Content-Based, Task-Based, Participatory Language Teaching
advertisement

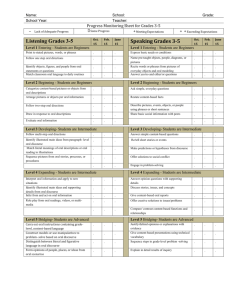
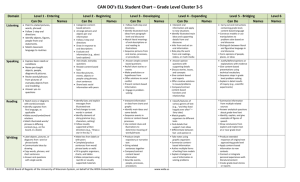
Content-based, Task-based, & Participatory Approaches Prepared by Doris Shih Outline for Today Content-based instruction Scaffolding Task-based instruction Participatory approach Activity Time Content-based Instruction (1) Use content from other disciplines in language teaching “Language across curriculum” movement started in England 1970 Content-based Instruction (2) Build on students’ previous knowledge Students motivated to learn because of relevance Teacher help to scaffold linguistic content Language is learned best when used to deliver interesting information Vocabs can be easily acquired with contextual cues Content-based Instruction (3) Teacher give examples & use comprehensive checks with authentic matters Learners use authentic materials to practice language Communicative competence = able to read, discuss, write about content of other fields Scaffolding: Vocabulary act Read the book The Giver by Lois Lowry Let the learners take a look at the book Pick out certain vocabularies/concepts Let student figure out how to act the words or paragraph Help students to build knowledge on words according to context Task-based Instruction (1) Teacher provides learners with a natural context for language use. Activity has purpose and need outcome Teacher go through a pre-task with students before they work individually Teacher go through the task step-by-step Level is i + 1 Task-based Instruction (2) Teacher-student negotiation; ask for feedback Teacher use language naturally without simplifying Teacher repeat the correct form to reinforce Students then complete a task in groups; practice authentic listening and speaking Task-based Instruction (3) Students receive feedback based on the content – completed task or not Students have input to the design & way of completing the task Participatory Approach (1) Originated with the work of Paulo Freire Started in 1980s Versus content-based: – Similarity: work on meaningful contents – Difference: nature of content Participatory Approach (2) Goal: “is to help students to understand the social, historical, or cultural forces that affects their lives, and then to help empower students to take action and make decisions in order to gain control over their lives.” (p.150) Teacher use contents relevant to students’ lives Curriculum is the result of problem-posed process Students are motivated; teacher is co-learner Participatory Approach (3) Students use their knowledge to act in the society Language skills are taught to prompt action for change Students create their own materials as text for others Students get to evaluate themselves Activity Time:Vocab. Act Patriotic Dwelling Overwhelming Anxious Rituals References Larsen-Freeman, D. (2000). Techniques and principles in language teaching. 2nd ed. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.