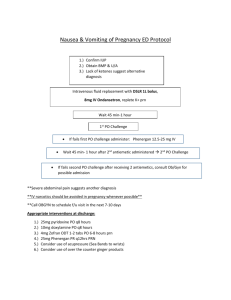
Eurocode 1: Actions on structures –
advertisement

EN1994-1-2:2003 Eurocode 4: Design of composite steel and concrete structures– Part 1–2: General rules – Structural fire design Annex F [informative]: Calculation of moment resistances of partially encased steel beams connected to concrete slabs www.structuralfiresafety.org Content General Basis of Design Material Properties Basic requirements Actions Material design values Verification methods Structural steel Concrete Reinforcing steel Tabulated data Annex B Stress-strain relationships for siliceous concrete Mechanical & thermal properties Partially encased beams Composite columns Unprotected / protected composite slabs Design Procedures Simple Models Composite beams Composite columns Constructional Details Composite beams Composite columns Connections Advanced Models Annex I Planning & evaluation of experimental models Annex A Stress-strain relationships for structural steel General aspects Thermal response Mechanical response Validation Annex C Stress-strain relationships for concrete adapted to natural fires Annex D Fire resistance of unprotected slabs Annex E Moment resistance of unprotected beams Annex F Moment resistance of partially encased beams Annex G Simple models for partially encased columns Annex H Simple models for concrete filled columns www.structuralfiresafety.org www.structuralfiresafety.org F.1(1) Flat slab system The section of concrete slab is reduced as follows: regardless fire classes fc/γM,fi,c beff Compressive stress in concrete Tensile stress in steel - ef + hc,h hc,fi hc h ew bc fay/γM,fi,a fay,x/γM,fi,a x krfry/γM,fi,s b kafay/γM,fi,a Table F.1 Standard fire resistance Slab reduction hc,fi (mm) R30 10 R60 20 R90 30 R120 R180 40 55 www.structuralfiresafety.org F.1(2-3) Other slab systems trapezoidal profiles transverse to beam re-entrant profiles transverse to beam hc,fi hc,fi hc,fi,min hc,fi ≥ hc,fi,min prefabricated concrete planks Table F.1 applies trapezoidal profiles parallel to beam hc,fi hc,fi,min hc,fi ≥ hc,fi,min Joint between precast elements which is unable to transmit compression stress hc,fi heff For calculation Annex D refer to www.structuralfiresafety.org F.1(4) Active width of upper flange (b - 2bfi) (b – 2bfi) varies with fire classes. Yield strength of steel is taken equal to fay/γM,fi,a. fay/γM,fi,a ef bfi bfi ew bc b Table F.2 Standard fire resistance R30 R60 R90 R120 R180 Width reduction bfi of upper flange (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 + 10 (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 + 30 (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 + 40 (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 + 60 www.structuralfiresafety.org F.1(5) Web division Web is divided into two parts: h ew bc x hh Top part hl Bottom part b hl are given for different fire classes: For h/bc ≤ 1 or h/bc ≥ 2 For 1< h/bc < 2 a1 a2ew hl bc bc h hl is given directly in Table F.3 Parameters a1 & a2 are given in Table F.3 Next www.structuralfiresafety.org Table F.3 Bottom part of web: hl Standard fire resistance a1 [mm2] 3 600 9 500 14 000 23 000 35 000 R30 R60 R90 R120 R180 ef h h/bc ≤ 1 a2 [mm2] 0 20 000 160 000 180 000 400 000 hl,min [mm] 20 30 40 45 55 a1 [mm2] 3 600 9 500 14 000 23 000 35 000 h/bc ≥ 2 a2 [mm2] 0 0 75 000 110 000 250 000 hl,min [mm] 20 30 40 45 55 a1 a2ew hl bc bc h ew bc hh x hl b hl,min ≤ hl ≤ hl,max = h – 2ef www.structuralfiresafety.org Table F.3 Bottom part of web: hl Standard fire resistance 1< h/bc < 2 hl,min [mm] R30 3600 bc 20 R60 e 9500 h 20000 w 2 bc bc h bc 30 R90 e e 14000 h 75000 w 85000 w 2 bc bc h bc h bc 40 R120 R180 e e 23000 h 110000 w 70000 w 2 bc bc h bc h bc e e 35000 h 250000 w 150000 w 2 bc bc h bc h bc 45 55 hl,min ≤ hl ≤ hl,max = h – 2ef www.structuralfiresafety.org F.1(7-8) Section yield strength fay/γM,fi,a Top web h ef e w bc hh x Bottom flange Standard fire resistance R30 R60 R90 R120 R180 Bottom web hl f ay , x kafay/γM,fi,a The reduced yield strength depends on distance x: x f ay 1 (1 k a ) hl a0 = 0.018 ef + 0.7 Reduction factor ka ka,min ka,max [1.12 – 84 / bc + h / 22bc] a0 [0.21 – 26 / bc + h / 24bc] a0 [0.12 – 17 / bc + h / 38bc] a0 [0.1 – 15 / bc + h / 40bc] a0 [0.03 – 3 / bc + h / 50bc] a0 0.5 0.12 0.06 0.05 0.03 0.8 0.4 0.12 0.10 0.06 www.structuralfiresafety.org F.1(9) Yield strength of rebars Yield strength decreases with temperature. Reduction factor kr depends on fire class & position of rebar: kr (u a3 a4 ) a5 / Am / V h bc 2h + bc u ew us h bc 3 12 u2 u1,3 www.structuralfiresafety.org Standard fire resistance R30 R60 R90 R120 R180 1 1 / ui 1 / us i 1 /(bc ew us i ) a3 a4 a5 kr,min kr,max 0.062 0.034 0.026 0.026 0.024 0.16 -0.04 -0.154 -0.284 -0.562 0.126 0.101 0.090 0.082 0.076 0.1 1 F.1(11) Shear resistance of web May be verified using the distribution of the design yield strength according to (7) If Vfi,d ≥ 0.5Vfi,pl,Rd Resistance of reinforced concrete may be considered www.structuralfiresafety.org www.structuralfiresafety.org Stress in concrete F.2 Yield strength of rebars 3b uh ul + ef - bc h Stress in steel Reduction factor ks depends on: Fire classes Position of rebars Table F.6 www.structuralfiresafety.org hc Bottom bars u = ui Top bars u = hc - uh hfi b Standard fire resistance R30 R60 R90 R120 R180 Reduction factor ks 1 0.022 u + 0.34 0.0275 u – 0.1 0.022 u – 0.2 0.018 u – 0.26 ks,min ks,max 0 1 F.2(2) Upper flange F.1(4) applies as follows: fay/γM,fi,a ef bc h hfi b Active width of upper flange: (b – 2bfi) varies with fire classes. Yield strength of steel is taken equal to fay/γM,fi,a. Standard fire resistance R30 R60 R90 R120 R180 Width reduction bfi of upper flange (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 + 10 (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 + 30 (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 + 40 (ef / 2) + (b – bc) / 2 + 60 www.structuralfiresafety.org F.2(3) Reduced concrete section 3b Section is reduced as shown. Compressive strength: bc h bc,fi hfi bc,fi fc/γM,fi,c b Standard fire resistance R30 R60 R90 R120 R180 hfi [mm] ≥ 25 165 – 0.4bc – 8(h / bc) ≥ 25 220 – 0.5bc – 8(h / bc) ≥ 45 290 – 0.6bc – 10(h / bc) ≥ 55 360 – 0.7bc – 10(h / bc) ≥ 65 not varying with fire classes Table F.7 bc,fi [mm] ≥ 25 60 – 0.15bc ≥ 30 70 – 0.1bc ≥ 35 75 – 0.1bc ≥ 45 85 – 0.1bc ≥ 55 www.structuralfiresafety.org F.2(4-5) Yield strength of rebars F.1(9) applies as follows: Reduction factor kr depends on fire class & position of rebar: kr (u a3 a4 ) a5 / Am / V 2h + bc 3b u bc ew us h 3 12 u2 u1,3 www.structuralfiresafety.org b h bc Standard fire resistance R30 R60 R90 R120 R180 1 1 / ui 1 / us i 1 /(bc ew us i ) a3 a4 a5 kr,min kr,max 0.062 0.034 0.026 0.026 0.024 0.16 -0.04 -0.154 -0.284 -0.562 0.126 0.101 0.090 0.082 0.076 0.1 1 F.2(6-7) Shear resistance Assumptions: Shear force is transmitted by steel web, which is neglected when calculating the hogging bending moment resistance. If Vfi,d ≥ 0.5Vfi,pl,Rd Resistance of reinforced concrete may be considered www.structuralfiresafety.org www.structuralfiresafety.org