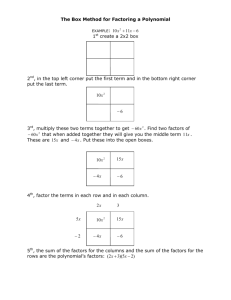
Disrupting Markets
advertisement

ELEC5701 Disrupting Markets sdfl Matt Barrie Chief Executive Freelancer.com matt@freelancer.com Bill Bartee Managing Director SXVP wbartee@gmail.com Matt Barrie matt@freelancer.com +61 4 11331123 What are we looking for • Problems – “No problem, no market” (Vinod Khosla) • Big markets - the size of Texas ($1bn++) Through exercise: which would you compromise out of Product, Team or Market? • Scalable businesses – unbounded capacity to grow revenue without a corresponding increase in costs or complexity e.g. hotel (unscalable) vs freelancer.com (scalable) Thought exercise: How do you make $1 million? • Pain killers, not vitamins What do we mean by DISRUPT? Better, faster, longer, stronger • • • • • • • 10x better 10x faster 10x cheaper 10x better customer service 10x better distribution 10x more convenient … Why 10x? • Switching costs are too high for 20% improvement • Cost of customer acquisition will be too high and the rate you can acquire too slow • Competitors can take defensive moves to lock in or leapfrog • Your competitive advantage is unlikely to be sustainable Disruption in the Music Industry Disruption in the Music Industry Disruption in the Music Industry Disruption in the Music Industry Disruption in the Music Industry Disruption in the Music Industry Competitive advantage • We are looking for sustainable competitive advantages • A lot of consumer Internet businesses you see today have no sustainable competitive advantage; they are betting on first to market and a quick flip. Hope is not a strategy. • Does the idea lend itself to building a company or is it a one hit wonder? • What is the “secret sauce” that competitors can’t replicate? 9 Ways for Opportunities to Disrupt 1. Increasing the value of a product or service 2. New applications of existing technologies (e.g. Magstripe) 3. Creating mass markets (e.g. Model T) 4. Customisation for individuals (e.g. Dell) 5. Increasing reach (e.g. Kogan, Spotify) 6. Supply chain dominance (e.g. Apple, Walmart) 7. Convergence of industries (e.g. Genetic engineering) 8. Process innovation (e.g. Fedex) 9. Economies of scale (e.g. US railroads) Industries to Disrupt • Look for inefficiency – there’s opportunity • Look for people with job descriptions that can be described (and replaced) by algorithms • Humans are inefficient, expensive, error prone and unreliable- look for businesses with lots of humans • Code is scalable, efficient and has global reach • Look for industries that are not yet dominated by a software business - “Software is eating the world” (Andreessen) • Look for industries that haven’t innovated forever, that are lazy, bloated, with fat profits and don’t employ rocket scientists (classic example: real estate) Industries to Disrupt • Find incumbents, pick off a vertical and do it better (e.g. as OKCupid, Airbnb and Freelancer has done to Craigslist, Etsy has done to eBay) • Look for industries with lots of infrastructure (e.g. Harvey Norman, LJ Hooker) and do it without it (e.g. Kogan, Leasate) • Look for industries where their business model has made them unable to innovate (e.g. Harvey Norman, LJ Hooker and their franchise models) • Dirty industries are great (less competitors). Vice is nice. Look for discontinuities Society Technology Markets Aging society Innovation Deregulation Lifelong education Disruptive technologies Supply chain disruption Food & population New knowledge Globalisation Regulation • Opportunities can be found where there are discontinuities • Capture opportunity by creating a response to it • Works best when there is a good fit with the team’s experience, skills and passion Look for trends 3-5 years out “I skate to where the puck is going to be, not where it has been” - Wayne Gretzky Examples of Trends Growth in computing power, cloud computing Reach of the internet, demographics Spread of mobile communications, personal area networks Miniaturisation of technologies Change in lifestyles Rising middle class in developing nations Cloud computing Aging of the population Evaluating Opportunities • How do you make money? • How large is the market? How large is it really? (segment) • Who will buy the dog food? Why will they buy? How much will they pay? How long does is the sales cycle? Is the sales process repeatable and scalable? • Where will the market be in 3-5 years? • Will the customer enable you to profit? • Can your team execute on the idea? What’s missing? • If it doesn’t work, can you fail fast with minor losses? Evaluation Frameworks • See the course blog for frameworks for the top VCs Factor Problem to be solved (P) 1 2 3 Small Under $100M Medium Up to $1B Large Over $1B Sophistication of solution (S) Non-proprietary Tech AND Non-existent channel Either proprietary Tech OR In-place channel Proprietary Tech AND In-place channel Quality of Entrepreneurial Team (E) Inexperienced Team OR No Team Some Related Experience Deep Background of Experience P, S, E out of 10 D = demerit points Value = P * S * E – D Things I personally want to disrupt • • • • • • • • • • • • • Real Estate Legal Accounting & Tax Recruiters Craigslist Paypal eBay Telecoms (PSTN) Media Guns Keys Wallet … What to do next • Describe the problem • Write the elevator pitch • Write the vision for the company • Write the mission statement • What is the business model? • Why is your solution compelling and does it have a sustainable competitive advantage? • Write up an executive summary • Do some basic modelling (e.g. how do you make $1m?) Homework • Read “Don’t Mean to be Alarmist, But The TV Business May Be Starting to Collapse” http://www.businessinsider.com/tv-business-collapse-2012-6