Report Writing in Chemistry
advertisement

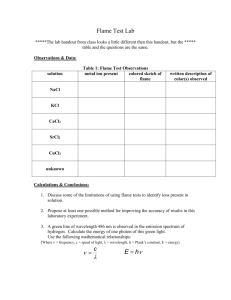
F.3 Report Writing Workshop I Limestone What ions does it contain? Limestone contains How can we test their presence? Calcium ion : Carbonate ion : Flame Test Dilute hydrochloric acid Delivery tube Limestone Lime water Q: How do we record the above tests ? What are the features of an experimental report? Task: Compare the two reports and find out the features of an experimental report. (10 mins) An experimental report should contain …….. 1. Title 2. Purpose 3. Chemical Reactions Involved 4. Apparatus and Reagents Used 5. Procedures 6. Observation 7. Conclusion 8. Discussion If we are going to write an experimental report about the test of limestone, we should include…… 1. Title: Chemical test of Limestone 2. Purpose: To identify the chemical composition of limestone 3. Chemical Reactions Involved: Other examples: Calcium ion Copper ion Sodium ion Potassium ion Golden yellow Brick red Bluish green Lilac 3. Chemical Reactions Involved: Carbonate Dilute hydrochloric acid Limestone Delivery tube Lime water Other example: Chloride Silver nitrate solution with dilute nitric acid milky Water Dry Cobalt(II) chloride paper Blue to pink 4. Apparatus and Reagents Used • • • • Platinum wire x 1 Test tube x 2 Evaporating dishes x 1 12 M Concentrated hydrochloric acid…… etc 5. Procedures: Task: Write down the procedures of the flame test of calcium ion in a sample. 5. Procedures: 1. 2. 3. 4. Dip the platinum wire into a test tube of concentrated hydrochloric acid and then heat it in the hottest part of the Bunsen flame until no characteristic colour is shown. After the cleaning, dip the wire into the concentrated hydrochloric acid again and then into the white solid. Heat the solid sample on the wire in the hottest part of the non-luminous flame. Observe and record the colour of the flame. Video of flame test Grammar features in an experimental report Past tense Passive voice 5. Procedures in an experimental report 1. 2. 3. 4. The platinum wire was dipped into a test tube of concentrated hydrochloric acid and then heated in the hottest part of the Bunsen flame until no characteristic colour was shown. After the cleaning, the wire was dipped into the concentrated hydrochloric acid again and then into the white solid. The solid sample on the wire was heated in the hottest part of the non-luminous flame. The colour of the flame was observed and recorded.