Flavors of Distributed Programming
advertisement

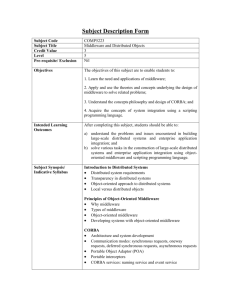
II. Middleware for Distributed Systems
Outline
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
CORBA, COM and Java/RMI
ORB Runtime
Resolving Heterogeneity
Dynamic Object Requests
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
1
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
Outline
Computer Networks
Types of Middleware
Object-oriented Middleware
Developing with Object-Oriented Middleware
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
2
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
Network Operating System
Facilitate physical interchange of electrical or optical signals as packets of
information
Detect and correct transmission errors
Implement routing of packets between hosts
Compose packets into messages
Application
Requesting operations from remote objects
Middleware
Shield lower level details from applications
Component-1
…
Component-n
Middleware
Network OS
Hardware
Host-1
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
3
Computer Networks
ISO/OSI Reference Model (7-layer model)
Application
Presentation
Session
Transport
Network
Data Link
Physical
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
4
Computer Networks
ISO/OSI Reference Model (7-layer model)
Application
Presentation
Middleware
Session
Transport
Network
Data Link
Physical
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
5
Available Middleware
Transaction-Oriented Middleware
Support transactions across different distributed db systems
Two-phase commit protocol to implement distributed transaction
Products: IBM’s CICS, etc.
Message-Oriented Middleware
Supports communication between distributed system components by facilitating message
exchange
Support asynchronous message delivery naturally
Support multi-casting
Fault tolerance (message queue on temporarily persistent storage)
De-coupling of client and server
Products: IBM’s MQSeries
Object Oriented Middleware
Has transaction-oriented middleware capabilities
Support synchronous communication with at-most-once semantics
Trend: to be integrated with message-oriented middleware
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
6
Available Middleware
RPC
Call across host boundaries
Origin of OO middleware
Interface Definition Language
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
7
Remote Procedure Calls
Presentation Layer
Resolution of data heterogeneity
Common data representation
Transmission of data declaration
Marshalling and Unmarshalling
static
Dynamic
Client and server stubs
Static implementations of marshalling and unmarshalling
Char * marshal() {
char * msg;
msg = new char[4*(sizeof(int) + 1) + strlen(name) + 1];
sprintf(msg, “%d%d%d%d%s”, dob.day, dob.month, dob.year, strlen(name), name;
return(msg);
};
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
8
Remote Procedure Calls
Session Layer
Enable client to locate an RPC server
Static binding: simple, lost location transparency
Dynamic binding: depending on a deamon
– Support location transparency
Print_person (char* host, Player * pers) {
CLIENT * clnt;
clnt = clnt_create(host, 105040, 0, “udp”);
if (clnt == (CLIENT*) NULL) exit (1);
if (print_0(pers, clnt) == NULL)
clnt_perror(clnt, “call failed”);
clnt_destroy (clnt);
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
9
General Pattern for Remote Invocation
Client Code
Server Code
Stub
Skeleton
Infrastructure
Serve:
Call:
marshal arguments
convert to network format
locate server
transmit data
receive data
convert & unmarshal
invoke method
marshal return value
transmit data
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
10
Object-Oriented Middleware
IDL
Object types as parameters;
Failure handling;
inheritance
Interface Player: Object {
typedef struct Date {
short day; short onth; short year; };
attribute string name;
readonly attribute Date DoB;
}
Interface PlayerStore: Object {
exception IDNotFound{};
short save (in Player p);
Player load(in short id) raises (IDNotfound);
Void print (in Player p);
};
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
11
Object-Oriented Middleware
Presentation Layer
Similar to RPC
Support client and server stubs
Perform marshalling and unmarshalling
Resolve heterogeneity of data representation
Different from RPC
Define representation of object references
Marshalling/unmarshalling object references
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
12
Object-Oriented Middleware
Session Layer
Object Request Broker
Map object references to hosts
Implements object activation policies in the object adapter
Object adapters need to be able to start up severs, which register in an
implementation repository or registry
Implement operation dispatch
Implement synchronization
Object Reference
Hosts
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
Processes
Objects
13
Developing with Object-Oriented
Middleware
Design
Interface
Definition
Server Stub
Generation
Server
Coding
Client Stub
Generation
Client
Coding
Server
Registration
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
14
General Architecture for a DOC System
Registration
Service
Object
Skeleton
Object
Storage
Server
Implementation
Object
Interface
Specification
IDL Compilers
Object Manager
Naming Service
Client Stub
Interface
Client Application
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
15
CORBA
OMG standard
Enable interoperability between applications in heterogeneous distributed
environment
Common architecture framework
Common framework across heterogeneous hardware platforms and operating
systems
Common framework for inter-communication of application objects
Open distributed object computing infrastructure
Automate many common network programming tasks, such as
object registration, location, and activation;
Request demultiplexing
Framing and error-handling
Parameter marshalling and un-marshalling
Operation dispatching
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
16
CORBA
CORBA
Message-passing
Object-oriented programming
ORB
Automate network functions
Sit on the host between the data and the application layer
Handles request messages from clients to servers in transparent manner
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
17
CORBA Objects
A CORBA Object has an interface and an implementation
Interface
Interface is not bound to a specific implementation PL,
Interface Definition Language
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
18
Interface Definition
Purpose of Defining Interface
Instantiate meta-models
Provide details to class diagrams
Govern interaction between client and server
Provide basis for distributing type information
Provide basis for automatically generate client and server stub
Reading Material
Brose’s book chapter 2
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
19
Stub Generation
Difference between Method Calls and Object Requests
Caller
Caller
Stub
Called
Called
Stub
Transport Layer (e.g. TCP or UDP)
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
20
IDL Compiler
For each .idl file, idl compiler generates 4 files
Test.idl
IDL-Compiler
Testcl.hh
Testsv.hh
Testcl.cc
Testsv.cc
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
21
Implementation of Client Objects
A static object request is made by a client calling a local method
of a client stub
Stubs are typed
Stubs can achieve access transparency
Middleware may shortcut a stub if server and client reside on
the same host
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
22
Implementation of Server Objects
The generated server stub has to call the server implementation
that an application builder designed.
Interfaces and inheritance make server object implementations
type safe.
<<uses>>
Player_Imp
Player_Dispatch
<<uses>>
Player_Dispatch
<<Interface>>
Player_Imp
<<Implements>>
Player_Server
Player_Server
Inheritance
Interface
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
23
Server Registration
Server object must be registered
Registry
Implementation repository
System administrator maintain the repository
Middleware provide tools for maintain the repository
Register new server objects
Startup server objects
Stop/delete existing server objects
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
24
Summary
OO middleware built on top of the transport layer
OO middleware implements the session and presentation layers
Other than OO middleware, there are transactional, messageoriented, remote procedure call middleware
Session layer implements an object adaptor
activating/deactivating objects, synchronize client and server
objects
Presentation layer resolve data heterogeneity
Development process for distributed objects
Idl, stub generation, coding, registration
Type safety
Implementation repository
Principles of Object-Oriented Middleware
25