Ling 390 - Intro to Linguistics - Winter 2005 Class 1
advertisement

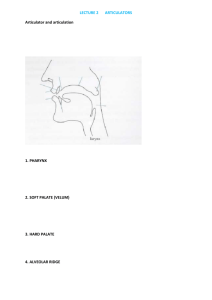
Phonetics Slide 1 Ch 2 Phonetics Chapter 2 Not responsible for Section 10 Section 8 we will talk about, but not focus Homework exercises: 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 15 due 4/15 Problem Set 1 due 4/17 http://web.pdx.edu/~connjc/Ling%20390%20Problem%20Set%201.pdf Language Mini-Research Project HW1 due 4/10 Phonetics Slide 2 Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 The study of speech sounds Articulatory or acoustic phonetics Speech sounds = phones, segments Consonants and vowels Phonetics Slide 3 Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Transcription International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) Break away from spelling IPA is one to one sound-symbol correspondence Phonetics Slide 4 Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Transcription Broad transcription Narrow transcription (uses diacritics) Phonetics Slide 5 Ch 2 Phonetics Sound classes PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Consonants, vowels and glides Sonorant Syllabic vs. nonsyllabic Glides Phonetics Slide 6 Ch 2 Phonetics Anatomy PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Parts of the body used for making speech (see video) Figure 2.1 page 19 The glottis - the space between the vocal folds (Figure 2.2) - Voiced, voiceless, whisper, murmur (breathy) Link for vocal fold video 1 2 Phonetics Slide 7 Anatomy Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Phonetics Slide 8 Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Consonant articulation See Figure 2.3 p. 23 (slide 7) The tongue The oral tract and places of articulation say: typical, sufficient Manners of articulation places and manner of articulation video Phonetics Slide 9 Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Consonant articulation palate (palatal) velum (velar) uvula (uvular) alveolar ridge lips (labial) teeth (dental) places and manner of articulation video Phonetics Slide 10 Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants say: typical = stops; sufficient = fricatives – vary in place of articulation Phonetics Slide 11 Labial Ch 2 Phonetics Places of articulation (for English) Dental Alveolar Palatal Lips Teeth Bilabial Labiodental Interdental Ridge Behind top Teeth Roof of Mouth Alveopalatal Postalveolar Palatoalveolar also Glottal Velar Soft Palate Phonetics Slide 12 Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Consonants Order of 3-part descriptive terms: Voicing -- Place o’ Articulation -- Manner o’ Articulation so [d] is a voiced alveolar stop Phonetics Slide 13 Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Consonants: Order of 3-part descriptive terms: Voicing -- Place o’ Articulation -- Manner o’ Articulation Phonetics Slide 14 Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 International Phonetic Alphabet Sound - symbol correspondence Transcription Download IPA font at www.sil.org, then go to computing in menu on bottom, then “Fonts in cyberspace”, then select “SIL fonts”, then “SIL IPA93” Go to Peter Ladefoged’s website: http://hctv.humnet.ucla.edu/departments/linguistics/VowelsandConsonants/ Phonetics Slide 15 Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants - Stops Oral or nasal (see video1 or 2) Glottal stop Complete obstruction in oral cavity 10 English stops Closure and then release http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8T3_Vpc44-0 Phonetics Slide 16 Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants - Fricatives Narrowing in oral cavity Near closure - forcing air through small space - hissing Fricatives are continuous air through the mouth (continuants) 9 English fricatives Phonetics Slide 17 Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants - Affricates Delayed release of stop causing fricative after 2 English affricates Phonetics Slide 18 Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants - Sibilants/Stridents Louder type of fricative/affricate 6 English stridents Phonetics Slide 19 Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants – Liquids and flap Liquids Laterals - air passes over sides of tongue r’s - bunched up tongue or retroflex 2 English liquids - plus flap (See video) Glottal stop vs. flap in the word little Phonetics Slide 20 Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants - Glides Almost no obstruction in oral cavity 2 English glides [w] is really labiovelar Phonetics Slide 21 Ch 2 Phonetics PHONETICS - Chapter 2 Consonants: Order of 3-part descriptive terms: Voicing -- Place o’ Articulation -- Manner o’ Articulation Phonetics Slide 22 Ch 2 Phonetics English Consonants (voiceless sounds on the left) Phonetics Practice 23 Ch 2 Phonetics Practice - Transcribe the following words - all of them have the vowel ej 1 game 2 faith 3 day 4 case 5 hate 6 waste Phonetics Practice 24 Ch 2 Phonetics Practice - Transcribe the following words - all of them have the vowel ej 1 Jake 2 shape 3 beige 4 hang ? 