Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory (Worksheet)
advertisement

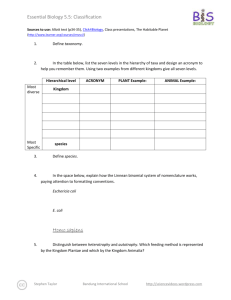
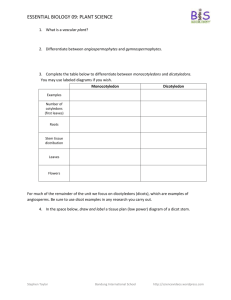
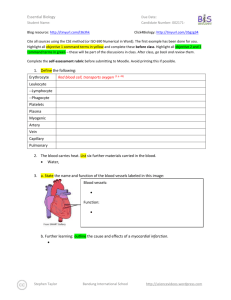
Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: Blog resource: http://tinyurl.com/29znhft Cite all sources using the CSE method (or ISO 690 Numerical in Word). The first example has been done for you. Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting to Moodle. You may print pages 3&4. 1. State the functions of life, as demonstrated by all living organisms. 2. Define the following terms, with examples: Unicellular Multicellular Acellular 3. State some examples of modern technology that have confirmed cell theory. 4. Outline the three fundamental statements of cell theory i. Cells are the smallest units of life ii. iii. Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: 5. Outline the significance of the work of these scientists in forming cell theory. i. Antonie van Leuwenhoek ii. Robert Hooke iii. Louis Pasteur and Robert Remak 6. Describe how the following examples might be exceptions to cell theory. a. Muscle cells and fungal hyphae b. Viruses c. Amoebae 7. Complete this table of SI units of length: Metric Equivalent scientific notation Unit Abbreviation kilometer km 1 000 m 103 m m 1m 1m centimeter Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor cm Bandung International School Whole 10-2 m http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: mm 0.001 m micrometer μm 0.000 001 m nanometer nm 10-3 m 10-9m 8. The diagram below shows the characteristic rod-shaped structure of E. coli bacteria. a. Calculate the magnification of the image. b. State the method (shown here) by which bacteria reproduce. 9. Calculate the actual size of the structures delineated in yellow. Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: 10. Calculate the magnification of these scale bars: Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: 11. What is the magnification of these images? a. Scale bar 10µm measures 40mm on the image. b. Scale bar 5µm measures 25mm on the image. 12. A micrograph has a scale bar of 2µm, which measures 40mm on the image. Measuring the maximum length of the cell in the image, the ruler reads 180mm. How long is the cell? 13. A student views an image of a cell magnified 350 times. The image is 250mm long. What is the actual length of the sample in the image? Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: 14. Compare the sizes of these structures. Use SI units. Plant cell Animal cell nucleus bacteria Mitochondria virus ribosome Membrane thickness molecules 15. Use some of these electron microscope resources to view molecules, cells and structures and to practice calculating magnifications and actual sizes. Virtual Electron Microscope: http://virtual.itg.uiuc.edu/ Microscopy UK: http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/ 16. As the volume of a cell increases, what happens to…? (increase/ decrease) a. Production of waste products. b. Usage of nutrients and oxygen. c. The surface area: volume ratio. 17. State the advantages of maximizing the surface area: volume ratio in a cell. 18. List some adaptations used by cells to maximize SA:Vol ratio. 19. List some adaptations used by multicellualr organisms to maximize SA:Vol ratio Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: 20. Describe how a large SA:Vol ration can be harmful or costly to small animals. 21. Describe how the invasive Caulerpa algae genus break the rules of SA:Vol. 22. Unicellular organisms carry out all the functions of life, multi-cellular organisms differentiate and show emergent properties. a. Describe what is meant by the term emergent properties. b. Outline the advantages of cells differentiating to carry out specific functions. 23. All cells in a living organism carry the same genetic information. a. Define stem cell. b. Define the following types of stem cells. Pluripotent Multipotent Nullipotent c. List two types of stem cell that can come from liver stem cells. 24. Outline the process of cell differentiation that leads from an uncommitted stem cell to a specialized cell, including the role of gene expression. A flow chart might help. Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: 25. Outline the relationship between structure and function in three types of specialized cells. Specialized cell Structure vs function Sperm cell Very small, low energy to produce. Hydrodynamic head with digestive enzymes to aid fertilization of the egg. Rotor section and tail to aid swimming. 26. Complete the table below to explain two ways in which stem cells can be used in medicine. Therapeutic cloning Stem cell transplants Used to treat Brief method: Ethical considerations Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: Extension Reading: Stem cells cure sickle cell anemia in mice: http://medgadget.com/archives/2007/12/scientists_cure_sickle_cell_anemia_in_mouse_model.html What human examples of stem cell therapy have been in the news recently? 10 amazing medical breakthroughs (read them all): http://www.time.com/time/specials/2008/top10/article/0,30583,1855948_1863993,00.html iPS Stem cells used to make human neurons: http://scienceblogs.com/notrocketscience/2008/08/stem_cells_created_from_als_patient_and_used_to_make_neurons.php What is special about iPS stem cells? Do a search for more recent stories – how is research progressing? How might this technology reduce objections to Giant bacterium with many genomes http://scienceblogs.com/notrocketscience/2008/04/enormous_bacterium_uses_thousands_of_genome_copies_to_its_ad.php How does this bacterium cope with being so large? Works Cited 1. Allott, Andrew. IB Study Guide: Biology for the IB Diploma. s.l. : Oxford University Press, 2007. 978-019-915143-1. Self Assessment: Essential Biology Criterion Presentation & Organisation Academic Honesty Objective 1 understanding Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor Complete (2) Partially complete (1) Complete and neat. All command NA terms highlighted, tables and diagrams well presented. Sources cited using the CSE (ISO 690 NA numerical) method, with Works Cited section complete and correct. All answers for the following Most answers for the following command terms correct: command terms correct: Define Draw Label List Measure State Bandung International School Assessment Self MrT http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 2.1 Cell Theory Due Date: Student Name: Objective 2 understanding Objective3 understanding Logic, notation, mathematical working Further research All answers for the following command Most answers for the following terms correct: command terms correct: Annotate Apply Calculate Describe Distinguish Estimate Identify Outline All answers for the following command Most answers for the following terms correct: command terms correct: Analyse Comment Compare Construct Deduce Derive Design Determine Discuss Evaluate Explain Predict Show Solve Sketch Suggest Answers are presented in a logical and concise manner. SI units used NA most times, with correct unit symbols and definitions of terms. All mathematical working shown. Evidence is apparent of research and reading beyond the textbook and presentations to find correct NA answers to challenging questions. If any questions are unanswered, this criterion scores zero. Total (max 10): Fargo—IB Biology LHS Courtesy of Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com