Essential Biology 6.4 Gas Exchange
advertisement

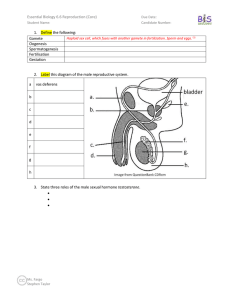
Essential Biology 6.4 Gas Exchange Student Name: Due Date: Candidate Number: 1. Define the following: Ventilation Movement of air into and out of the lungs. Gas exchange Cell respiration Deoxygenated Oxygenated 2. Explain the need for ventilation in humans. Size Humans are large, land-based organisms that cannot exchange gas sufficiently with the air through diffusion alone. A central ventilation system allows gases to be exchanged with the blood and carried around the body to the cells that require it. Oxygen Carbon dioxide Concentration gradient 3. Deduce the number of membranes an oxygen molecule must pass through in order to enter an erythrocyte. Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.4 Gas Exchange Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: 4. Label the features of the alveoli and describe how they are adapted for their function. a. b. Many invaginations and millions of alveoli – large surface area c. Moist membranes. d. Membranes only one cell thick. 5. Label this diagram of the human ventilation system. a. Trachea b. c. d. e. Also don’t forget to be able to draw and label a magnified alveolus. Practice these drawings on paper – you might need them in the exam! Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.4 Gas Exchange Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: 6. Explain the method of ventilation of the lungs. Feature Inhalation External intercostal muscles Contract, pulling ribcage up and out. Exhalation Internal intercostal muscles Diaphragm Abdominal muscles Lung volume Pressure in lungs Decreases, sucking air into the lungs. Data-based question practice, from the IB Biology QuestionBank CDRom. 7. A major requirement of the body is to eliminate carbon dioxide (CO2). In the body, carbon dioxide exists in three forms: dissolved CO2, bound as the bicarbonate ion, and bound to proteins (e.g. haemoglobin in red blood cells or plasma proteins). The relative contribution of each of these forms to overall CO2 transport varies considerably depending on activity, as shown in the table below. CO2 Transport in Blood Plasma at Rest and During Exercise Rest Exercise Arterial Venous Venous mmol I–1 blood mmol I–1 blood mmol I–1 blood dissolved CO2 0.68 0.78 1.32 bicarbonate ion 13.52 14.51 14.66 0.3 0.3 0.24 14.50 15.59 16.22 7.4 7.37 7.14 Form of transport CO2 bound to protein Total CO2 in plasma pH of blood [Source: Geers and Gros, Physiological Reviews (2000), 80, pages 681–715] Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.4 Gas Exchange Student Name: Due Date: Candidate Number: (a) Calculate the percentage of CO2 found as bicarbonate ions in the plasma of venous blood at rest. (1) (b) (i) Compare the changes in total CO2 content in the venous plasma due to exercise. (1) 8. (ii) Identify which form of CO2 transport shows the greatest increase due to exercise. (1) 9. (c) Explain the pH differences shown in the data. (3) (Total 6 marks) Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Essential Biology 6.4 Gas Exchange Due Date: Candidate Number: Student Name: Works Cited 1. Allott, Andrew. IB Study Guide: Biology for the IB Diploma. s.l. : Oxford University Press, 2007. 978-019-915143-1. 2. Mindorff, D and Allott, A. Biology Course Companion. Oxford : Oxford University Press, 2007. 978099151240. 3. Clegg, CJ. Biology for the IB Diploma. London : Hodder Murray, 2007. 978-0340926529. 4. Campbell N., Reece J., Taylor M., Simon. E. Biology Concepts and Connections. San Fransisco : Pearson Benjamin Cummings, 2006. 0-8053-7160-5. 5. Taylor, Stephen. Science Video Resources. [Online] Wordpress, 2010. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com. 6. Burrell, John. Click4Biology. [Online] 2010. http://click4biology.info/. 7. IBO. Biology Subject Guide. [Online] 2007. http://xmltwo.ibo.org/publications/migrated/productionapp2.ibo.org/publication/7/part/2/chapter/1.html. Self Assessment: Essential Biology Criterion Presentation & Organisation Academic Honesty Objective 1 understanding Objective 2 understanding Objective3 understanding Logic, notation, mathematical working Further research Assessment Complete (2) Partially complete (1) NA Complete and neat. All command terms highlighted, tables and diagrams well presented. Sources cited using the CSE (ISO 690 numerical) method, with Works Cited section complete and correct. All answers for the following command terms Most answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Define Draw Label List Measure State Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Annotate Apply Calculate Describe Distinguish Estimate Identify Outline Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Analyse Comment Compare Construct Deduce Derive Design Determine Discuss Evaluate Explain Predict Show Solve Sketch Suggest Answers are presented in a logical and concise manner. SI units used most times, with correct NA unit symbols and definitions of terms. All mathematical working shown. Evidence is apparent of research and reading beyond the textbook and presentations to find correct answers to challenging questions. If any NA questions are unanswered, this criterion scores zero. NA Total (max 10): Ms. Fargo Stephen Taylor Bandung International School Self MrT