5 change Phonetics Practice 25 Ch 2 Phonetics Exercise Examples Phonetics Slide 26 Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants - Other Syllabic nasals and liquids Voiceless liquids and glides – after voiceless stops, no s- in front Phonetics Slide 27 Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants - Aspiration Puff of air after initial voiceless stop Not after s- Phonetics Practice 28 Ch 2 Phonetics Practice - Transcribe the following words in narrow transcription - all of them have the vowel [ej] 1 shave 2 taste 3 whale 4 clay 5 ladle 6 tray Phonetics Slide 29 Ch 2 Phonetics Vowels Different from consonants A lot more variation (different dialects) Vowels are in a continuous space and gradient Described by tongue height and backness Also by rounding and tense/lax Vowels are a 5 part descriptive terms: Height -- Back/Front -- Un/Rounded -- Tense/lax -- Vowel vowel videos Phonetics Slide 30 Ch 2 Phonetics vowel words Phonetics Practice 31 Ch 2 Phonetics Transcription (aspiration if you can) 1 boot 2 book 3 boat 4 bought 5 pot 6 putt Phonetics Practice 32 Ch 2 Phonetics Transcription 1 beat 2 bick 3 bait 4 bet 5 bat Phonetics Practice 33 Ch 2 Phonetics Transcription 1 dive 2 down 3 boy 4 about Phonetics Practice 34 Ch 2 Phonetics Transcription – Aspiration if you can Phonetics Practice 35 Ch 2 Phonetics Broad Transcription 1 fast 2 loaf 3 cheese 4 made 5 baby 6 throw 7 should 8 fantastic Phonetics Practice 36 Ch 2 Phonetics Transcription 1 car 2 sir 3 horse 4 floor 5 cheer 6 there Phonetics Practice 37 Ch 2 Phonetics Practice - Transcribe (narrow if possible) the following words 1 craft 2 sigh 3 frog 4 paddle 5 loaf 6 through Phonetics Practice 38 Ch 2 Phonetics Practice - Transcribe the following words – syllabic nasals and liquids 1 oven 2 ice 3 voice 4 thunder 5 joint Phonetics Slide 39 Ch 2 Phonetics Suprasegmentals (prosody) pitch loudness length Phonetics Slide 40 Ch 2 Phonetics Pitch to change pitch, change tension of vocal folds (raise and lower Adam’s apple) Tone - meaningful differences signaled by different pitches Intonation - pitch changes in spoken utterances not related to differences in word meaning (but that do contain information) Phonetics Slide 41 Ch 2 Phonetics Tone register tones - level tones (Mpi tones, Hmong tones) contour tones - moving pitch on a word that signals different meanings of words (Chinese tones, Cantonese tones) Phonetics Slide 42 Ch 2 Phonetics Intonation “Don’t use that tone with me, young lady/man!” Terminal contour Nonterminal contour High rising terminal contours - One time, at band camp Downdrift Phonetics Slide 43 Ch 2 Phonetics Length Geminate consonants in Italian Vowel length in Danish Phonetics Slide 44 Ch 2 Phonetics Stress More prominence - realized by length, pitch and/or loudness Always relative Primary and secondary Can be meaningful in English produce vs. produce - insult Phonetics Slide 45 Ch 2 Phonetics Speech Production Coarticulation - more than one articulator is active - please Articulatory processes - adjustments made during normal speech (not laziness, but often for ease of articulation) Assimilation Dissimilation Deletion Epenthesis Metathesis Vowel Reduction Phonetics Slide 46 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes - Assimilation Assimilation - when the features or characteristics of one sound spread to another sound Regressive assimilation - if two sounds are together in sequence XY, then some characteristic of Y spreads to X (backwards). Vowel nasalization before a nasal consonant - bed vs. Ben Progressive assimilation - if two sounds are together in sequence XY, then some characteristic of X spreads to Y (forward). Voiceless liquids and glides - bride vs. pride Phonetics Slide 47 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes - Assimilation Voicing assimilation - a sound