Safety Lecture - Miss. Perry at Lincoln High School
advertisement

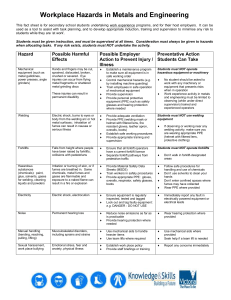
Module 1 Upon completion of this module, you will be able to: 1. Identify some common hazards in welding. 2. Explain and identify proper personal protection used in welding. 3. Describe how to avoid welding fumes. 4. Explain some of the causes of accidents. 5. Identify and explain uses for material safety data sheets. 6. Explain safety techniques for storing and handling cylinders. 7. Explain how to avoid electric shock when welding. 8. Describe proper material handling methods. There is a lot more to welding than simply applying an electric arc to the base metals. Welding safety and safe practices are paramount in the welding industry. Welders must be trained on how to act safely to ensure that no one gets hurt or killed. Many hazards are associated with welding, cutting, and related processes. Some of these are electric shock, infrared rays, ultraviolet (UV) rays, hot metal, slag, sparks and associated welding fumes. Beginning Welders must understand the hazards of welding and develop the proper attitude toward safety. Welders must understand the need for proper clothing, eye protection, and face protection, along with general shop safety. Accident can often be traced to personal factors such as poor health, lack of experience, and the improper use of alcohol and medications. Studies show that a person who lacks experience is more likely to take risks that cause accidents. An inexperienced person often is not able to foresee the outcome of an action or just lacks the knowledge to know what works and what doesn’t. People who consume alcohol or use illegal drugs while working risk their lives and the lives of their co-workers, and will not be tolerated. Personal protective equipment (PPE). Leather and fire resistant protective coverings. Foot Protection: OSHA requires that protective footwear be worn when working where falling, rolling, or sharp objects pose a danger of foot injuries and where feet are exposed to electrical hazards. Safety shoes or boots 8 inches or taller should be worn. Hand Protection: Gloves must be selected on the basis of the hazards involved. Gauntlet-type welding gloves must be worn when welding or cutting. Soft, flexible, leather gloves can be used for light-duty work and operations such as GMAW, GTAW, TB, OFC and OAW. Do not use gloves if they have oil on them or if they have holes. Ear Protection: Welding areas can be very noisy, ear plugs and/or ear muffs should be worn at all times. Ear protection can also keep sparks out of your ear canals. Eye, Face and Head Protection: The heat and light produced by cutting or welding operations can damage the skin and eyes. Injury to the eyes may result in permanent loss of vision. Proper lens shade selection: Make sure you use the proper shade for the type of work you are doing. Many varieties of helmets are available. You should choose the right welding helmet for the right type of job. Passive lenses. Auto Darkening welding helmets Can choose different shades with the touch of a button. Shade 3 to 4 when turned off. The gases, fumes, and dust produced by welding and cutting processes can be hazardous. Adequate ventilation must be provided to prevent workers from breathing these products. There are three methods to remove fumes and gases: 1. Natural ventilation: ◦ The movement of air through the work place caused by natural forces is often sufficient to remove fumes and gases. 2. Mechanical ventilation ◦ If natural ventilation is not adequate, portable or fixed fans can be used to provide the necessary ventilation. 3. Source extraction ◦ This method uses a mechanical device to capture welding fumes at or near the arc. Regardless of the ventilation method used, it is important to avoid breathing in the welding fumes. This means keeping your head up and away from the fume plume. In addition to the fume plume, some consumables and base metals contain toxic materials that require special ventilation. These materials include: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Barium Cadmium (found in some steel and fasteners) Chromium (found in stainless steel) Base metal coatings such as paint Cobalt Copper Manganese Nickel Silica Zinc (found in galvanized metals) Respirators: Special metals require the use of respirators to protect welders from harmful fumes. There are three types of respirators: ◦ Air-purifying respirators ◦ Supplied-air respirators (SARs) ◦ Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) Types Respirators: Air-purifying respirators: ◦ Provide the lowest level of protection. Supplied-air respirators (SARs): ◦ Provide a supply of air for extended periods of time via high pressure hose. Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA): ◦ Can be used in oxygen-deficient atmospheres, in poorly ventilated or confined spaces. Typical respirator. A belt-mounted respirator. Reusable half-mask air purifying respirator. Powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR). Supplied-air respirator. Self-contained breathing apparatus. Use the right respirator for the job. Respiratory Program: A respirator must be properly selected (based on the contaminant present and its concentration level), properly fitted, and used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. A confined space refers to a relatively small or restricted space, such as storage tank, boiler, or pressure vessel or small compartments, such as underground utility vaults, small rooms or the unventilated corners of a room. Effects of an Increase or Decrease in Oxygen Levels. Worker entering a confined space with a restricted opening for entry and exit. An important factor in area safety is good housekeeping. The working area should be picked up and swept clean. The floors and workbenches