Matrix Sample 5-1
advertisement

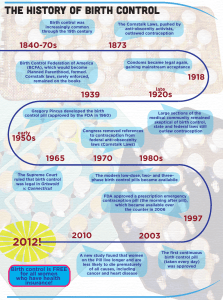
UNIT 2 SYNTHESIS MATRIX Name: Anonymous Topic: Male methods of contraception Research Question: Why are there so many contraceptive options for females but so few for males? Works Cited: Cheng, C. Yan, and Dolores D. Mruk. "New Frontiers in nonhormonal male contraception." Contraception 82 (2010): 476-482. Elsevier Web 21 March 2013. Clinaero, Inc. MedTV. 2013. 24 March 2013. <http://women.emedtv.com/birth-control-pills/list-of-birth-control-pills.html>. Eberhardt, Judith, Anna Van Wersch, and Neil Meikle. "Attitudes towards the male contraceptive pill in men and women in casual and stable relationships." Journal of Family and Reproductive Health care 35.3 (2009): 161-165. BMJ Group. Web 21 March 2013. Espey, Eve, MD, MPH, Ellen Cosgrove, MD, and Tony Ogburn, MD. "Family Planning American Style: Why It's So Hard to Control Birth in the US." Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics 34.1 (2007): 2-12. MD Consult. Web 21 March 2013. Littlejohn, Krystale E. "Hormonal Contraceptive Use and Discontinuation Because of Dissatisfaction: Differences by Race and Education." Demography 49 (2012): 1433-1452. EBSCOhost Business Source Complete. 20 February 2013. Liu, Peter Y. and Rober I. McLachlan. "Male Hormonal Contraception: So Near and Yet so Far." Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 93.7 (2008): 2474-2476. Highwire Press Free. Web 21 March 2013. McDonald, Peter. "Gender Equity in Theories of Fertility Transition." Population and Development Review 26.3 (2000): 427-439. JSTOR. Web 21 March 2013. Naz, Rajesh K. and Shon Rowan. "Update on Male contraception." Current Opinion in Obstetrics and Gynecology 21 (2009): 265-269. Ovid SP. Web 21 March 2013. Sheldon, S. ”'Sperm Bandits', Birth Control Fraud and the Battle of the Sexes." Legal Studies 21.3 (2001): 460-480. Wiley Online Library. Web 21 March 2013. Wang, Christina and Ronald S. Swerdloff. "Hormonal Approaches to Male contraception." NIH Public Access Author Manuscript 20.6 (2010): 520-524. Ovid SP. Web 21 March 2013. Wersch, A. Van, J. Eberhardt, and F. Stringer. "Attitudes towards the male contraceptive pill: psychosocial and cultural explanations for delaying a marketable product." Andrologie 22 (2012): 171-179. openrepository.com Web 21 March 2013. UNIT 2 SYNTHESIS MATRIX Big Idea/Step/Category 1: Significance – Explain why your topic and question are important: The occurrence of unplanned pregnancy in the United States is frequent. In addition, women must take most of the responsibility for preventing pregnancy, creating gender inequality. Introduction of more male contraceptive options into the marketplace may help reduce the number of unplanned pregnancies and create a higher level of gender equality within families and heterosexual couples. Area 1: High rate of unplanned pregnancies in the United States Point 1 Espey "The United States possesses...one of the highest overall unintended pregnancy rates (49%) among developed nations." (2) Point 2 Espey "Similar to unintended pregnancy, the U.S. abortion rate of 21.3 per 1,000 women aged 15 to 44 compares unfavorably with rates in other developed countries." (2) Point 3 Littlejohn "Surprisingly, almost one half (48%) of unintended pregnancies in 2001 occurred in a month when birth control was used; and in 2002, 82% of women who had ever had sex had ever used oral contraceptives ("the pill"). This suggests that a large proportion of unplanned pregnancies is not solely the result of couples never having used birth control. Instead, inconsistent use and contraceptive failure play an important role..." (1434) Area 2: There are a large number of contraceptive options available to women, and very few available to men. Area 3: Many more women in heterosexual relationships are responsible for contraception than men. Area 4: Point 1 Clinaero, Inc. "Many different types of birth control pills are available. In fact, the current list of birth control pills available includes over 60 different medicines. This list would be even longer if those pills no longer made were included: Point 1 Eberhardt "Men only use contraception in around one-third of heterosexual partnerships." (161) Point 1 Alesse®, Altavera®, Alyacen™, Amethia™ , Amethia™ Lo, Amethyst™, Apri®, Aranelle™, Aviane®, Azurette™, Balziva™, Beyaz™ , Brevicon®, Briellyn™, Camila®, Camrese®, Camrese®Lo, Caziant™, Cesia, Cryselle®, Cyclafem™ , Cyclessa®, Dasetta™, Desogen®, Elinest™, Emoquette™, Enpresse®, Enskyce™, Errin®, Estarylla™, Estrostep® Fe, Falmina™ , Femcon™ Fe, Gianvi™, Gildess® Fe, Heather®, Jolivette®, Jolessa™, Junel Fe™, Junel™, Kariva®, Kelnor™, Kurvelo®, Leena®, Lessina™, Levlite™, Levonest™ , Levora®, Lo/Ovral®, Loestrin®, Loestrin® Fe, Loestrin® 24 Fe, Lo Loestrin™ Fe, Loryna™ , LoSeasonique®, Low-Ogestrel®, Lutera™, Lybrel™, Microgestin®, Microgestin® Fe, Mircette®, Myzilra™, Modicon®, Mono-Linyah™, MonoNessa®, Natazia™ , Necon®, Nora-BE®, Nordette®, Norinyl®, Nor-QD®, Nortrel®, Ocella™, Ogestrel®, Ortho Micronor®, Ortho Tri-Cyclen Lo®, Ortho Tri-Cyclen®, OrthoCept®, Ortho-Cyclen®, Ortho-Novum®, Orsythia™, Ovcon®, Philith™, Portia®, Previfem®, Quasense™, Reclipsen™, Safyral™ , Seasonale®, Solia™, Sprintec®, Point 2 Naz "65% of women thought contraceptive responsibilities fall too much on women." (265) Point 3 Naz "The main objective of this study was to examine whether the participants were willing to use male contraception; 55.1% expressed willingness to use it." (265) Point 2 Point 3 UNIT 2 SYNTHESIS MATRIX Sronyx™, Syeda™, Tilia™ Fe, Tri-Linyah™ , Tri-Legest® Fe, TriNessa®, Tri-Norinyl®, Triphasil®, Tri-Estarylla™, Tri-Previfem®, Tri-Sprintec®, Trivora®, Velivet™, Vestura™, Wera™, Yasmin®, Yaz®, Zarah™, Zenchent™, Zeosa™, Zovia™." Point 2 Naz "Current methods of male contraception are coitus-dependent such as condoms or coitus interruptus or permanent such as vasectomy." (265). Point 3 Naz "Near-perfect condom usage results in pregnancy rates as low as 3% but typical use is as high as 14%." (266). Point4 Naz "Drawbacks to vasectomy include the fact that it is surgical and not easily reversed...Complications from the surgery include bleeding and hematoma, sperm granulomas, chornic pain, and epididymitis." (266). Point 5 Handelsman "Yet whereas the last few decades saw the introduction of a variety of reliable and reversible contraceptives for women, not a single new contraceptive method for men was introduced during the last century." (559). UNIT 2 SYNTHESIS MATRIX Big Idea/Step/Category 2: A large volume of research on male contraception has been conducted, yet there are no male hormonal contraceptives in the market. Area 1: History of research Point 1 Eberhardt "Although research into MHC has been ongoing since the early 1970s, a male contraceptive pill has yet to be implemented." (161). Point 2 Handelsman "Novel targets for male contraception continue to be identified but their clinical development remains well into the future. The closest to practical implementation for a new male contraceptive is the hormonal approach. Curiously, it has long been known that hormonal suppression of gamete production was as feasible for men as it was for women. (559) Point 3 Wang "The use of androgens to suppress spermatogenesis was initiated in the 1970s by the Contraceptive Development Branch of NICHD, NIH and other research agencies." (2) Area 2: Types of research conducted Area 3: Funding for continued research and development Area 4: Point 1 Cheng "Reversible inhibition of sperm under guidance involves injection of steric maleic anhydride combined with dimethyl sulfoxide into the vas deferens to create a partial obstruction, and as sperm passes, its plasma and acrosomal membranes, midpiences and tails are severely destroyed, resulting in infertility." (477). Point 1 Wang "Despite a very high rate of suppression of spermatogenesis to sever oligozoospermia, the pharmaceutical companies decided not to proceed with male hormonal contraception development." (4) Point 1 Point 2 Cheng "Immunocontraception involves the use of antigens/antibodies to target different aspects of gamete production an d function as a means of inducing infertility." (477) Point 3 Handelsman "...far more mechanistic, efficacy, and safety information is now available about male methods [of contraception] than when female methods were introduced in 1960 to an eager market." (560). Point 4 Wang "A steroidal SARM, 7 alpha-methyl-19nortestosterone has undergone clinical trials as implants and others such as dimethandrolone are in development as Point 2 Point 2 Naz "Several pharmaceutical companies have withdrawn from this field because of lack of potential profitability, longterm investment, and medico-legal reasons." (268-269) Point 3 Naz "Funding continues through organizations such as WHO, Contraceptive Research and Development Program, and National Institutes of Health (NIH). The first large scale androgen-progestin contraceptive efficacy study has been initiated in seven countries. WHO has identified the development of effective male hormonal contraception has a priority." (269) Point 4 Handelsman Point 3 UNIT 2 SYNTHESIS MATRIX potential components for male contraceptives." (5) "The major practical obstacle has been the disinterest of the pharmaceutical industry contrasting vividly with their enthusiastic adoption of hormonal contraception and replacement therapy for women." (560). UNIT 2 SYNTHESIS MATRIX Big Idea/Step/Category 3: side effects of hormonal contraception for men and women Area 1: Area 2: Attitudes of men toward potential side effects of hormonal birth control Area 3: Some predicted side effects of male contraceptives Area 4: Point 1 Littlejohn "Of all women who had ever used hormonal contraception, approximately 37% had discontinued at some point in time because of dissatisfaction." (1444) Point 1 Eberhardt "...demonstrated that the male pill may receive considerable uptake, with most male respondents ranking it as their first choice of contraception, although over 70% of those questioned indicated that they would not tolerate any possible side effects." (161) Point 1 Naz "It was also found that all men using hormonal male contraception will have full recovery of spermatogenesis. Four to five months are required to regain a sperm concentration of 20 million/ml in an Asian or white man treated with a long-lasting testosterone preparation for 1 year." (267) Point 1 Point 2 Littlejohn "Of all hormonal contraceptive users ages 23-44 who had ever discontinued the pill, the shot, and Norplant (the most widely used hormonal methods) because of dissatisfaction, 59.3% listed side effects as the reason they were dissatisfied." (1444). Point 2 Wersch "Even though both types of studies have yielded largely positive results regarding acceptability, attitudes towards the possibility of a male contraceptive pill seem to vary across research projects in various cultures, in line with the outcome of a multinational survey which reported an average acceptance rate of 55%." (174) Point 3 Attitudes of women towards hormonal birth control-related side effects Point 3 Point 2 Point 2 Naz "Significant predictors of recovery to fertility include age, baseline sperm concentration, luteinizing hormone levels and speed of spermatogenesis levels." (267) Point 3 Point 3 Liu "No single method is used universally by all women; in a way this is analogous to the less than 5% of men who may not adequately suppress their sperm output and in whom this method would not be suitable." (2475) UNIT 2 SYNTHESIS MATRIX Big Idea/Step/Category 4: Women have traditionally been responsible for birth control, but it may be in the best interest of both women and men for men to take a more active role Area 1: Women have more interest in not getting pregnant Area 2: Men may have increased interest in preventing pregnancy, due to issues such as pregnancy fraud Area 3: Women want men to take more responsibility for contraception Area 4:Although some men may be willing to take more responsibility, others may not Point 1 McDonald "In high-fertility contexts, gender inequity within the family may be experienced by women as, inter alia, a generalized dissatisfaction with the rigors and dangers of a constant round of childbearing and childrearing imposed by spousal, familial, and societal expectations." (428) Point 1 Sheldon "the court emphasised that any wrongful conduct on the part of the mother should not alter the genetic father's duty to provide support for his child." Point 1 Naz "Only 2% of the women surveyed said they would not trust their male partner to use hormonal contraception." (265). Point 1 Eberhardt "...being involved in casual sexual relationships or no relationship, and having low trust in its effective use by themselves reliably predicted a negative attitude." (164) Point 2 McDonald "In contemporary market-based economies, the rewards for market production far exceed the rewards for social reproduction." (430) Point 3 Point 2 Point 2 Eberhardt "Thus, being female and having trust in men's effective use of the male pill reliably predicted a positive attitude towards the male pill." (164) Point 2 Wersch "Compared to women, men have less regular contact with health care professionals and are less likely to seek preventive reproductive and sexual health information." (174) Point 3 Point 3 Point 3