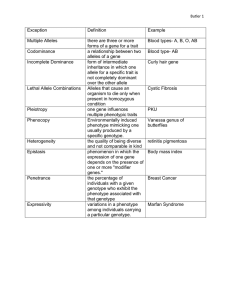
Genetics Test Study Guide Alleles: alternate forms of a gene for a
advertisement

Genetics Test Study Guide Alleles: alternate forms of a gene for a given trait Recessive: trait that can be hidden, symbolized by a lower case letter Dominant: trait that hides another, symbolized by a upper case letter Genotype: type of alleles an organism has; an organisms genetic make up Phenotype: outward appearance of a gene Heterozygous: genotype with two different alleles Homozygous: genotype with two of the same alleles Goals of the human genome project: what can the info be used for? To map gene locations and determine DNA sequence of each gene; could possibly be used against you by employers, insurance companies, police, etc Probability—multiplication method: The probability of having a boy = 1/2, the probability of having a girl = 1/2, the probability of having 3 girls in a row = ½ x ½ x ½ = 1/8, Given the parents AaBbCcDc x aabbccdd, what is the probability of getting a child who is aabbccdd? ½ x ½ x ½ x ½ =1/16 Types of gametes produced by different genotype individuals: use the foil method AABB can make only AB gametes; AaBb can make AB, Ab, aB, ab; aaBB can make only aB; AaBB can make either AB or aB Ideal ratios for monohybrid and dihybrid crosses: monohybrid is from your index cards; dihybrid: AaBb x AaBb you get a 9:3:3:1; AAbb x aaBB you get 16/16 AaBb Tay-sachs disease: caused by an autosomal recessive gene Sex determination: male determines the sex in humans since they are heterozygous (XY) for the sex chromosomes; they give their X to their daughters and their Y to their sons; in chickens female determines the sex since she is heterozygous (ZW) Sex-linkage; presence of traits in males vs. females: Mothers give an X chromosome to both sexes of offspring; males only get 1 X (from Mom) so if they get 1 recessive allele they show the recessive trait; females get an X from both parents so they need to get 2 recessive alleles to show the recessive traits; females can be carriers if they are heterozygous Human blood types: know the chart in your lecture notes for the genotypes and phenotypes Examples of polygenic traits: controlled by more than 1 gene; examples are eye color, skin color, height in humans Pedigree chart: be able to determine the genotype of individuals on a pedigree chart Non-disjunction: failure of chromosome pairs to separate in meiosis; causes gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes