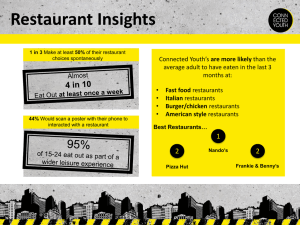
Commercial food services
advertisement

Food and Beverage HISTORY of the food service industry Egypt and Rome • Originally for celebrations, rituals • Egyptians would meet in public places to share food • Pompeii has the ruins of bars, snack bars and fast food restaurants • Romans had big banquets with entertainment and portable food services for their troops French • Fancy French dining began in 1789 • Royals were being killed, and chefs became unemployed • Chefs opened small, fine dining restaurants that were for the upper class United States • Delmonico’s was the first restaurant that opened in the USA New York City in 1827 Antoine’s opened in New Orleans in 1840 – Fine dining – Survived Hurricane Katrina Fast Food • The use of cars brought about fast food restaurants such as A&W, KFC, and McDonald’s • A&W created the “drive-up” restaurant Changes in Business • 1970s many restaurants had been closed for breakfast, but with busier lifestyles people wanted breakfast Marketing • Fast food began associating their products with television shows and movies – so toys became an incentive to come to their stores 1990s • Family-style restaurants became popular, as they focused on providing families with quick service, good food, and decent prices TRENDS Trends… Casual Dining • Fine dining is being replaced, as people are more price conscious • Interiors tend to be neutral, with plants and wood instead of fancy silverware and chandeliers Trends… Takeout • Takeaway represents around 50% of revenue • Grocery stores have started to offer ready to eat meals Trends… Dining Out with Children • Restaurants cater to children by providing a children’s menu, children eat free day, crayons and a placemat to color on, a play area … Trends… Nutrition • Health has become a concern: reduce saturated fat and cholesterol • Introduced carb-free, fat-free, and low-fat to grocery stores and restaurant menus • Restaurants have switched to vegetable oil or vegetable shortening • Diet trends • Healthier menu options Trends …Allergy Awareness Restaurant staff must be able to identify ingredients Trends… Legal Issues • Laws regarding alcohol and smoking have changed restaurant revenue and owner liability • Before drinking and driving legislation changed, 50%+ of restaurant revenue could come from beverage sales; it is now less than 25% • Upselling is done to replace drink revenue • Example: soup, salad, or dessert with coffee or tea Commercial Food Service Limited-Service Restaurants Fast-food Take-out Food Court Commercial Food Service Drinking Establishments Pubs, Taverns, Bars Non-commercial Food Service Social & Contract Caterers Airlines, railways, special events Non-commercial Food Service Institutional Food Services Hospitals, nursing homes, schools, prisons… Non-commercial Food Service Other food services Stadiums, movie theatres, vending machines Definitions • Commercial food services: primary business is the service of food and drink • Non-commercial food services: primary business is something other than the food and beverage sector Part III: Restaurant Ownership • • • • Three ways: Independent - majority Single corporate structure Franchise agreement Independents • Independent restauranteurs • Have flexibility to change menus, redecorate, or make other changes when they want • Can be risky as it requires lots of time, energy, and money • 80% of independent restaurants will be bankrupt, so franchises are becoming more popular MacGregor’s Tea Room, Pictou Open for breakfast and lunch Multi-Unit Corporate Restaurants • One corporate headquarters will run multiple restaurants • Headquarters will provide leadership, control, and planning for the restaurant • Managers are trained by the corporation – Must meet profit quota – Must follow policies – But “operate independently” • Examples: Boston Pizza International (Vancouver) and Lone Star (Ottawa) Multi-Unit Corporate Restaurants • Companies may own and operate restaurants that are very similar, or very different • Example: SIR Corp., from Burlington, ON – Jack Astor’s Bar and Grill – Armadillo Texas Grill – Brasserie Frisco – Alice Fazooli’s Multi-Unit Corporate Restaurants • Larger corporations will also try to buy other successful chains • Example: Cara Operations has purchased Kelsey’s Corporation (Oakville) Franchises • Own your restaurant, but get more training and experience • Examples McDonald’s, Swiss Chalet, Boston Pizza, Tim Horton’s • Banks are more willing to lend money to brand name restaurants • Help in finding a location, layout is predetermined, training for all staff Franchises • Purchasing is less expensive because you are purchasing as part of a group • Disadvantages: – costs a lot to purchase and your yearly percentage is high – Cannot change to meet needs of a community or follow trends • But attracts tourists because they know what they are going to see and get when they go to these restaurants Franchises • Franchises can fall under a corporate chain • Examples: • Cara Operations owns Swiss Chalet, Kelsey’s Neighbourhood Bar &Grill, Montana’s Cookhouse, and the Canadian franchise rights to Outback Steakhouse Part IV: Major Divisions of the Food Service Industry • Commercial Food Service A. Full-service restaurants: sit down and are served B. Limited service restaurants (ie. Cafeteria, fast food) C. Drinking establishments • Non-Commercial Food Service Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants Haute Cuisine – Elegant and expensive – Fancy décor, well trained staff, service should be above expectations, striking table settings – Has silverware, crystal goblets, fine linen, and flower arrangements Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants • Wait staff have various positions: • Commis (junior waiter) • Chef de rang (chief server) • Maitre d’ (head waiter) • Sommelier (wine steward) • Commis (left) • Sommelier (below) Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants • Food is fresh, prepared daily, and will have items prepared specifically for that restaurant • May have a different menu every day • Food may be prepared next to your table, and may be flambeed by the chef de rang • There will be a wine cellar • Was very popular in late 1800s for the wealthy • The quality of silverware and crystal may have changed to maintain costs, but the service, wine, and food have not changed • Example: George V Hotel in Paris Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants • George V Hotel by Four