that I can add integers with the same or different signs. I’ll know I’ve got it if I can accurately solve the following expression. 37 + (-82) Date Lesson Page # 8/24 Multiplication Table 1 8/24 Divisibility Rules 2 8/25 Adding Positive and Negative Integers 3 Unit 1 Absolute Value - The distance of a number from zero on a number line. Absolute value is always positive. Additive Inverse – The opposite of a number. The sum is always zero. Integer – The set of whole numbers and their opposites. … -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 … You can use colored counters to add positive integers and to add negative integers. =1 = -1 3+4 How many counters are there in total? We can use negative counters to add two negative numbers. -5 + (-3) How many counters are there in total? To add integers with the same sign, add the absolute values of the integers and use the sign of the integers for the sum. Model 4 + (-3) Model -7 + 5 You can use colored counters to model adding integers with different signs. When you add a positive integer and a negative integer, the result is 0. One red and one yellow counter form a zero pair. =1 = -1 1 + (-1) = 0 Model 3 + (-2) What is left when you remove the zero pairs? Same signs add and keep, Different signs subtract. Then keep the sign of the larger number And you will be exact. Page Due 17, #16-25 at the start of next class