takes on the same voicing as a nearby sound voicing - voiceless sound becomes voiced devoicing - voiced sound becomes voiceless Phonetics Slide 48 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes - Assimilation Assimilation of place of articulation - a sound takes on the same place of articulation as a nearby sound Palatalization - making the place of articulation more palatal Also term used for changing alveolar sound to post-alveolar Homorganic nasal assimilation - a nasal consonant changes depending on the place of articulation of the following consonant Phonetics Slide 49 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes - Assimilation Assimilation of manner of articulation - a sound takes on the same manner of articulation as a nearby sound Nasalization - making vowel nasalized Flapping - between two vowels, an alveolar stop becomes a flap (where first syllable is stressed and second is not) (Flaps are considered continuant so more vowel like) Phonetics Slide 50 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes - Dissimilation Two sounds become less alike Rare process Phonetics Slide 51 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes - Deletion Process that removes a segment from certain phonetic contexts Phonetics Slide 52 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes - Epenthesis Process that inserts a segment in certain phonetic contexts Phonetics Slide 53 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes - Metathesis Reordering of the sequence of segments Phonetics Slide 54 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes - Vowel Reduction In unstressed syllables, vowels become more central Common reduced vowels in English: high central unrounded vowel Phonetics Slide 55 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory processes - Review adjustments made during normal speech (not laziness, but for ease of articulation) Assimilation - regressive or progressive Of voicing - voicing or devoicing Place of articulation - palatalization, homorganic nasal assimilation Manner of articulation - nasalization, flapping Dissimilation - orange juice Deletion - fifs, husban Epenthesis - warmpth Metathesis - aks, pisghetti Vowel Reduction - Ohio or Ohia? Missouri Examples of stressed, unstressed and reduced vowels Phonetics Slide 56 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes What processes are involved? ij = i uw = u Phonetics Slide 57 Ch 2 Phonetics Articulatory Processes To identify articulatory process involved, you need to look at differences between the starting (usually careful pronunciation) and ending pronunciation (normal speech) If a sound is missing = deletion If a sound has been added = epenthesis If the order of sounds has changed = metathesis If a sound has changed: Determine how the sound has changed (what phonetic property has changed: voicing, place or manner of articulation) Compare this phonetic property to nearby sounds If the changed phonetic property matches nearby sounds = assimilation If the changed phonetic property does not match nearby sounds = dissimilation Ch 2 Phonetics Consonants!!! #2.)Place of Articulation #3.) Manner of… 3 (main) Descriptive Terms!!! #1.) Voicing (left = voiceless right = voiced) Therefore: [d] is a voiced alveolar stop Remember this!!! *note! (exclamation points are great learning tools!) Ch 2 Phonetics Vowels!!! #1.) High or Low 4 (main) Descriptive Terms!!! #2.) Front or Back #3.)Rounded Or Unrounded #4.) Tense or Lax Ch 2 Phonetics Ways to memorize the IPA chart!!! Learn to draw it from memory in less than 1min! WOW!!! No seriously, pay attention this is awesome… Ch 2 Phonetics #1.) How big is it? 8 PLACES 6 M A N N E R S 6 by 8 Ch 2 Phonetics #2.) Make up a story! Your story could go here! B STORY#1 S(top) F(ricking) A(round) N(ow) p(eanut) b(utter) STORY #2 AND HERE AND HERE AND HERE L(azy) AND HERE G(uy) AND HERE L I A t(astes) d(elicious) Ap P V G k(ola) g(od) ? Ch 2 Phonetics #3.) Remember cell numbers Get it? Cell numbers… Ha ha ha! (how many symbols in each row/column?) Like a phone number 5-227-4152 5 - 2 2 7 - 4 1 7 9 2 3 2 5 5 2 Ch 2 Phonetics #1.) Remember the shape of the distribution PLACES (Where do the symbols exist)? M A N N E R S Want more? Vowels? Come to study sessions and office hours!!! Ch 2 Phonetics Diacritics (there are 3 you need to know!) Ch 2 Phonetics For next time: Start Ch 3 Phonology – More theoretical and difficult than Ch 2!