Wisconsin Division of Energy
advertisement

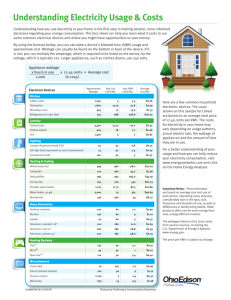
What can students do about global warming? Sara Krauskopf (Madison East High School) Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center Advanced Biology class--11 and 12th grade All students have taken one year of biology and chemistry Overview of Advanced Biology Global Warming Unit Guest speaker introduction Review of atmosphere—distinguish greenhouse effect from ozone layer from global climate change Examples of effects of global climate change, esp biological/ecosystem changes Sources of air pollution and effects on human health Wisconsin contributions stats East High electricity bill/ retrofitting projects Home electricity audit Group research projects on topics related to air pollution/alternative fuels/effects of global climate change Wisconsin Energy Statistics 2006 Wisconsin Division of Energy--Department of Administration Wisconsin Energy Statistics 2006 Wisconsin Division of Energy--Department of Administration Google “Wisconsin Energy Statistics” or “Wisconsin Division of Energy” pdf file to download or view online two versions available-condensed and complete What is a kilowatt? Visual demonstration of a kilowatt (10 100W bulbs) If we left these on for one hour, this would be one kilowatt hour. Conversion Rates (Coal-fired electricity) CO2= 1 kg/KWH SO2 = 5.8 grams/KWH NOx = 2.5 g/KWH Electricity $.10 per KWH. Use local rates from utility companies. Source Madison Gas and Electric Local Utility Bills School bills--obtain from District Facilities Manager or KEEP course (UWSP) Bring in home bills/photocopy yours Discuss various charges Peak/offpeak rates Distribution service/KWH + Electricity Service per KWH Madison East’s Energy Bill Typical Lightin g Retrofit Existin g Lighting Room 330 The e xisting lightin g consisted of (20) flourescent fixtures each using (4 ) 4 foot fluorescent lamps an d (2) magneti c ba llasts. Ballasts ar e requir ed in all fluorescent fixtures to prov ide the proper voltage and current to operate the lamps . The flourescent lamps wer e each 34 watts, w hil e each ballast used aproximate ly 12 watts. The total wattage per fixtur e was 160 watts. Cost to Operate the Existing Lightin g System The total wattage o f the existing lighti ng syst em is : 20 fixtures x 160 watts = 3,200 watts or 3.2 Kil owatts (KW) The estimated hours 10 hours/day of operation of these fix tures is: x 5 days/week x 42 weeks/yea r = 2,100 hours The avera ge electri c rate for MGE is about 0.06 $/kilowatt annual cost to operate these fixtures is: -hour (KWH ), therefor e the 3.2 KW x 2,100 hours x 0.06 $/KWH = $403.20 LIGHTING RETROFIT PROJECT The lightin g retrofi t project im plemented by Honeywe ll consisted of re placing th e (4) fluorescent lamps an d (2) magneti c ba llasts w ith 2 energ y efficient T8 , 1î diameter , lamps, a n energ y efficient electronic ballast and an aluminum reflector install ed behin d the lamps i n orde r to improve the ef ficiency of the fixture by ma ximi zing th e amount of light the fixtur e produces . Th e total wattage of the retro fit fixtures is 58 watts. The estimated cost to retrofit this room was $1,400 Cost to Operate the New Determine the annua Total wattage Lightin g System l savings from this new system. Show your wor k. (in KW): Annual cost: Annual Savings How many from ori gina l: years wi ll it tak e to pay off the cost of the ne w system? Home Energy Bill Electricity Audit of Your Home Analyze the amount of electricity used in your home. Choose one room that has the greatest number of appliances and lights to use for the audit (You may do two rooms for up to 10 points extra credit). Create a data table showing the name of the room, appliances, wattage for each appliance, hours used per week, total watt-hours used per week and total KWH. a. To determine wattage, look directly on the back or bottom of the appliance to get an accurate number. (Remember watts=volts x amps) Otherwise use the appliance survey sheet for assistance. 21 students—pledged 27,670 lbs CO2 of savings (12,577 kg) East High Unplugged http://www.mmsd.o rg/mmsdtv/streamin g/4269-snewsunplugged.mov Sara Krauskopf skrauskopf@glbrc.wisc.edu Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center University of Wisconsin--Madison Genetics Biotechnology Rm 1320 425 Henry Mall Madison, WI 53706 608-263-0809 MGE Website Earth Science students bring in an energy bill from their home or use the computer lab to find out the average energy use for their home. http://www.mge.com/myaccount/averagecost/ Home Energy Audit Adapted from Project Learning Tree Scaffolded in its design Students have one week to do the energy survey at home, math calculations are done together in class. A. Staying Warm and Keeping Cool 1. How do you heat your home or apartment during the winter? (circle one) 2. What is the temperature setting on your thermostat (winter)? 