Seasons Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants Fine Dining: • Do not have the same levels of wait staff, nor the expensive table settings • Staff are still highly skilled • Flambee not common (due to costs) • Food is prepared fresh, and presentation is important (mixture of colors, etc) • Still may have wine cellars Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants Dining • Covers the rest – from diners to cafes • Casual atmosphere, menu, price • Bistros (café, trattoria): – casual dining with unique food (such as homemade desserts, stone-baked pizza) – Décor is simple – Restaurant tends to be small Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants • Dining • • • • • Family-style restaurant Suburbs, or near tourist attractions Fast service and comfort foods Provide high chairs and boosters Children’s menus and children-friendly décor Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants • • • • • Dining Specialty Restaurant Serves one kind of food Swiss chalet and St. Hubert = chicken Red Lobster = seafood Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants • • • • • Dining Ethnic Restaurants Specialize in national dishes French, British, and American has always been available, but now you can pretty much get any type Three reasons for this category’s success – Canadians are travelling, or watching tv – Canadians themselves are more diverse – Grocery stores are providing more products Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants • • • • • • Dining Theme restaurants theme parks = theme restaurants Entertainment can be before, during, and/or after the meal Theme can be part of food choices, and at times theme is more important than the food Do not have to be big, but very expensive to create, so they tend to be big to make up the cost Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants • Theme restaurants are usually in a big city, so can cater to locals, tourists, conventions • Example: Medieval Times (Toronto) • http://www.medievaltimes.com/ • Originated in Orlando, Florida. • Own the largest breeding farm in the world. • Breed Andalusian stallions and train for their shows • Can serve 2500 customers at a time Commercial Food Service – Full Service Restaurants • Dining • Buffet House • 1980s saw this become popular (not a new idea though) • Variety of food, lots of it, hot or cold • Serve yourself • All-you-can-eat • Serving staff will remove your empty dishes and serve your drinks Commercial Food Service – Limited Service Restaurants • Fast food • Customer orders, receives food, finds napkins, straws, condiments, place to sit, and should clean up after themselves • Less staff = less expensive meal • Drive-thru makes it even cheaper since you feed more people and don’t have to worry about where they will sit • Examples: Taco Bell, KFC, Tim Horton’s, DQ, Extreme Pita • Found along highways, by resorts, attractions • Will find many fast food restaurants in the same area Commercial Food Service – Limited Service Restaurants • Some fast food restaurants are independently owned, and will serve regional food • In Quebec, can find poutine • In Ottawa, can find Beavertails (fried pastry that you add toppings to); became so popular that now are at Walt Disney World Commercial Food Service – Limited Service Restaurants • Coffee Houses • Serve international coffees, lattes, cappuccinos, and specialty teas • Examples: Tim Hortons, Second Cup, Starbucks • Can sell bagels, muffins, cookies, and other treats to go with the coffee Commercial Food Service – Limited Service Restaurants • • • • • Cafeterias Choose your food, but portions are preset May be served by someone Staff will clean tables May have real tableware Commercial Food Service – Drinking Establishments • Pubs and taverns try to remind you of a pub in England or Ireland, in terms of food, beer and atmosphere • Example: D’Arcy McGee’s Non-commercial Food Service • • • • Primary business is not serving food Caterers supply food to airlines and trains Also found in museums, sports arenas By hiring a professional food service, a business can focus on their primary business • Cara Operations is Canada’s largest contract food service company Non-commercial Food Service • Train, bus, and airport terminals also have restaurants and bars located within them to serve their customers • Compass Group is the world’s largest food service contractor – Handles food service for large events, such as 2002 Winter Olympics in Salt Lake City – Served more than 3.5 million people at this one event Non-commercial Food Service • Institutional food services are not directly linked to tourism • Hospitals, schools, and offices will hire people who have done culinary training (therefore linked to tourism) • Retail food services are in department stores. May have cafeteria style or elegant, depending on the store Non-commercial Food Service • Festivals, stadiums, and seasonal events also in this category • Dollar Dog Hockey Night at Scotiabank Place in Ottawa, where they served 15 000 hot dogs in 3 hours • Also has fine dining, casual dining, and Penalty Box ($45 to watch game and have all you can eat sandwiches) Non-commercial Food Service • Contract food service • Not as popular in Canada as US • But found on campuses, and school cafeterias – ARAMARK, Cara, Sodexho • Retirement homes may also offer this (more upscale ones) Part IV: Marketing • Remember, 80% of independently owned restaurants go bankrupt in first five years • Success limited to – Good service – Food products – purchasing, prep, storage – Cost control – Sales and promotion Part IV: Marketing • Menu is a marketing tool • Food descriptions must be well written – so that they will order something, and next time may order something different • Pricing should reflect the establishment • Menus can vary in color, materials, shape • Displaying menus for people passing by helps Part IV: Marketing • Couponing – example 2 for 1 • Number of additional customers must be weighed against loss in sales revenue (research shows that people who use coupons often do not return) • “Early Bird Specials” gets people in the door during a slow time • Frequent diner cards to reward guests for loyalty Part IV: Marketing • The least expensive and most effective method: word of mouth • May partner with the community by sponsoring sports teams • Make sure they are listed in “where to eat” lists at tourism bureaus • may set up a food booth at a festival or special event A Taste of Nova Scotia A Taste of Nova Scotia • Seafood • Fiddleheads • Apples • Wine