should be free of dirt, scrap metal, grease, oil, and anything that is not essential to accomplishing the given tasks. It is important to keep flammable liquids as well as rags, wood scraps, piles of paper, and other combustibles out of the welding area. Sparks can smolder for hours and then burst into flames. The most common welding accident is burned hands and arms. Report all accidents, no matter how minor, to the instructor. Always write the word “HOT” on any hot metal, tools, tables, etc. that you leave unattended. Turn off all electrical equipment before working on it. Always have a fire extinguisher nearby. Always have first-aid equipment nearby. Eliminate tripping hazards. Keep floor free of electrodes. Work in a dry area, don’t use wet gloves. Use portable screens to protect other personnel from the arc or reflected glare. Screens are not a replacement for welding helmets. Do not stare at the arc through a screen. Hot Work Permits: Are official authorization from the site manager to perform work that may pose a fire hazard. Fire Watches are needed when welding or cutting on or around any flammable material. Someone other than the person welding or cutting has to be the fire watch. Fire watches must constantly scan the work area for fires. Fire watches must only be watching for fires and should not be distracted by any other type of work. Fire watch personal must have ready access to fire extinguishers and alarms and know how to use them. Most welding environment fires occur during oxy-fuel gas welding or cutting. Never point a torch tip at anyone when lighting it or using it. Never point the torch at the cylinders, regulators, hoses or anything else that may be damaged and cause a fire or explosion. Never lay a lighted torch down on the bench or work piece, and do not hang it up while it is lighted. If the torch is not in the operator's hands, it must be turned off. When cutting or welding with oxy-fuel gas equipment, clear the area of all combustible materials. Never use oxygen as a substitute for compressed air. Do not use damaged or leaking equipment or cylinders. Do not tamper with equipment or cylinders. Do not force open or close cylinder valves. Only use approved torch lighter. Keep the striker to the side of the gas flow when lighting a torch. As a general rule you should never cut into a container, unless you know what used to be stored in it. Containers must be cleaned by steam cleaning, flushing with water, or washing with detergent until all traces of the material have been removed. After cleaning the container, fill it with water or a purging gas, such as carbon dioxide, argon, or nitrogen to displace the explosive fumes. Without oxygen, combustion cannot take place. When using water, position the container to minimize the air space. When using an inert gas, provide a vent hole so the inert gas can purge the air. Oxygen and fuel gas cylinders or other flammable materials must be stored separately. Inert gas cylinders may be stored separately or with either fuel cylinders or oxygen cylinders. Empty cylinders must be stored separately from full cylinders. Always store cylinders vertically with their safety caps on. Always secure cylinders so they cannot fall over. Always store cylinders away from sparks and heat sources. Never use Acetylene gas at pressures greater than 15 pounds per square inch. Never withdraw Acetylene gas at a rate greater than 1/7th the total contents of the cylinder. Never use a damaged cylinder. All power tools must be properly grounded to prevent electric shock. Never use a power tool that you have not been properly trained to use. Never alter or remove any power tool’s guard or other safety device. Always wear protective equipment when using power tools. Always use the proper size extension cord. Do not use power tools near flammable materials. Only use power tools in a dry environment. Electric shock from welding and cutting equipment can kill or cause severe burns by coming in contact with bare skin. The amount of current the passes through the human body determines the outcome of an electric shock. The higher the voltage, the greater the chance of a fatal shock. Electric current flows along the path of least resistance to return to its source. If you come in contact with a live conductor you become a load. The potential for shock increases dramatically if the skin is damp. Currents of less than 1 amp can severely injure and even kill a person. Under the right conditions, even a small current can cause serious injury or death. This figure shows how much resistance the human body presents under various circumstances and how this converts into amps or milliamps when the voltage is 110 volts. All manufactures of potentially hazardous materials must provide detailed information regarding possible hazards resulting from the use of their product in the form of a material safety data sheet (MSDS). Any MSDS must be provided to anyone using the product or anyone working in the area where the product is in use. Proper lifting, moving, and handling of large, heavy, welded assemblies is important to the safety of the workers and the weldment. When lifting a heavy object, distribute the weight of the object evenly between both hands. Use your legs to lift, not your back. Do not try to lift a large or bulky object without help if the object is heavier than you can lift with one hand. Improper work habits can cause serious personal injury and/or damage to equipment and materials. Planning is critical to safety. Accidents occur if you let them, but if you anticipate and plan ways to avoid them, accidents can be reduced or eliminated. The jobsite should always be evaluated to reveal any hazard such as confined spaces, unguarded openings, possible electrical hazards and environmental hazards. Are there any questions?