3. Is your thermostat on a timer that automatically controls it at night or during the day when no one is home? 4. Do you use an air conditioner in your home during the summer? 5. If yes, it is a central air or a room air conditioner? 6. What is the temperature setting on your thermostat (summer)? OIL NATURAL GAS ELECTRIC OTHER o F YES or NO YES or NO CENTRAL or ROOM o F B. Keeping it Bright 7. How many light fixtures (lamps, overhead lights) are in your home? 8. Do any of them have compact fluorescent bulbs? YES or NO 9. Does anyone in your home every leave the lights on when they are out of the room? YES or NO 10. Does anyone in your home leave a TV or radio on when they are out of the room? 11. Look at 5 light bulbs in your home. What are their wattages? (usually printed on top) YES or NO 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C. Out the Door and Window 12. How many windows are in your home? 13. How many have storm windows or get covered with plastic in the winter? 14. Check to see if any of your windows have drafts (hold a piece of ribbon in front and see if it flutters.) How many have drafts? 15. Do any of the outside doors in your house have drafts? 16. Look at 5 light bulbs in your home. What are their wattages? (usually printed on top) YES or NO 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. D. Down the Drain 17. What temperature is your hot water heater set at? (if you can’t find out, measure the temperature of the water with a thermometer) 18. Does your hot water heater have an insulated cover? YES or NO 19. Do any faucets or pipes in your house leak? YES or NO 20. Do you usually wash your clothes in hot, warm, or cool water? 21. Do you clean the lint trap on your dryer before drying a load of clothes? 22. If you have a dishwasher, do you run the drying cycle or just let them air dry? HOT or WARM or COOL YES or NO DRYING CYCLE or AIR DRY E. Watt does it cost to use it? Circle the electronic devices you use at least once a week below and how many hours per week you use them. Most have a wattage listed on them; fill it in if you can find it. Electronic device Television VCR or DVD player Computer I pod or walkman Cell phone Video game machine Microwave Refrigerator Electric Stove Toaster Aquarium Vacuum Cleaner Blow-dryer Flat Iron or Curling Iron Hours per week used Wattage Wattages of Small and Medium Sized Electrical Appliances Watt does it cost to use it? Electronic device Wattage Television 30 VCR or DVD player 27 Computer 160 I pod or walkman 10 Cell phone 10 Playstation 2 30 XBOX 70 XBOX 360 165 Microwave 1500 Refrigerator 300 Electric Stove 5000 Toaster 1500 Aquarium 150 Vacuum Cleaner 700 Blow-dryer 1200 Flat Iron or Curling Iron 30 Calculation Sheet – Can we save a ton of CO2? A.Electronic B.Wattage C.Wattage/1000=kW D.Hours Item (B/1000=kW) used per week 1.1. 1. 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. F. kilowatt hours (kWh) (C x D) G. Cost per week (F x 0.10) H. Cost per year (G x 52) Leaking Watts Chart Small appliances use energy when they are turned off but still plugged in. Type of Appliance Air Condidtioner Alarm Clock Amplifier Answering Machine Answering Machine/Cellular Phone Computer (personal) Baby Monitor Battery Charger Boom Box Cable Box Cassette Deck CD Player Clock Radio Cordless Phone Dishwasher DSS DVD Equalizer Garage Door Opener Internet Apliance Linear Power Supply Machintosh PC Massager Microwave Oven Mini Audio System Modem (external) Power PC Power Speaker Printer Range Receiver Rice Cooker Security System Shaver TV TV/VCR Combo Vacuum Cleaner VCR Video Game Minimum (Watts) Average (Watts) 0 0 0.7 1.3 0 1.4 1.8 3 2.5 2.8 1.3 2.1 0.7 1.2 0.2 1.4 0.7 2.2 4.8 11.6 0 2.8 0 3.1 0.9 1.7 1.1 2.7 6.4 6.4 11.3 15 1.6 4.3 0 3.1 3.5 3.8 7.5 7.5 0.1 1.3 0 2 1.1 2.7 1.6 3.2 1.3 9.3 1 1.4 1.3 1.5 0 1.6 3.5 3.5 1.8 3 0 1.8 1.5 2 15 18.3 0.4 0.9 0 4.3 2.5 9.8 1.7 2.1 1.5 5.6 0 1.1 Maximum (Watts) 0 2 5.5 5.2 3.1 2.8 1.6 3.2 7.7 18 6.6 8 3.2 5 6.4 18.4 7.1 5.9 4 7.5 3.2 3.5 4.2 6 28.6 1.8 1.6 3.1 3.5 4.1 5.9 2.5 21.5 1.4 12.3 19.5 2.6 12.8 2 Overview of Earth Science Energy Use What is a watt? Where does our energy come from? Reading a home energy bill (or MG&E website) Waste Watchers Energy Survey – Can we save a ton of CO2? Energy survey calculations School energy bill Graphing school energy use Investigating alternative energy sources